Questions: How Erosion Builds Mountains
advertisement

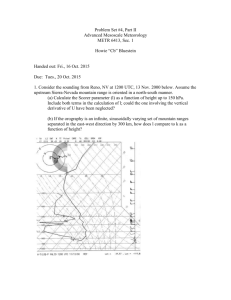
Medjber/Seddon Reading Questions for Student-Led Discussions: How Erosion Builds Mountains 1) What are the three processes that interact to shape and build the world’s mountain ranges? Which process seems to be the strongest of the three? 2) What was one of the first models that attempted to explain how mountains evolved? What is the most recent model proposed by geologists? 3) What is the key process that drives the plate tectonic model? What are the two ways plate tectonics contributes to the thickening of the Earth’s crust? Briefly explain the two ways in which the convergence of tectonic plates occurs. 4) Briefly explain how erosion and climate affect mountain building. What are the some of other links between erosion, climate, and topography? 5) What is isostasy, and how does it contribute to the mountain building process? Give an example of mountain building without tectonic activity. 6) What evidence do geologists use to infer about the extent of mountain at different times in Earth’s history? Briefly explain the two opposing theories about mountain building and climate that have been developed from the analysis of the geologic and climate data. 7) What kind of role does gravity play in mountain growth? Considering the role of gravity, what is meant when mountain ranges are said to be in steady-state topography? With many mountains having achieved steady-state topography at some time in their history, describe the three stages of a mountain range’s “life”. Snowball Earth 1) What kept the Earth’s surface from becoming a solid chunk of ice during the Neoproterozoic? How did this one process help the Earth “break free” from the grips of this ice age? 2) What do geologists and climatologists use to study the climate of the Neoproterozoic? Describe some of the problems geologists and climatologists faced for decades in studying this form of evidence. 3) What type of evidence did Harland use to hypothesize that the continents had clustered together near the equator in the Neoproterozoic? From this how far did the glaciation extend during the Neoproterozoic ice age? 4) What were the results of Budyko’s climate simulation and why did it face such strong disbelief? What sort of evidence caused the scientific community to rethink and reassess the plausibility of the Budyko simulation? 5) According to Kirschvink, during the snowball Earth phase what role did volcanoes play? How much carbon dioxide in the atmosphere would it take for the Earth to overcome a runaway freeze? 6) Describe how carbonates authenticated Kirschvink’s hypothesis. 7) What role did the Neoproterozoic glaciation play on the evolution of life? 8) What caused the Earth to fall into such an extensive glaciation and why have there not more such events? Plateau Uplift and Climatic Change 1) What was the climate like 40 million years ago? 2) Briefly explain some of the different hypotheses on what drives the Earth’s climate and its climate shifts. What role does mountain building have on the Earth’s climate? What effect does mountain building have on carbon dioxide levels? 3) The development of what mountain ranges has affected the climate of Earth? What evidence is there that the climate has changed on these mountains? 4) What tools did geologists and climatologist use to understand the link between plateau uplift and climate? 5) What were the three scenarios run on the general-circulation computer models? Briefly describe the results from the three scenarios. Specifically, did the uplift affect the upper atmosphere and oceans? If so, how? How did the researchers verify the results of the climate models? Briefly describe the evidence used to verify the results. 6) How did the model simulations compare with the actual observed temperature changes? Did the model simulations account for the full amplitude of the observed temperature changes?