The Cognitive approach
advertisement
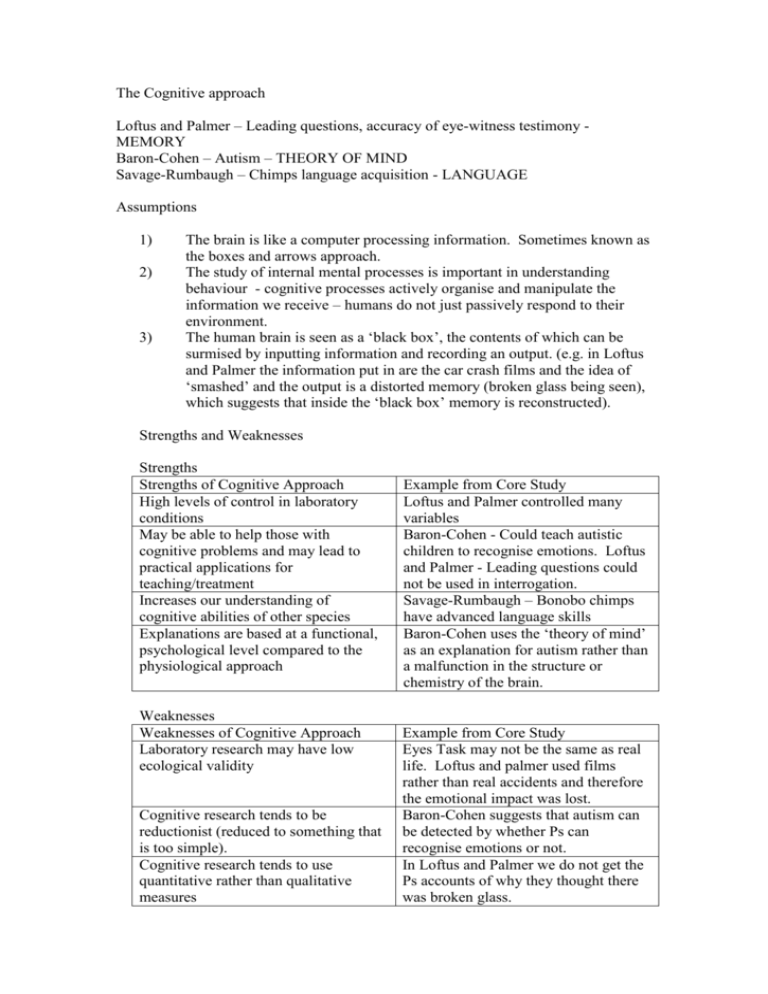
The Cognitive approach Loftus and Palmer – Leading questions, accuracy of eye-witness testimony MEMORY Baron-Cohen – Autism – THEORY OF MIND Savage-Rumbaugh – Chimps language acquisition - LANGUAGE Assumptions 1) 2) 3) The brain is like a computer processing information. Sometimes known as the boxes and arrows approach. The study of internal mental processes is important in understanding behaviour - cognitive processes actively organise and manipulate the information we receive – humans do not just passively respond to their environment. The human brain is seen as a ‘black box’, the contents of which can be surmised by inputting information and recording an output. (e.g. in Loftus and Palmer the information put in are the car crash films and the idea of ‘smashed’ and the output is a distorted memory (broken glass being seen), which suggests that inside the ‘black box’ memory is reconstructed). Strengths and Weaknesses Strengths Strengths of Cognitive Approach High levels of control in laboratory conditions May be able to help those with cognitive problems and may lead to practical applications for teaching/treatment Increases our understanding of cognitive abilities of other species Explanations are based at a functional, psychological level compared to the physiological approach Weaknesses Weaknesses of Cognitive Approach Laboratory research may have low ecological validity Cognitive research tends to be reductionist (reduced to something that is too simple). Cognitive research tends to use quantitative rather than qualitative measures Example from Core Study Loftus and Palmer controlled many variables Baron-Cohen - Could teach autistic children to recognise emotions. Loftus and Palmer - Leading questions could not be used in interrogation. Savage-Rumbaugh – Bonobo chimps have advanced language skills Baron-Cohen uses the ‘theory of mind’ as an explanation for autism rather than a malfunction in the structure or chemistry of the brain. Example from Core Study Eyes Task may not be the same as real life. Loftus and palmer used films rather than real accidents and therefore the emotional impact was lost. Baron-Cohen suggests that autism can be detected by whether Ps can recognise emotions or not. In Loftus and Palmer we do not get the Ps accounts of why they thought there was broken glass. Too cold – ignoring the emotional life of humans, their conscious experience and possible use of freewill. In L&P the Ps personal experiences of accidents in terms of emotion are ignored. One weakness of the cognitive approach is that most of the data collected is quantitative, meaning that it is numbers that can be analysed, for example in L&P we are told that more people estimated faster speeds when given the verb ‘smashed’ in the leading question, also the same word seems to cause participants to think they saw broken glass when in reality there had not been broken glass. The cognitive approach should look at people’s reasons for their actions. This type of data is known as quantitative data. For example in Loftus and Palmer it would have been useful to know why participants thought they had seen broken glass. Notice I have made a mistake, which if I did not re-read my answer I would have left as it is and therefore lose marks. The last ‘quantitative should have been ‘qualitative’. Similarities and differences between studies The cognitive approach Studies Loftus and Palmer and Savage-Rumbaugh Loftus and Palmer and Baron-Cohen Savage-Rumbaugh and Baron-Cohen Similarity Both used a laboratory setting to test Ps Both have useful practical applications. Both collected quantitative data Both used Ps with deficits. Savage-Rumbaugh used common chimps with poor language skills and BaronCohen used Tourettes and Autistic Ps. Both have useful practical applications. Difference Loftus and Palmer used humans whereas SavageRumbaugh used chimps Loftus and Palmer was a lab expt whereas BaronCohen was a quasi experiment. L&P generalises to whole population, whereas B-C generalises to specific groups. As the first box. Savage Rumbaugh tested for language whereas Baron-Cohen tested for the ‘theory of mind’ Also Savage-Rumbaugh was a longitudinal case study, Baron-Cohen used many participants in a snapshot study. b) Describe how the cognitive approach could explain errors in recall from an eyewitness. (4) Or b) Describe how the cognitive approach could explain language acquisition. (4) Or b) Describe how the cognitive approach could explain autism. (4)









