Answers
advertisement

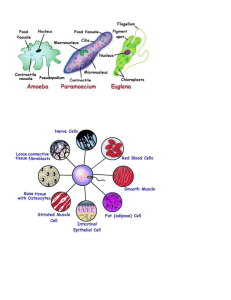
Cell Unit Study Guide – Part #1 (Cell Growth and Function) Vocabulary to know and understand: Cell Growth Specialized cell/tissue (differentiation) Unicellular Organism Multi-cellular Organism Cell function Tissues Organs Organ Systems Cells Organisms Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Concepts to know and understand: What are all organisms made of? What is the difference between unicellular organisms and multicellular organisms? What is the order of an organism’s make up (from most basic to the most complex)? How are cells specialized? What functions must all cells perform to survive? Cells must grow and develop to continue their species. When do they grow in size and when do they grow in number? Give some examples of diffusion and osmosis. Give some examples of unicellular and multi-cellular organisms. Explain how cells function in a similar way in all organisms. Relate this to how cells in a multi-cellular organism are specialized. Discuss an example of diffusion and osmosis. Answer Guide Cell Unit Study Guide – Part #1 (Cell Growth and Function) Vocabulary to know and understand: Cell Growth – The processes of increasing the number of cells or the size of the cell. Specialized cell/tissue (differentiation) – When cells or tissues perform a specific job/function. This occurs in multi-cellular organisms. Unicellular Organism – An organism made of one cell. Growth occurs due to increased cell size. Cells aren’t specialized to perform a specific function. Multi-cellular Organism – An organism made of more than one cell. Growth occurs due to increased cell size & cell reproduction. Cells are specialized to perform specified functions. Cell function – The processes of cells that enable them to stay alive and reproduce. Tissues – Cells of similar structure working together for a specific reason. Organs – Different types of tissues working together to perform a specific function. Organ Systems – Different types of organs working together for a specific reason. Cells – The building material of all living things. Organisms – All living things. Diffusion – Movement of molecules from areas where there are more of them to areas where there are fewer of them. Osmosis – The diffusion of water. Active Transport – The movement of a substance through a cell membrane that requires energy. Concepts to know and understand: What are all organisms made of? All organisms are made of cells. What is the difference between unicellular organisms and multicellular organisms? Unicellular organisms are made of one cell and grow by getting larger. Multicellular organisms are made of more than one cell and grow by reproducing and by getting larger. Both unicellular organisms and multicellular organisms are able to perform the functions necessary for survival. What is the order of an organism’s make up (from most basic to the most complex)? Cells Tissues Organs Systems Organisms How are cells specialized? Cells are specialized to perform special functions. What functions must all cells perform to survive? Get and use energy/food/nutrition/water Get and use air/oxygen Have the ability to move Have the ability to reproduce Have the ability to excrete waste Have the ability to adapt to a compatible environment Cells must grow and develop to continue their species. When do they grow in size and when do they grow in number? Uni-cellular grow in size. Multi-cellular grow in number and in size. Give some examples of diffusion and osmosis. Diffusion – Being able to smell something from across the room, dropping a sugar cube in a cup of coffee, stirring kool-aid into a pitcher of water, eventually being able to smell cologne or vinegar across the room. Osmosis – strawberries getting smaller and ending up in juice, your body ‘pruning’ up when in water for a long time, putting carrots in water so they stay hydrated. Give some examples of unicellular and multicellular organisms. Unicellular – bacteria, duck eggs, yeast, protozoa Multi-cellular – plants, animals, fungi, algae Explain how cells function in a similar way in all organisms. Relate this to how cells in a multi-cellular organism are specialized. All cells in both unicellular and multi-cellular organisms perform certain functions to survive. All cells must eliminate waste, grow, reproduce, consume/produce food for energy, etc. In multi-cellular organisms, as the cell divides, they specialize to do certain task and can only complete their task. An example of this would be a blood cell. Discuss an example of diffusion and osmosis. An example of osmosis is when you put strawberries in a bowl and add sugar. The sugar begins to dissolve in the small amount of water on or near the surface of the strawberry. This then becomes more diluted by moisture diffusing out of the strawberries and into the sugar solution. The water molecules diffuse across the strawberries semi-permeable membranes in an attempt to reach an equal concentration on both sides of the membrane. The strawberries become shriveled and soft because their internal moisture has been depleted (and somewhat dehydrated) when the water in the strawberry moves from the higher concentration to the lower concentration outside the strawberry.