Chapter 16
advertisement
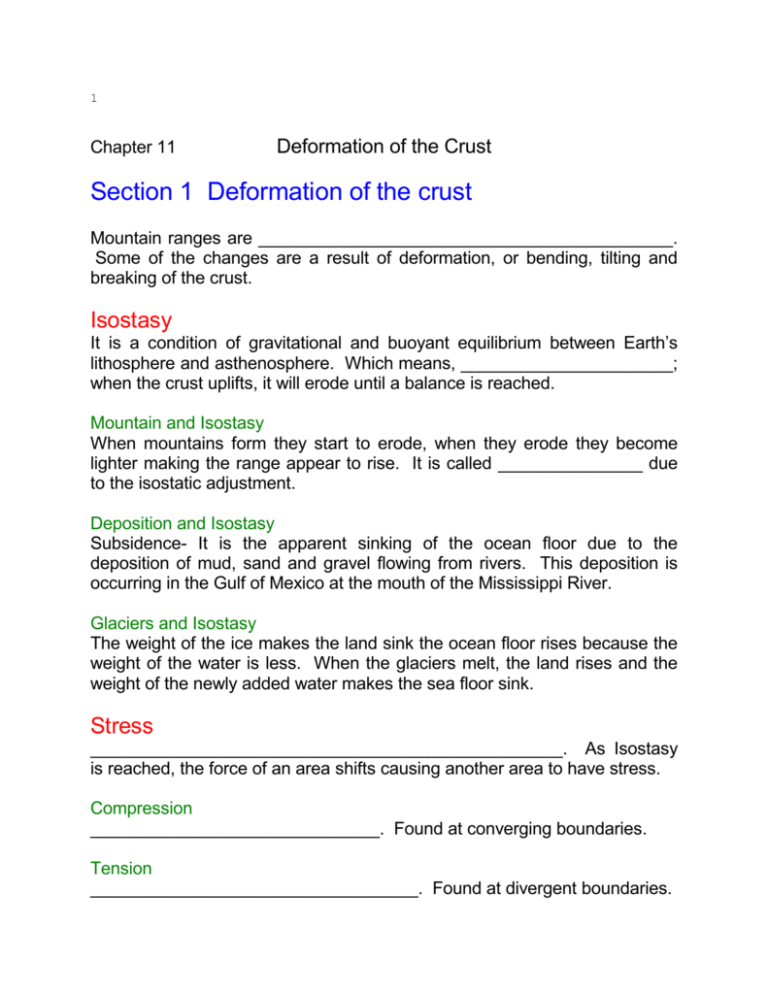
1 Chapter 11 Deformation of the Crust Section 1 Deformation of the crust Mountain ranges are ___________________________________________. Some of the changes are a result of deformation, or bending, tilting and breaking of the crust. Isostasy It is a condition of gravitational and buoyant equilibrium between Earth’s lithosphere and asthenosphere. Which means, ______________________; when the crust uplifts, it will erode until a balance is reached. Mountain and Isostasy When mountains form they start to erode, when they erode they become lighter making the range appear to rise. It is called _______________ due to the isostatic adjustment. Deposition and Isostasy Subsidence- It is the apparent sinking of the ocean floor due to the deposition of mud, sand and gravel flowing from rivers. This deposition is occurring in the Gulf of Mexico at the mouth of the Mississippi River. Glaciers and Isostasy The weight of the ice makes the land sink the ocean floor rises because the weight of the water is less. When the glaciers melt, the land rises and the weight of the newly added water makes the sea floor sink. Stress _________________________________________________. As Isostasy is reached, the force of an area shifts causing another area to have stress. Compression ______________________________. Found at converging boundaries. Tension __________________________________. Found at divergent boundaries. 2 Sheer Stress This distorts a body by pushing parts of a body in opposite directions. Commonly found at transform boundaries. Strain Any change in the shape or volume of a rock that is the result from stress. Some stresses on a rock may not be permanent if the pressure is done slowly and for a short time. However, longer periods of stress can lead to physical changes. Types of Permanent Strain Brittle – ___________________________________________________ Ductile – __________________________________________________ Factors that Affect Strain a. _____________________________________________________ b. _____________________________________________________ c. _____________________________________________________ Folds A fold is when rock layers collide, the land bends up & down. It is caused by extreme stress. 3 Anatomy of a fold Limb are the sloping sides of a fold Hinge is where the limbs meet at the bend. Axial plane occurs when both halves are identical. Types of folds Syncline - ________________________________________________ Anticline - ________________________________________________ Monocline 4 Sizes of folds The sizes of folds vary with the type and the area that has been affected. They can be small areas, or as large as mountains. Faults A fault _______________________________________________________ Fracture – a break along rock that has no movement Fault Plane – is the surface where motion occurs. Normal Faults ____________________________________________________________ _ Reverse Faults ____________________________________________________________ _ Strike-slip fault 5 ____________________________________________________________ _ Sizes of faults The sizes of the faults vary according to the area. One of the larges faults is the San Andreas Fault. Section 2 How mountains form Orogeny It is the mountain building process through the movement of the crust or volcanism. Many mountain ranges form this way due to extreme deformation. Mt Everest, whose elevation is more than 8km above sea level, is the highest mountain. Mt. St. Helen’s is a volcanic mountain that grows each year. Mountain Ranges and systems A mountain range is a group of adjacent mountains that are related to each other in shape and structure. Mt Everest is part of the Great Himalaya Range Mt. St. Helen’s is part of the Cascade Range 6 Mountain System - Is a group of mountain ranges The Great Smoky, the Blue Ridge, the Cumberland, the Green & White ranges make up the Appalachian Mountain Range. Mountain Belts – The largest mountain systems joined together Circum-Pacific belt Eurasian-Melanesian Belt Plate tectonics and Mountains Both the Circum-Pacific and the Eurasian-Melanesian belts are located along convergent plate boundaries. This is evidence that most mountains form as a result of collision between tectonic plates. Collisions between continental and oceanic crusts When ocean and continental crusts collide, the ocean crust being denser will subduct under the continental crust. This drives mountains upward. Areas of frequent earthquakes & volcanoes because pressure is built up and needs to be released either through eruptions and earthquakes. Collisions between oceanic and oceanic crusts The Mariana Islands in the North Pacific are volcanic mountains caused by ocean to ocean collisions. One oceanic plate subducts below another. The denser one sinks, partially melts and breaks through the crack causing an arc of volcanic mountains. 7 Collisions between two continental crusts The leading edge of a continental crust is oceanic so when it collides with another continental crust, it will subduct and continue to subduct until it reaches the continental edge. Then the two continental crusts will thrust each other upward forming mountains. The Indian plate collided with the Eurasian one in the same manner and the result was the Himalayan Mountains. Types of Mountains Folded Mountains and Plateaus ____________________________________________________________ ___________________. Parts of the Alps, the Himalayas, the Appalachians and Russia’s Ural mountains are folded. 8 Plateau – the large, flat areas of rock high above sea level which were formed when thick, horizontal layers of rock are slowly uplifted. The Tibetan Plateau by the Himalayas and the Colorado Plateau by the Rockies. Fault Block Mountains and Grabens 9 Parts of the crust are stretched and broken into large blocks, faulting may cause them to tilt and drop relative to other blocks. Sierra Nevada range of California is this type of mountain. Graben______________________________________________________ Death Valley and the Basin and Range Province of Western U.S. are Grabens. Dome Mountains _________________________________________________________ They are gently sloping away from the centers. Plutonic dome mountains1. __________________________________________________ 2. __________________________________________________ 3. __________________________________________________ Tectonic dome mountains` 1. __________________________________________________ 2. __________________________________________________ Volcanic Mountains 10 Are mountains that form when magma erupts. They are common along convergent plate boundaries. The Cascade Range of Washington, Oregon and Northern California are this type of mountains, the Azores in the North Atlantic Ocean. Hot Spots are active areas that lie in the middle of a tectonic plate. Hawaiian mountains are among some of the tallest in the world and are made from hot spots; 10 km above sea level and 1160 km wide. Tallest Mountains of the world Mount Everest 8850m (29035 ft) Nepal Qogir (K2) 8611m (28250 ft) India (Kashmir) Kangchenjunga 8586m (28169 ft) Nepal 11 Lhotse 8501m (27920 ft) Nepal Makalu I 8462m (27765 ft) Nepal Cho Oyu 8201m (26906 ft) Nepal Dhaulagiri 8167m (26794 ft) Nepal Manaslu I 8156m (26758 ft) Nepal Nanga Parbat 8125m (26658 ft) Pakistan Annapurna I 8091m (26545 ft) Nepal TALLEST MOUNTAINS (On Each Continent) Mount Everest 8850m (29035 ft) Asia Aconcagua 6959m (22831 ft) S. America Mount McKinley 6194m (20320 ft) N. America Mount Kilimanjaro 5963m (19563 ft) Africa Mount Elbrus 5633m (18481 ft) Europe Mount Willhelm 4509m (14789 ft) Oceania Vinson Massif 4897m (16066 ft) Antarctica