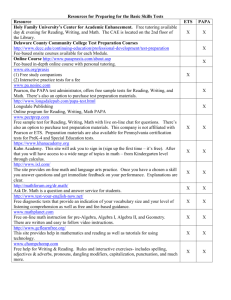
Chapter 9
Computer and Internet Research
CHAPTER SUMMARY
The earlier chapters of the text focus on the techniques for conducting research using print
resources such as texts and bound volumes. This chapter presents an overview of the various
non–fee-based Internet and other computer-based legal research sources such as CD-ROMs
(compact disc, read-only memory)..
But it is important to know how to research using print resources for at least four reasons:
A familiarity with the print source makes it much easier to understand the structure of
the electronic database and conduct electronic research.
The material you are looking for may not be in an electronic database.
An occasion may occur where access to electronic research is unavailable, such as
when the local server is down.
Cost concerns may limit the amount of time you can spend using commercial
electronic services.
Experienced researchers do not rely exclusively on computer-assisted legal research.
There are thousands of non–fee-based Web sites that provide access to various types of legal
information on the Internet. There are no laws or regulations governing the accuracy of the
content of non–fee-based Web sites; therefore, they do not have a legal duty to provide
information that is accurate or up to date. You must verify the accuracy and determine whether
any information you obtain from such sites is up to date. When selecting a non–fee-based site,
always consider the author/publisher of the information, consider the content of the information,
and check the site to determine how frequently the information is updated.
A limitation of most non–fee-based Internet sources is that they do not have databases that are as
extensive as the commercial sources mentioned in Chapter 10. Many sites that provide statutory
law do not include the annotations. Many sites that provide access to case law do not allow
searches based on search words or terms (Boolean searches).
The chapter discusses and provides the Web addresses for many of the non–fee-based Web sites
that provide access to various types of legal information. Included are federal and state
government Web sites, secondary authority and specialty area sources, and e-mail discussion
groups (listservs).
The chapter closes with a discussion of legal research information available on CD-ROMs.
© 2010 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Chapter 9
Chapter OUTLINE
I. Introduction—Importance of knowing how to research using print resources
The organization and elements of the electronic databases are based on the structure of
the print material.
The material you are looking for may not be on an electronic database.
An occasion may occur where access to electronic research is unavailable, such as when
the local server is down.
In addition, cost concerns may limit the amount of time you can spend using commercial
electronic services.
A. Ethics
B. Limitations—non–fee-based Internet sites
II. Non–Fee-Based Law-Related Web Sites—URLs
A. Search Terms—Boolean searching/terms-and-connectors searches
1. State the issue you are researching as specifically as possible in the context of the facts.
2. Formulate the search query.
B. General Access and Links
General access and links to legal research sites
Law schools
C. Federal Government Sources
1. General access sources
2. Federal courts opinions
U.S. Supreme Court
U.S. circuit courts of appeal
U.S. district courts
3. Federal statutes, court rules, and regulations
United States Code
Federal Court Rules
Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R.).
Federal Register
4. Legislation
5. Congress and federal agencies
D. State Sources
E. Secondary Authority and Specialty Areas
Westlaw or LexisNexis, Amicus Attorney, LawyerExpress
© 2010 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
1. Specialty area sources
a. Arbitration and mediation
b. Administrative law
c. Bankruptcy
d. Civil litigation
e. Civil rights
f. Consumer law
g. Corporate law
h. Criminal law
i. Elder law
j. Environmental law
k. Estate planning
l. Family law
m. Immigration
n. International law
o. Intellectual property and copyright
p. Legal documents and forms
q. Personal injury
r. Real property and landlord tenant law
s. Tax law
t. Uniform commercial code
2. Secondary authority and other sources
a. Law reviews, journals, and periodicals
b. Legal dictionaries
c. Uniform state laws and model acts
d. Law firms
F. LISTSERVS—What they are and types
1. Unmoderated
2. Moderated
G. Organizations
III. CD-ROM
IV. Key Points Checklist—Computers and Legal Research
V. Application
A. Chapter Hypothetical
B. Chapter 1 Hypothetical, Reins v. Stewart
C. Chapter 2 Hypothetical, United States v. Canter
© 2010 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Chapter 9
WEB ASSIGNMENTS
ASSIGNMENT 1
The client is charged with a federal crime. When must the trial commence under federal law?
Include the statutory citation.
ASSIGNMENT 2
The client owns a movie theater. Last week the district attorney filed a civil complaint alleging
that the theater was exhibiting obscene films contrary to state law. Your assignment is to locate a
U.S. Supreme Court case from the early 1970s on the topic. Your supervisory attorney does not
remember the name or citation of the case, but he remembers that the name of the film in
question was Magic Mirror. What is the case name and citation?
ASSIGNMENT 3
Does the State of New York recognize holographic wills (include the statutory section)?
ASSIGNMENT 4
You are looking for some general information on blue-sky laws. Where would you look?
Describes the steps you would take. Hint: This involves corporate law.
ASSIGNMENT 5
Your firm is working on an industrial lease. Your assignment is to locate an industrial lease
form. Where would you look to locate the form and what is the cost?
ASSIGNMENT 6
What is the telephone number for the clerk’s office for the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Third
Circuit?
ASSIGNMENT 7
How often is the economic census of the United States taken? How can you access economic
census data?
ASSIGNMENT 8
What section of the Savannah, Georgia, municipal code governs speed limits? What is the speed
limit unless otherwise posted?
© 2010 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.