Sec 11.1
advertisement
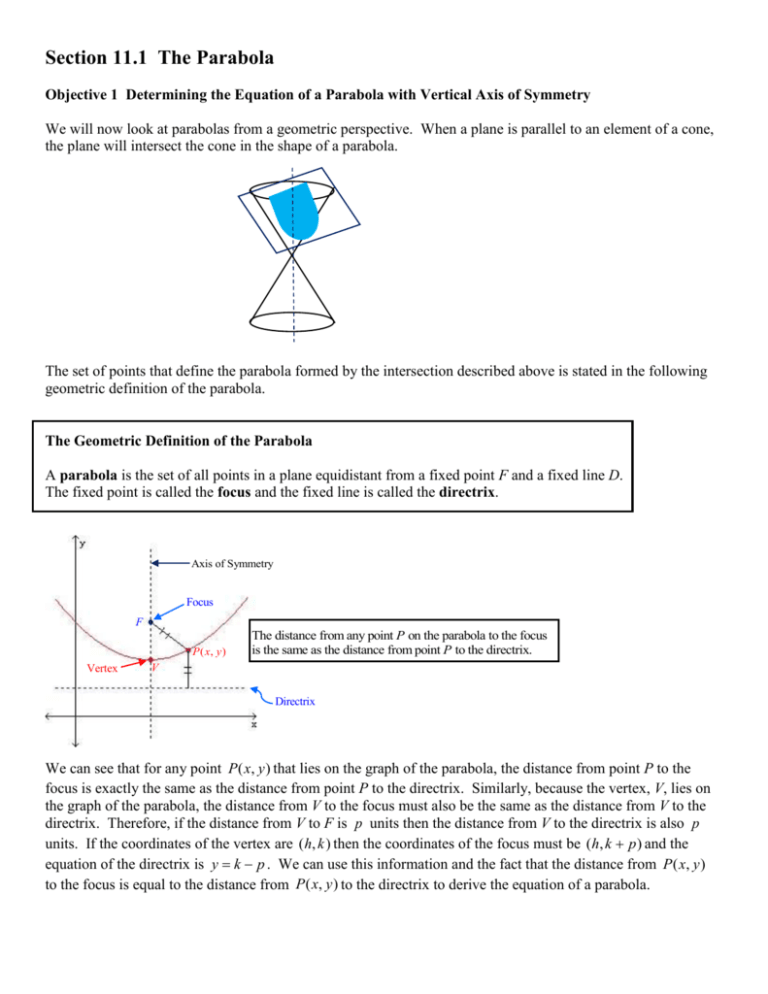
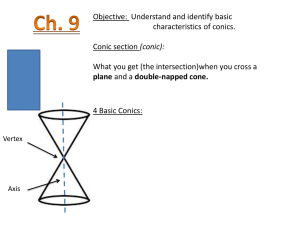
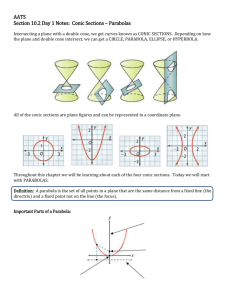
Section 11.1 The Parabola Objective 1 Determining the Equation of a Parabola with Vertical Axis of Symmetry We will now look at parabolas from a geometric perspective. When a plane is parallel to an element of a cone, the plane will intersect the cone in the shape of a parabola. The set of points that define the parabola formed by the intersection described above is stated in the following geometric definition of the parabola. The Geometric Definition of the Parabola A parabola is the set of all points in a plane equidistant from a fixed point F and a fixed line D. The fixed point is called the focus and the fixed line is called the directrix. Axis of Symmetry Focus F P ( x, y ) Vertex The distance from any point P on the parabola to the focus is the same as the distance from point P to the directrix. V Directrix We can see that for any point P ( x, y ) that lies on the graph of the parabola, the distance from point P to the focus is exactly the same as the distance from point P to the directrix. Similarly, because the vertex, V, lies on the graph of the parabola, the distance from V to the focus must also be the same as the distance from V to the directrix. Therefore, if the distance from V to F is p units then the distance from V to the directrix is also p units. If the coordinates of the vertex are ( h, k ) then the coordinates of the focus must be ( h, k p ) and the equation of the directrix is y k p . We can use this information and the fact that the distance from P ( x, y ) to the focus is equal to the distance from P ( x, y ) to the directrix to derive the equation of a parabola. The Equation of a Parabola in Standard Form with Vertical Axis of Symmetry The equation of a parabola with vertical axis of symmetry is ( x h) 2 4 p( y k ) where: The vertex is V (h, k ) . p distance from the vertex to focus distance from the vertex to directirx. The focus is F (h, k p ) . The equation of the directirx is y k p . The parabola opens upward if p 0 or downward if p 0 . F ( h, k p ) k ykp V ( h, k ) k V ( h, k ) ykp F ( h, k p ) h h p0 p0 Objective 2 Determining the Equation of a Parabola with Horizontal Axis of Symmetry The graph of a parabola could also have a horizontal axis of symmetry and open “sideways”. We derive the standard form of the parabola with a horizontal axis of symmetry in much the same way as we did with the parabola with a vertical axis of symmetry. The Equation of a Parabola in Standard Form with Horizontal Axis of Symmetry The equation of a parabola with vertical axis of symmetry is ( y k ) 2 4 p( x h) where: The vertex is V (h, k ) . p distance from the vertex to focus distance from the vertex to directrix. The focus is F (h p, k ) . The equation of the directrix is x h p . The parabola opens right if p 0 or left if p 0 . x h p x h p V ( h, k ) V ( h, k ) k k F ( h p, k ) F ( h p, k ) h p0 h p0