The Water Cycle By: Caycie Herring P.8 Science The water cycle is
advertisement

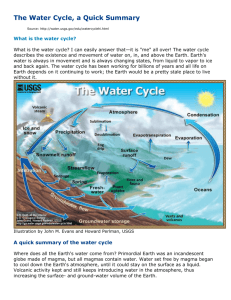
The Water Cycle By: Caycie Herring P.8 Science The water cycle is the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of earth. Because the water cycle is a cycle, there is no beginning or end; it keeps on going. Water can change stages among liquid, vapor and ice. The sun heats up the water in the oceans and the water evaporates as vapor into the air. Ice and snow can sublimate into water vapor. Evapotranspiration is water transpired from plants and evaporated from the soil. Rising air currents take the vapor up into the atmosphere where cooler air temperatures cause the vapor to condense into a cloud. Air currents move the clouds around the sky and they group with other clouds then fall to the ground as precipitation (rain). Some precipitation falls as snow which could turn into ice caps or glaciers. Ice caps and glaciers can hold frozen water (ice) for thousands of years. Snowpacks thaw and melt, and the water flows over land as snowmelt. Most waterfalls flow back into an ocean or onto land as rain, where the water flows over the ground as surface runoff. A portion of runoff goes through rivers, vallies and the landscape, with stream flow moving water towards the oceans. Runoff and groundwater usually stored as fresh water in lakes. Not all runoffs flow into rivers and lakes, most of it soaks into the ground as infiltration. some water infiltrates deep into the ground and replenishes aquifers, which store fresh water for a long time. Some infiltration stays close to the land surface and can seep back into surface – water bodies (and the ocean) as groundwater discharge. Some groundwater finds openings in the surface and comes out as freshwater springs. Over time, the water returns to the ocean where the cycle started. Ocean is the main water source Water is evaporataed into the air as water vaper. the water is condensed into a cloud. Rain falls down from the clouds. some of the rain flows down in rivers and some seaps into the ground. the wataer is evaporated back into the air as a cloud, rains again and will soon end up back into the ocean where it begun. Vocabulary Precipitation: Rain, snow, hail, fog drip, graupel and sleet. Canopy Interception: The precipitation that is intercepted by plants and is evaporated back into the atmosphere instead of falling to the ground. Snowmelt: The runoff produced by melting snow. Runoff: The varieties of ways the water flows across the land. This includes both surface runoff and channel runoff. Infiltration: The flow of water from the ground surface into the ground. Surface flow: The flow of water underground in the vadose zone and aquifers. Sublimation: The change from solid to liquid Advection:the movement of water in solid, liquid, or vapor states through the atmosphere. Condensation: The transformation of water vapor to liquid water droplets in the air, producing clouds and fog. Transpiration: The release of water vapor from plants into the air.