Chp 5 pg 76
advertisement

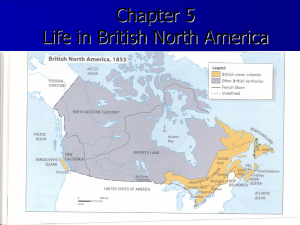
Chapter 5: Life in British North America (BNA) Terms: 1. Colony – a territory of the “home” country in another part of the world 2. Rural – living on farms or in other places outside towns and cities 3. Urban – living cities or towns 4. Census – the government counts the people and gathers other information such as their type of work, where they live and what their heritage is 5. Elite - upper class people with more political, social & economic power 6. Immigrant – a person who comes to live in a country that is not his or her original home 7. Prejudice – a dislike or distrust of a person or group based on biased ideas or information 8. Discrimination – unfair treatment based on prejudice 9. Habitants – farmers who lived in rural areas 10. Racism – a prejudice based on a person’s heritage or skin color 11. Title – legal record that land belonged to a particular person Pg. 76 (BNA) Life in British North America ~ Introduction - use various sources to learn about life in BNA in 1800’s - England owned land that is Canada today - political boundaries changed several times - Nfld. – only place with a French shore - Rupert’s Land stretched from Canada’s Quebec to BC - BC was called New Caledonia in BNA - only area west of Province of Canada in BNA that was populated was Vancouver’s Island Pg. 77 ~ Facts and Figures - Politics colonies: territory owned by, but not attached to, the mother country Vancouver’s Island, NS NB, PEI, Nfld, Province of Canada were British Colonies Rupert’s Land, NWT, New Caledonia were controlled by British fur trading company (HBC) no First Nations land was to be taken over without agreement all important decisions about the colonies were made by Great Britain French shore is the area covered by a treaty that was in place from 1783-1904 Pg. 78 ~ Population - 1851 ~ pop 2, 536, 000 - 2003 ~ pop 31, 000, 000 - Montreal was largest city in BNA (58, 000) - 85% rural by mid 1800’s –mostly farming - Most of population lived in East BNA - Europeans=majority/First Nation & Inuit = minority (in colonies) - First Nations=majority in territories - The British and the Irish (Pg. 82-83) Loyalists - The Elite of BNA - British people who were loyal to the British crown during the American Revolution - Rewarded by British crown with o Land o Social position o Business opportunities o Gov’t jobs o Money Religion - British (mostly Protestants) - Irish (mostly Roman Catholics) ~ British & Scottish immigrants had advantages when settling in BNA ~ Irish & others (Russians, Germans, Spanish, Polish) immigrants had disadvantages when settling - discrimination - unfamiliar with controlling gov’t laws / methods - unfamiliar language People of French Heritage (Pg. 84-85) ~ French of Canada East - 1763 Great Britain took control of BNA - Moved /stayed within an area with other French (modern Quebec) - British allowed some privilege o Own language o Customs o Laws o Religion ~ Acadians - Strong communities based on farming & fishing culture - 1600-1700 had strong settlements - Expulsion (8,000-10,000) - Mid 1800’s Acadian communities becoming strong - Dyke building specialists - Strong Roman Catholic faith Aboriginal Peoples (pg. 86-87) ~ Loss of Land - 2 beliefs systems resulted in Aboriginal Peoples losing the use of land when British took ownership of it o British – believed people could own land o Aboriginal – believed people could not own land - caused Aboriginals to lose hunting grounds & fishing areas - British Loyalists were given land that was needed by Aboriginals for survival - left with small areas of bad land ~ Drop in population - unfamiliar diseases ( eg. Tuberculosis, chicken pox) caused approx. 400,000 deaths - starvation because of lack of hunting grounds, fishing areas, & farm land - residential schools – loss of generations of families ~ The Métis: Finding Their Place - Red River Settlement (currently southern Manitoba) was/is largest Métis settlement in BNA - Honoured French/English & Aboriginal cultures in their backgrounds - Became a unique culture as a result of being discriminated against by French and Aboriginal - Most employment was involved in fur trade o Fur traders o Supplied food to traders o Transported goods (by canoe, wagon, foot) - Discrimination resulted in never being promoted Black Colonists (Pg. 88-89) ~ Black Loyalists - Received smaller chunks of land & had problems getting land titles - Set up strong communities supplying their own medical, religious and educational needs ~ Slavery Outlawed in BNA - 30, 000 black immigrants came 1840-1860 to escape slavery in US - Most settled in Canada West (now Ontario) and NS - Some settled in NB, Rupert’s Land, Vancouver Island