Mississippi in the 20th Century
advertisement

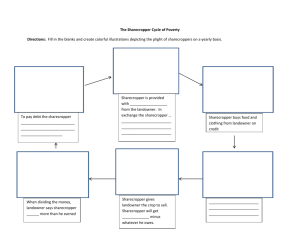
Mississippi in the 20th Century Chapters. 7 and 8 The dawn of the 20th century Mississippi became one of the ________states in the Union after the Civil War. Very little industry existed (expect __________________) Agriculture _____________________the region. ______________________ led to poverty and misery for most people – black and white. Sharecropping ________________________ - tenants that had a contract to work a piece of land for a landowner. The sharecropper and his family worked and lived on the land. “_______________” - a line of credit issued to the sharecropper Landowner received ________ of the crop and the sharecropper sold the other half for his own profit. However, the sharecropper had to pay back the “furnishes” with _________________and support his family for one year. Sharecroppers were generally • Lived in _________________ • Had ___________ diets (cornbread, salt, and molasses) • Were in deep ______________ to their landowner Sharecropping was much like ____________________. Planters often cheated the sharecroppers. Sharecroppers usually could not repay their furnishes and became ____________ tied to the Planter through debt During 1890’s most sharecroppers were____________, but by the 1930’s most were white and former small landowners. Early Lumber industry Giant ____________ trees covered Mississippi at the turn of the century. Between 1880 and 1930, lumber companies __________________ the entire state. By the end of ________________ the lumber boom had ended and all the valuable trees were gone. Fast growing ____________________ pines eventually became profitable and people started to replant. Page 1 Many cities in Mississippi got their start from the _______________________. (Hattiesburg, Laurel, D’Lo) Early 20th century Politics BY 1902 the new Democratic Party had approved a “_____________________” primary. James K. ________________________ emerged as the premier politician of early 20th century Mississippi. Vardaman is known today for helping the poor farmer and his ___________________ of the time. • Believed _______________ children should not be educated • Convict _________________ system (state hired out prisoner to individuals for work) • Believed in breaking up _______________________ and distributing the land to small farmers. MS in WWI In 1917 America enters _____________, on the side of Great Britain and France against Germany and Austria. Most of MS __________________ the US entering WWI. ______________________ loses popularity in MS after WWI, because he opposed the war. Almost ________________ men (black and white) served in the armed forces during the war. The Great Migration (the Black Exodus) During WWI blacks began _____________________ MS in large numbers looking for a better life This ___________________white leaders in MS, b/c the labor force was leaving. Northern Labor ____________promised Black Mississippians a better life away from the oppression and economic woes of MS This _____________________ continued through the Great Depression and WWII When it was all over MS had lost _____ of its black population Today African Americans make up ______ of MS pop. the highest in the U.S. The Flood of 1927 The flood of _______ was the worst flood in Mississippi history. ______________ people had to evacuate different areas of the state. Page 2 The National Guard was sent to help ___________ victims. ___________ were evacuated, ________ were set up in camps. The camps were set up more like prisons than help camps, eventually the problem was ____________. (p. 188) The flood water did not _________________ until late summer. Prohibition in MS In 1920 the United States added the ________ amendment to the constitution which made alcohol illegal to make and drink in America. This was known as _____________________. During Prohibition the MS Gulf Coast (particularly the ________) became famous for supplying Chicago gangsters with moonshine. This became known as “Kiln __________________.” ______________________ is illegally distilled liquor. MS ________________ became a major illegal port of entry for alcohol. The _________________________ era ended this boom. The Great Depression in MS The Great Depression of the 1930’s was the ______________ economic disaster in modern history. MS farmers were greatly ______________________because they could not pay back their loans. In April of 1932, ___________ of all MS land was auctioned off because of unpaid taxes. Unemployment rate was 25% and ___________________ farmers were being kicked off land by the landowners. People went hungry ________________ rich farmland. Though both black and white suffered, segregation and inequality were________________________ in the state. MS Governor Mike ____________________concentrated all his efforts to solving the financial crisis in MS. • Creating ___________________ tax • Cutting government _______________________(jobs) President Franklin D. Roosevelt came up with the ____________. The “___________________” was a series of laws and programs designed to pull the country out of the Great Depression. MS Senator Pat __________________ was key in the New Deal as head of the Senate Finance committee. Several key programs were operated in MS and gave many new jobs. Page 3 • • • • Works _____________________ Administration (WPA) __________________ Works Administration (PWA) Civilian Conservation ________________________ (CCC) _____________________ Adjustment Administration (AAA) Theodore Bilbo ______________________ was twice governor of MS (1916-20 and 1928-32) and served in the US senate for MS (1935-1947) Bilbo was known for his ________ and unscrupulous activities. He used_____________ tactics against his opponents and during his time in the senate he turned these tactics against blacks. John_________________ replaced Theodore Bilbo in the Senate, after his death from cancer. Mississippi in WWII On Dec. 7 1941 the Japanese bombed Pearl Harbor and this brought America into ___________________. 1 out of every ____ (over 250,000) Mississippians served in the armed forces during WWII. Many young ________________ went to fight and did not return in sacrifice for their country. __________________ brought great change to MS. Pascagoula, the home of Ingall’s Shipyard, became a______________. Biloxi and Hattiesburg expanded with the arrival of ______________________________and the expansion of ________________________. On the home front during the war items were _____________________, citizens had curfews and people had to do without. People moving in and out of the state brought new ____________ to the area. _____________________ began to play a larger role in the workforce to replace the men who were off at war. Military pay and benefits and wartime prosperity __________________________ the state’s average income between 1941 and 1945. By 1945 the state was modernizing and changing, but ___________________________ was still a major issue to be overcome. th Page 4