Era: Precambrian
advertisement

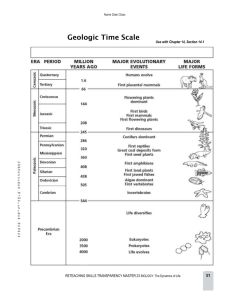
Era: Precambrian Period: no period Time: Birth of Earth to approximately 600mya. The Precambrian makes up about 87% of Earth’s History! During this era most organisms were simple unicellular (one-cell) plants and animals living in the sea. Bacteria were also abundant. By the end of the Precambrian, the first simple multicellular (many cells) organisms, like jellyfish and sponges, started to appear in the oceans. Era: Paleozoic Period: Cambrian Time: 590 – 492mya During the Cambrian period, a burst of life occurred. Fossils show the appearance of hundreds of new multicellular plants and animals in the oceans in a short amount of time, in what is now known as the “Cambrian explosion”. Most of these new organisms eventually went extinct, but some survived and evolved. Fossils also show the appearance of simple fish for the first time. Era: Paleozoic Period: Ordovician Time: 491 – 445mya Fish become very common in the oceans of the Ordovician. Simple plants like mosses began colonizing land, followed by fungi. Era: Paleozoic Period: Silurian Time: 443 – 418mya The Silurian was the Age of Fish! Fishes dominated the oceans. The first complex plants capable of photosynthesizing began to colonize land, forming primitive forests. Era: Paleozoic Period: Devonian Time: 417 – 355mya In the Devonian, the fish continued to dominate the oceans. The first sharks appeared. Land plants continued to evolve, producing oxygen through photosynthesis. Thanks to this oxygen, the first amphibians began to leave the water and walk the land. Era: Paleozoic Period: Carboniferous Time: 354- 295mya Amphibians very common and fossils suggest that the first early reptiles appeared. Insects appeared and become abundant too. Fossils show that the Earth was covered in huge tropical forests. When this plant matter died it formed the large deposits of coal and oil that we use nowadays for transport and production of electricity. Era: Paleozoic Period: Permian Time: 290 -250mya During the Permian, mosses and ferns became abundant. Reptiles and amphibians were also abundant, including advanced reptiles that begin to show mammal characteristics like warm blood, fur and live-birth. Unfortunately, at the end of the Permian a mass-extinction event, the biggest in the history of Earth, happened: approximately 96% of all life on Earth was killed, possibly by extreme changes in climate. Era: Mesozoic Period: Triassic Time: 249 – 210mya The Triassic marks the beginning of the Mesozoic Era. After the mass-extinction of the Permian there was plenty of living space for new plants and animals to take over. The first early dinosaurs appear and began to spread out. Also, the first early mammals appeared. Era: Mesozoic Period: Jurassic Time: 206 – 145mya The Jurassic was the age of the dinosaurs, but even though they dominated they were not the only ones: the first early birds also appeared. Weather was generally warm, and plants like cycads, yuccas and palm trees were common in warm parts. In the cooler parts of the planet, pine forests dominated large areas of land. Flowering plants (those that produce flowers) first appeared during this time, quickly spread around the Earth, and soon became the dominate plant group. They still are! Era: Mesozoic Period: Cretaceous Time: 144-67mya The Cretaceous marked the end of the Mesozoic, and the end of the dinosaurs! A massive extinction event killed most of the dinosaurs, but many mammals, birds, fish and amphibians survived. In total, approximately 65% of all animal and plant species disappeared. Scientists believe that this mass extinction was produced by a meteorite falling on Earth. Era: Cenozoic Period: Tertiary Time: 65- 1.8mya During the Tertiary the weather on Earth was cooled a lot. A very important organism appeared: grasses. This was very important, because a lot of animals eat grass. Mammals now become very abundant (no more dinosaurs to hide from), and some of them grew to huge sizes! Some of the more characteristic mammal groups, like whales and monkeys, appeared at around this time. The very first early humans appeared. Era: Cenozoic Period: Quaternary Time: 1.7mya to present time The most important events during the quaternary where the various Ice Ages that happened: cold periods (ice ages) alternating with warmer periods (interglacial ages). As the Earth became colder and snow-covered, animals that could survive the cold, like mammoths, bears and sabre-tooth tigers survived. Modern humans finally appeared. During the final stages of the Quaternary the Earth warmed up, and the majority of the great land mammals (mammoths, giant sloths, sabre-tooth tigers) went extinct. We are currently in the Quaternary, living in an interglacial period.