Phonological Awareness - Tewksbury Township Schools
advertisement

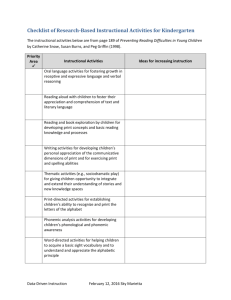
Unit Overview Content Area: English Language Arts Unit Title: Phonological Awareness Timeline: Ongoing Target Course/Grade Level: First Grade Unit Summary: Phonological Awareness instruction will offer students a strong understanding of the sounds in spoken language, an essential concept before students can understand written language. Throughout the year students will receive multiple opportunities to experience oral language. Phonological awareness is not an innate skill and therefore must be acquired through training and practice. The path to phonemic awareness is sequential and occurs in five stages. Phonemic instruction prepares students to learn about their letter symbols in phonics. Primary interdisciplinary connections: Technology, Speech and Language 21st century themes and skills: Creative Thinking and Problem Solving, Communication and Collaboration, Life and Career Skills; -flexibility and adaptability, initiative and self-direction, social skills, productivity and accountability, leadership and responsibility. Anchor Standards: Reading Foundational Anchor Standards are not recognized in the Common Core. Learning Targets/Activities Domain: Foundational Skills Cluster: Phonological Awareness Standard # Standards RF.1.2 Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables and sounds (phonemes) RF.1.2.a Distinguish long from short vowel sounds in spoken single-syllable words. RF.1.2.b Orally produce single-syllable words by blending sounds (phonemes), including consonant blends. RF.1.2.c Isolate and pronounce initial, medial vowel, and final sounds (phonemes) in spoken singlesyllable words. RF.1.2.d Segment spoken single-syllable words into their complete sequence of individual sounds (phonemes). Unit Essential Questions What makes one word sound different than another? How can I put sounds together to make a word? How can I manipulate sounds? Unit Enduring Understandings Phonemic awareness includes the ability to isolate, blend and manipulate sounds in spoken words. Ones understanding of the spoken word is developed through phonemic awareness. Phonemic awareness is a prerequisite and necessary for phonics work to be effective. Unit Learning Targets Students will ... Identify and create a series of rhyming words. (RF.1.2.a) Identify the word that does not rhyme in a series (oddity task). (RF.1.2.a) Identify words with matching initial, medial and final sounds. (RF.1.2.d) Blend syllables to make words. (/ta/-/ble/) (RF.1.2.b) Blend onset/rimes of words. (/p/-/an/) (RF.1.2.b) Blend individual phonemes to create words. (/s/-/a/-/t/) (RF.1.2.b) Segment words into syllables. (RF.1.2.d) Segment words into onset/rime. (RF.1.2.d) Segment words into individual phonemes. (RF.1.2.d) Isolate and produce initial, medial vowel and final sounds in words. (RF.1.2.d) Add, delete, or substitute initial, medial, final syllables and sounds to create new words. (e.g. cow to how, cat to can) (RF.1.2) Listen and identify the number of syllables in a word. (RF.1.2) Distinguish long from short vowels. (RF.1.2.a) Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features of print including that text is read leftto-right, top-to-bottom (directionality), first word, capitalization and ending punctuation. (RF.1.1.a) Learning Activities Sound/picture/objects sorts Word building puzzles Matching/memory games Word ladders Literature and rhymes Syllable sorts Clapping and tapping activities/games Sound boxes/chips Sorting stamped images Poems and songs Word families Word pairs Sound hunts/sound detectives Evidence of Learning Formative Assessments Student participation Anecdotal records Teacher observation Work station checklist/folders Performance tasks: sorting, literacy centers Summative Assessments Phonological Awareness Inventory RESOURCES/TECHNOLOGY Teacher Instructional Resources: Project Read: Phonology Read Aloud/Mentor Texts Poems/songs Calkins Units of Study/Curricular Plans Beginning to read: Thinking and learning about Print by M.J.Adams Reading First by Creative Teaching Press Phonemic Awareness: Playing with Sounds to Strengthen Beginning Reading Skills by Creative Teaching Press Phonemic Awareness Handbook by Anthony D. Fredericks Phonics from A to Z: A Practical Guide by Wiley Blevins The Complete Phonemic Awareness Handbook, by Anthony Fredricks Phonemic Awareness in Young Children, Marilyn Adams, Barbara Foorman, Ingvar Lundberg, Terri Beeler Florida Center for Reading Research Literacy Leaders by Sheila Clark-Edmonds, Yopp & Yopp Integration of Technology: interactive whiteboard (SMARTBoard) websites computers document camera (Elmo) Technology Resources: Click the links below to access additional resources used to design this unit: www.pinterest.com (online pin board) www.teacherspayteachers.com (open marketplace) www.havefunteaching.com (worksheets, activities, etc.) www.abcya.com (free computer games and activities) www.starfall.com (free systematic & interactive website) http://wik.ed.uiuc.edu/index.php/Phonic_awareness http://www.proteacher.com/070171.shtml (list of phonemic awareness activities) http://www.ed.gov/teachers/how/tools/initiative/summerworkshop/valdes/index.html http://www.readingresource.net/ http://www.plattscsd.org/oak/smartboard/phonemic.htm (**interactive games) http://www.readingrockets.org/ (teacher resource) http://www.earobics.com/ (computer-based intervention program) http://www.scilearn.com/ (Fast Forword – computer-based intervention program) Opportunities for Differentiation: Learning centers/stations (specific to level of phonemic awareness stage) Flexible grouping VAKT modeling Leveling of sorting activities Teacher Notes: Phonemic Awareness instruction includes the teaching of: phoneme isolation, phoneme identity, phoneme categorization, phoneme blending, phoneme segmentation, phoneme deletion, phoneme addition, and phoneme substitution. All segmenting and blending activities should include consonant blends, diagraphs and diphthongs of most one-syllable words. Science and Social Studies content should be integrated into appropriate ELA lessons.