Worksheet - Cambridge Essentials
advertisement
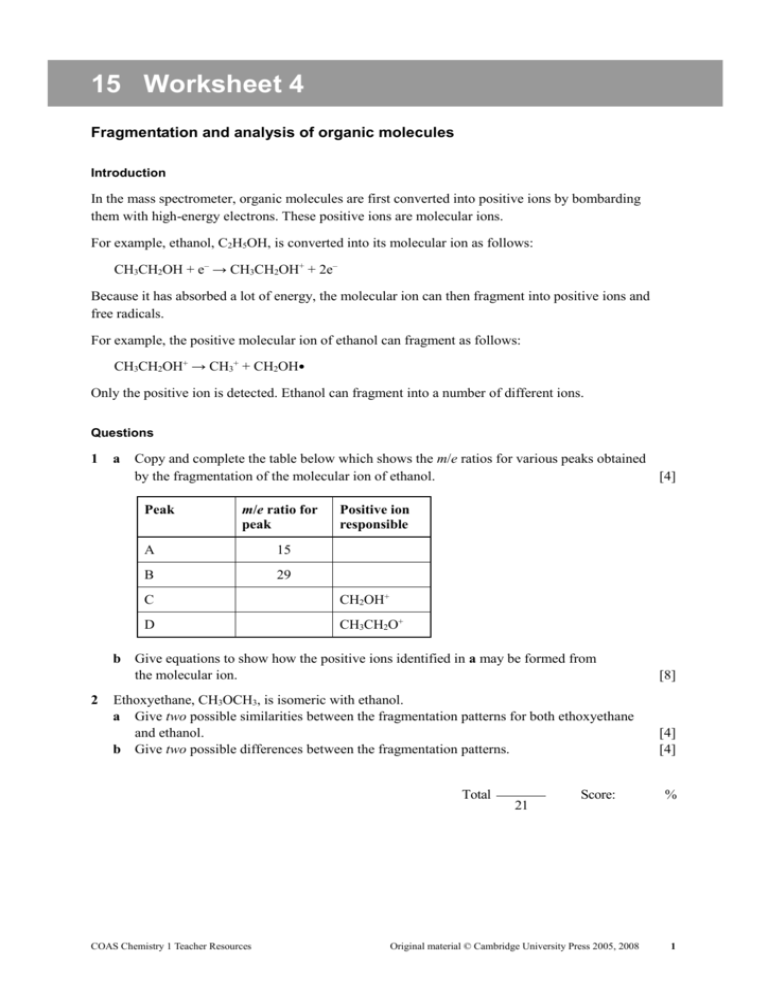
15 Worksheet 4 Fragmentation and analysis of organic molecules Introduction In the mass spectrometer, organic molecules are first converted into positive ions by bombarding them with high-energy electrons. These positive ions are molecular ions. For example, ethanol, C2H5OH, is converted into its molecular ion as follows: CH3CH2OH + e– → CH3CH2OH+ + 2e– Because it has absorbed a lot of energy, the molecular ion can then fragment into positive ions and free radicals. For example, the positive molecular ion of ethanol can fragment as follows: CH3CH2OH+ → CH3+ + CH2OH Only the positive ion is detected. Ethanol can fragment into a number of different ions. Questions 1 a Copy and complete the table below which shows the m/e ratios for various peaks obtained by the fragmentation of the molecular ion of ethanol. [4] Peak 2 m/e ratio for peak A 15 B 29 Positive ion responsible C CH2OH+ D CH3CH2O+ b Give equations to show how the positive ions identified in a may be formed from the molecular ion. [8] Ethoxyethane, CH3OCH3, is isomeric with ethanol. a Give two possible similarities between the fragmentation patterns for both ethoxyethane and ethanol. b Give two possible differences between the fragmentation patterns. [4] [4] Total COAS Chemistry 1 Teacher Resources 21 Score: Original material © Cambridge University Press 2005, 2008 % 1