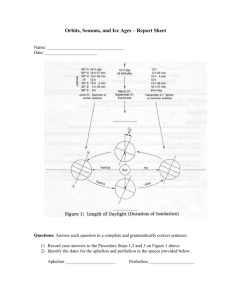
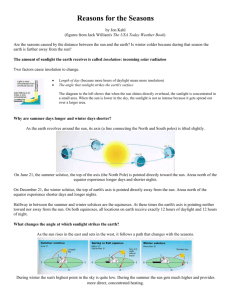
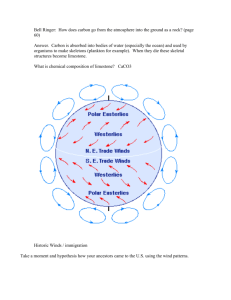
Period 6/7
advertisement

Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons Solar Radiation and Insolation (p.85) 1. Describe the relationship between temperature and the wavelength of electromagnetic energy emitted from a body of matter. THE HIGHER THE TEMPERATURE OF A BODY OF MATTER THE SHORTER THE WAVELENGTH 2. Define INSOLATION: INCOMING SOLAR RADIATION – SUNLIGHT 3. What form of electromagnetic energy does the sun radiate with the maximum intensity? (figure 6-1) VISIBLE LIGHT Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons Effects of Earth’s Atmosphere on Insolation (p.86) 4. What happens to some of the insolation before it reaches the Earth’s surface? ABSORBED BY ATMOSPHERE, REFLECTED BACK TO OUTER SPACE. Absorption of Ultraviolet and Infrared 5. What molecule in Earth’s upper atmosphere absorbs most of the ultraviolet radiation? OZONE (03) 6. What has recently been happening to the amount of ozone in the atmosphere? DECAYING BECAUSE OF CFC’S – CHLOROFLOUROCARBONS. 7. What health problems can occur if too much ultraviolet radiation is absorbed by a human SKIN CANCER Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons 8. What molecules in the atmosphere absorb long wave radiation? WATER VAPOR & CARBON DIOXIDE. Reflection and Scattering 9. What does incident mean? INCOMING 10. What do clouds do to incoming radiation? ABSORB, OR REFLECT BACK TO OUTER SPACE 11. What do aerosols cause? DESTRUCTION OF OZONE. Balance of Energy from Insolation and Earth’s Surface Radiation (p.87) 12. Over large periods of time what is generally the amount of energy the Earth absorbs and emits? ENERGY IN = ENERGY OUT ABSORPTION = RE-RADIATION (EMITTED) Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons Factors Affecting Absorption and Reflection of Insolation 13. How does the angle of insolation (angle of incidence or altitude of the sun) affect the THE HIGHER THE SUN IS IN THE SKY, THE HIGHER THE ANGLE OF INCIDENCE THE MORE INSOLATION ABSORBED. amount of energy absorbed? MORE DIRECT RAYS MORE ABSORPTION Surface characteristics 14. Describe how texture and color affect absorption of insolation. ROUGHER SURFACES AND DARKER SURFACES ABSORB MORE THAN SMOOTH AND LIGHT. Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons Changes of State and Transpiration PROCESS BY WHICH PLANTS RELEASE WATER VAPOR TO THE AIR. 15. Define transpiration: Land and Water Heating 16. Why does water heat up slower than land? a. HIGH SPECIFIC HEAT OF H2O b. MORE LIGHT TRANSMITTS THROUGH WATER THAN LAND c. WATER CONVECTS, LAND DOESN’T d. WATER REFLECTS MORE ENERGY THAN LAND The Greenhouse Effect (p.88) Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons 17. Earth’s surface radiation consists mostly of LONG INFRA-RED RADIATION 18. What molecules absorb long wave radiation? 19. These molecules are called 20. How does carbon dioxide (CO2) get into the CO2 & H20 & methane GREENHOUSE GASES BURNING OF FOSSIL FUELS (COAL, OIL, NATURAL GAS) atmosphere? 21. If the Earth’s global temperature increases ICE CAPS & GLACIERS WOULD MELT why would sea level rise? Answer questions 1-10 on pp.88 & 89 Variation of Insolation (p.89) Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons 22. In what two ways does insolation vary? INTENSITY & DURATION (LENGTH OF TIME) Variation in Intensity of Insolation 23. What angle of incidence produces the maximum intensity of insolation? 90º Effect of Earth’s Shape (p.90) 24. If the Earth were flat and perpendicular to the sun, how would the angle of incidence and the intensity of insolation change with location on the Earth’s surface? SAME! IT WOULD BE THE Effect of Latitude 25. On what dates is the intensity of insolation greatest at the equator? 3/21 & 9/23 Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons 26. On June 21st, where is the intensity of insolation the greatest? CANCER (23½ºN) 27. TROPIC OF On December 21st, where is the intensity of TROPIC OF CAPRICORN (23.5ºS) insolation the greatest? Effect of Seasonal Changes (p.91) 28. Why does the angle of incidence change for VARIES WITH SEASONS AS EARTH REVOLVES. any given latitude? Effect of Time of Day 29. Describe how the angle of incidence changes INCREASES TIL SOLAR NOON, DECREASES TIL SUNSET. throughout the day. Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons The sun rises in the AM, and falls in the PM. Variation in Duration of Insolation (p.92) 30. When is the duration of insolation the LONGEST 6/21 SHORTEST 12/21 longest? Shortest? Effects of latitude and season 31. Compare the number of daylight hours of northern areas to southern areas on the summer NORTHERN AREAS HAVE MORE SUNLIGHT THAN THE SOUTHERN AREAS solstice (June 21st). Relationship of Surface Temperatures to Insolation Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons 32. Surface temperature depends on the BALANCE BETWEEN ENERGY IN (ABSORBED RADIATION) AND ENERGY OUT (SURFACE RE-RADIATION) balance of what? 33. How does the intensity of insolation affect HIGHER INTENSITY HIGHER TEMP’S surface temperatures? 34. How does the duration of insolation affect LONGER DURATIONS HIGHER TEMP’S surface temperatures? Times of Yearly Maximum and Minimum Temperatures Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons 35. When does the maximum surface temperature usually occur for mid-latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere? EARLY AUGUST END OF JULY, 36. Why doesn’t’ the maximum surface temperature occur on the day of maximum insolation?BECAUSE THE EARTH ISN’T RE-RADIATING TOO MUCH ENERGY INTO THE ATMOSPHERE YET Time of Daily Maximum and Minimum Temperatures 37. When is the hottest part of the day? ~2PM 38. When is the maximum intensity of insolation? SOLAR NOON Answer questions 11 -31 on pp.93 -95. Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons Heat Budget and Climate Change (p.95) 39. Define heat budget: RESULT OF THE BALANCE BETWEEN THE TOTAL AMOUNT OF ENERGY RECEIVED AND THE ENERGY LOST. Ice Ages and Long, Warm periods on Earth 40. During what geologic time period did the last ice age occur? PLEISTOCENE 10kya El Nińo and Nińa Events (p.96) 41. What happens during an El Nińo event? FLOODING, DROUGHT, & HEAT WAVES Global Warming (p.97) 42. What has happened to the global average temperature of Earth since 1860? THE TEMPERATURE HAS INCREASED! Causes of Heat Budget Shifts (p.98) Changes in Solar Energy Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons 43. Describe the relationship between the number of sunspots and the Sun’s energy output. MORE SUNSPOTS MORE ENERGY OUT Changes in the Earth’s Orbit and Axis Tilt 44. Over what kind of time period does the tilt of the Earth’s axis and the eccentricity of Earth’s orbit change? THOUSANDS OF YEARS. (27kys) Volcanic Eruptions and Climate Changes 45. How could the eruption of Pinatubo affect ASH BLOCKS SUNLIGHT REDUCING TEMP. global temperatures? Human Causes 46. Does deforestation cause the global temperatures to rise or fall? RISE Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons 47. How does urbanization, contribute to the greenhouse effect? WITHOUT THE TREES TO TAKE IN THE CARBON DIOXIDE, THERE WILL BE MORE CO2 IN THE AIR. Answer questions 32 – 38 on p.99 Seasons (p.99) 48. Describe the seasonal variation in temperature of locations near the equator. NOT MUCH VARIATION. Direct Causes of the Seasons 49. What causes the shift in the angle of incidence? TILT OF EARTH’S AXIS Astronomical Causes of the Seasons (p.100) Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons 50. What are the three astronomical causes of the seasons a. EARTH’S REVOLUTION b. EARTH’S TILT c. PARALLELISM OF EARTH’S AXIS Tilt of Earth’s Axis 51. What would happen to the seasons if Earth were tilted more than 23.5º? SUMMER WOULD BE HOTTER, AND WINTER WOULD BE COLDER. Parallelism of Earth’s Axis 52. To what star does the north end of Earth’s axis always point? POLARIS Revolution of the Earth around the Sun 53. Which end of the Earth’s axis is tilted N. POLE INCLINED TOWARD SUN @ 23.5º toward the sun on June 21st? Name: _____________________ Topic 6 – Insolation & the Seasons 54. Which end of the Earth’s axis is tilted S. POLE INCLINED TOWARD THE SUN @ 23.5º toward the sun on December 21st? 55. How is the axis of rotation inclined to the sun on March 21st and September 23rd? NONE. IT’S NOT TILTED TOWARD, NOR AWAY FROM THE SUN. Small Seasonal Effect of Earth’s Elliptical Orbit (p.101) 56. Compare the seasonal variation on the Northern Hemisphere to the Southern SOUTHERN HEMISPHERES SEASONAL SWING IS GREATER THAN THE NORTHERN HEMISPERES SWING. Hemisphere.