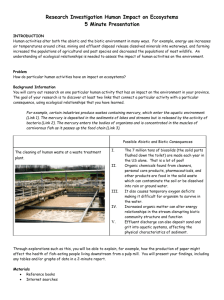
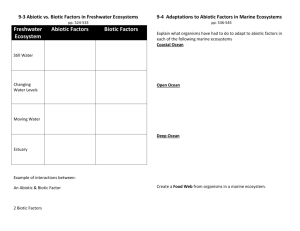
AP Biology Assignment Sheet for - Community Unit School District 308
advertisement

Ecology Unit Syllabus 2015-2016 Chapters 52-56 Date Class Discussion Topic/Activity Wednesday Sept. 16 Introduction to Ecology, Levels of Organization Terrestrial Biomes – Graphing Activity Thursday Sept. 17 Assignment (Unless otherwise noted assignments are due the next day class meets) Learning Targets Chapter 52: An Introduction to Ecology & the Biosphere (sections 52.2-52.3 only) 1. I can explain how all biological systems from cells and organisms to populations, communities, and ecosystems are affected by complex biotic and abiotic interactions involving exchange of matter and free energy, such as: a. temperature b. water and nutrient availability c. sunlight d. pH e. salinity Aquatic Biomes – Jigsaw & Organizer Chart Read chapter 52 (sections 52.2 and 52.3 only) Begin to actively read, take notes on chapter 53 Chapter 53 one pager due Thursday 9/24 Friday Sept. 18 Set up AP Lab 10: Energy Dynamics Quiz – chapter 52 Population Density, Dispersion, & Demographics (53.1) Chapter 53: Population Ecology I can explain how the stability of populations, communities and ecosystems is affected by interactions with biotic and abiotic factors such as: a. Water and nutrient availability b. Availability of nesting materials and sites c. Population density d. Predator-prey relationship I can explain how a population of organisms has properties that are different from those of the individuals that make up the population. The cooperation and competition between individuals contributes to these different properties. I can explain how reproduction and rearing of offspring requires free energy beyond that used for maintenance and growth. Different organisms use various reproductive strategies in response to energy availability. a. Seasonal reproduction in animals and plants. b. Life-history strategy (biennial plants, reproductive diapause) I can use mathematical models and graphical representations to illustrate population growth patterns and interactions. a. I can explain how reproduction without constraints results in the exponential growth of a population. b. I can explain how a population can produce a density of individuals that exceeds the system’s resource availability. c. I can explain how as limits to growth due to density-dependent and densityindependent factors are imposed a logistic growth model generally ensues. d. I can explain how demographics data with respect to age distributions and fecundity can be used to study human populations. I can explain how models allow for the prediction of the impact of change in biotic and abiotic factors. a. Competition for resources and other factors limits growth and can be described by the logistic model. b. Competition for resources, territory, health, predation, accumulation of wastes and other factors contribute to densitydependent population regulation. Videos to watch: Population Growth Population Dynamics Monday Sept. 21 Tuesday Sept. 22 Exponential Growth (53.2) Logistic Growth & Carrying Capacity (53.3) AP LAB 13 - ENZYMES DUE! Life History (53.4) Wednesday Sept. 23 Thursday Sept. 24 Limiting Factors (53.5) Human Populations (53.6) Quiz – chapter 53 AP Lab 10: Energy Dynamics Data Friday Sept. 25 Finish chapter 53 NO SCHOOL – Teacher Institute Mastering biology ch. 53 quiz by 11:59pm Ch. 53 one pager due tomorrow! Begin to actively read, take notes on chapter 54 Chapter 54 one pager due Thursday 10/1 Monday Sept. 28 Competitive Exclusion Activity (54.1) Organism Interaction Webquest (54.1) Tuesday Sept. 29 Biodiversity & Community Stability, Keystone Species (54.2/54.4) Chapter 54 Community Ecology 1. I can explain how the stability of populations, communities and ecosystems is affected by interactions with biotic and abiotic factors such as: a. Water and nutrient availability b. Availability of nesting materials and sites c. Population density d. Predator-prey relationship 2. I can explain how the structure of a community is measured and described in terms of species composition and species diversity. 3. I can explain how the diversity of species in an ecosystem may influence the stability of the ecosystem. a. Natural and artificial ecosystems with fewer component parts and with little diversity among parts are often less resilient to changes in the environment. b. Keystone species, producers, and essential abiotic and biotic factors contribute to maintaining the diversity of an ecosystem. The effects of keystone species on the ecosystem are disproportionate relative to their abundance in the ecosystem and when they are removed from the ecosystem, the ecosystem often collapses. 4. I can explain how species-specific and environmental catastrophes, geological events, the sudden influx/depletion of abiotic resources or increased human activities affect species distribution and abundance, such as: a. Loss of keystone species 5. I can use mathematical or computer models to illustrate and investigate population interactions within and environmental impacts on a community, such as: a. Predator-prey relationships spreadsheet model b. Symbiotic relationships c. Graphical representation of field data d. Introduced species e. Global climate change models 6. I can explain how interactions between populations affect the distributions and abundance of populations. a. Competition, parasitism, predation, mutualism and commensalism can affect population dynamics. b. Relationships among interacting populations can be characterized by positive and negative effects and can be modeled mathematically (predator/prey, epidemiological models, and invasive species). c. Many complex symbiotic relationships exist in an ecosystem, and feedback control systems play a role in the functioning of these ecosystems. 7. I can explain how cooperative behavior within or between populations contributes to the survival of the populations, such as: a. Niche and resource partitioning b. Mutualistic relationships c. Biology of pollination 8. I can explain how many adaptations of organisms are related to obtaining and using energy and matter in a particular environment. a. I can explain how changes in free energy availability can result in changes in population size. Videos o o o Video: Biodiversity Colorations Niches Ecological Succession Wednesday Sept. 30 Energy in Ecosystems (54.2) Chapter 54 one pager due tomorrow! Mastering Biology: chapter 54 quiz by 11:59pm Begin to actively read, take notes on chapter 55 Chapter 55 one pager due Thursday 10/8 Trophic Level Review Thursday Oct. 1 Friday Oct. 2 Monday Oct. 5 Owl Pellet Lab Collect Data AP Lab 10: Energy Dynamics Data Ecological Succession (54.3) Quiz – chapter 54 Ecological Succession (54.3) Energy & Ecosystems (55.1) Primary/Net/Gross Productivity (55.2/55.3) Tuesday Oct. 6 AP Lab 10: Energy Dynamics Data Wednesday Oct. 7 Primary/Net/Gross Productivity (55.2/55.3) Biogeochemical Cycles (55.4) Thursday Oct. 8 Collect Data AP Lab 10: Energy Dynamics Chapter 55: Ecosystems and Restoration Ecology (sections 55.155.4) 1. I can explain how the stability of populations, communities and ecosystems is affected by interactions with biotic and abiotic factors such as: a. Water and nutrient availability b. Sunlight c. Temperature d. Salinity e. Food chains and webs 2. I can explain how all interactions among living systems and their environment result in the movement of matter and energy. a. Energy flows, but matter is recycled. b. Changes in regional and global climates in atmospheric composition influence patterns of primary productivity. c. Organisms within food chains interact. d. Food webs and food chains are dependent on primary productivity. 3. I can explain how organisms use free energy to maintain organization, grow and reproduce. a. I can explain how excess acquired energy versus required free energy expenditure results in energy storage or growth. b. I can explain how insufficient acquired free energy versus required free energy expenditure results in loss of mass and, ultimately, the death of an organism. 4. I can explain how changes in free energy availability can result in disruptions to an ecosystem, such as: a. Change in the producer level can affect the number and size of other trophic levels. b. Change in energy resources levels such as sunlight can affect the number and size of the trophic levels. Videos to watch: Chemical Cycles Chapter 55 one pager due tomorrow Mastering Biology: chapter 55 reading quiz by 11:59pm Begin to actively read, take notes on chapter 56 (sections 56.1 & 56.4 only) Biogeochemical Cycles (55.4) Friday Oct. 9 Quiz – chapter 55 Human Impact (56.1/56.4) Generating Heat Activity Monday Oct. 12 NO SCHOOL – Columbus Day Tuesday Oct. 13 Human Impact (56.1/56.4) Chapter 56: Conservation Biology and Global Change (sections 56.1 and 56.4 only) 1. I can explain how disruptions to ecosystems impact the dynamic homeostasis or balance of the ecosystem, such as: a. Invasive and/or eruptive species b. Human impact c. Hurricanes, floods, earthquakes, volcanoes, fires d. Water limitation e. Salinity 2. I can explain how human impact accelerates change at local and global levels, such as: a. Logging, slash and burn agriculture, urbanization, monocropping, infrastructure development (dams, transmission lines, roads), and global climate change threaten ecosystems and life on Earth. 3. I can explain how human activities impact ecosystems on local, regional and global scales, such as: a. As human populations have increased in numbers, their impact on habitats for other species has magnified. b. In turn, this has often reduced the population size of affected species and resulted in habitat destruction, and in some cases, the extinction of species. 4. I can explain how an introduced species can exploit a new niche free of predators or competitors, thus exploiting new resource. 5. I can explain how geological and meteorological events impact ecosystem distribution, such as: a. El Nino b. Continental drift c. Meteor impact on dinosaurs Global Climate Change POGIL Wednesday Oct. 14 Human Impact (56.1/56.4) Your Carbon Footprint Thursday Oct. 15 Friday Oct. 16 Review Ecology Unit Exam AP Lab 10: Energy Dynamics Data (SIP day – End of 1st Quarter) Begin Unit 3: Evolution See next syllabus for assignment AP Lab 10: Energy Dynamics continues into next unit (?)