Solutions Chapter 4
advertisement

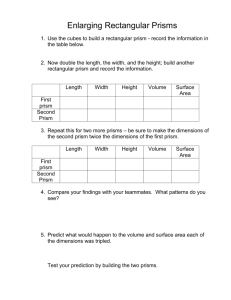
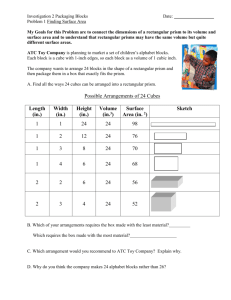
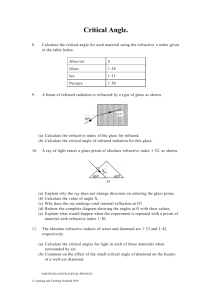
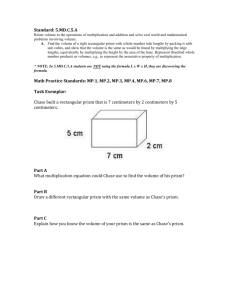
Solutions Chapter 4 4.1 In order for a 6 ft tall man to see himself from head to toe, how tall a mirror needs to be placed at the following distances from the man? a. b. c. 4.2 6 ft away 10 ft away 20 ft away What are the glass numbers for a. b. c. NBK7 SF11 LaSFN9 a) NBK7: 517642 b) SF11: 785258 c) LaSFN9: 850322 4.3 Which glass has a higher dispersion in the visible spectrum, crown or flint? Flint glasses have lower Abbe numbers and therefore higher dispersion than crown glasses. Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 1 4.4 For a penta prism: a. b. Make a layout of the unfolded diagram to get the PPP If the input surface of the penta prism is 1 cm wide, what is the total OPL, if the glass index is 1.5? a) 1cm 1cm 2 cm 1cm b) The diagram above shows that the total path through the glass is 1cm+1cm+ 2 cm = 3.41cm. The 2 was found by the Pythagorean theorem. Total optical path length = tn = (3.41cm)1.5 = 5.12cm 4.5 The new “Back-Saving Horizontal Reading Glasses” for watching TV while lying down are being sold. As a student of geometrical optics, studying prisms, you should be able to answer the following questions. a. What is the optical diagram for using a right angle prism to view the TV? b. How do these eyeglasses work, especially considering parity and handedness of the image? a) b) How does this configuration work considering handedness and parity? The image is right side up, but the single reflection causes the parity to be reverted left and right. Words are written backwards from the way they would appear on the screen. A more complex system would allow the glasses to work as show below by providing two reflections so that the parity is correct: Half reflecting side Mirror Side Mirror Side Deviation is not 90 degrees Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 Half the light is lost every time the hypotenuse is reached 2 4.6 What is the parity for an image which has traversed a: a. b. c. penta prism dove prism corner cube a) b) c) Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 3 4.7 Calculate the angle of deviation for F, d and C light for a prism made of SF4 (755276) glass with a 22 apex angle and 30 angle of incidence. 4.8 Derive the expression for angle of deviation for a thin prism. 4.9 What is the handedness (parity), and orientation of an image seen through the following prisms? How will the image be changed when looking though the prism at the letter R? a. b. c. Abbe Prism Penta Prism Right Angle Prism (1) Light reflected by the hypotenuse (2) Light reflected at the two smaller faces (Porro) Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 4 4.10 What is the correct orientation and description of the R in the final space? 4.11 A student has two glass rods. Rod A is # 300800 glass and rod B is # 900400 glass. a. b. c. What is the ratio of velocities of light in glass (A) to glass (B)? In which rod is the velocity of light slower, (A) or (B)? Which is the crown glass? Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 5 4.12 There are two pieces of glass, each 10 cm in length. Glass A has a glass # of 200700 and Glass B is 600350. a. What is the ratio of the velocity of light in glass A to glass B? b. Which glass has the higher speed of light? c. Which is the flint glass? 4.13 Plot the deviation angle () for a prism made of F2 with apex angle of 25 versus incidence angle (I) using d-wavelength light. a. What is the minimum deviation for d-light? Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 6 b. 4.14 What is the minimum deviation for d-light if we assume a thin prism? For SF11 glass, what is the index of refraction calculated to five decimal places for the following wavelengths: a. b. c. d. 400 nm 500 nm 600 nm 700 nm Using Matlab to calculate n: Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 7 4.15 For the following optical systems, draw the orientation of the letter at the observation plane. Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 8 4.16 What is the minimum refraction index that a right angle prism must have to reflect the light by 90 with Total Internal Reflection (TIR)? 4.17 For the drawing below using an isosceles glass prism (n = 1.5) the apex angle (2.5) is such that the ray is parallel to the axis inside the prism. What is the optical path length for the ray? What is it along the axis? Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 9 4.18 What are the Abbe numbers and glass numbers for: From the Schott Catalog: a. b. c. d. e. Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 SF59 SF59 F14 F14 BK1 BK1 BaK4 BaK4 FK54 FK54 20.4 38.2 63.5 56.0 90.7 glass number 952204 601382 510635 569560 437907 10 4.19 A crown (BaK4) thin prism with an apex angle of 15 is to be combined with a flint prism (SF12) so as to produce no net deviation for d-light a. b. Find the apex angle for the contact flint prism. Find the angular deviation for C-light for this prism combination. a) b) 4.20 A hollow (and empty) 60 apex angle is immersed in a liquid of index 1.74. What is the angle of minimum deviation? 4.21 A glass prism with n = 4.62 shows an angle of minimum deviation of 48.2. What is the apex angle? Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 11 4.22 A 5 ft tall lady would like to buy a mirror to use while dressing. She requires that it be large enough so that she can see her shoes and hair simultaneously. If she sets the mirror at distances of: (a) 3 ft, (b) 5 ft, and (c) 10 ft away, what is the smallest mirror she should obtain for each case? This problem is similar to problem 4.1, in which a 6ft tall man wants to see himself from toes to eyes. In this case, we have a 5ft tall woman. A ray leaving her shoes must be reflected back to her eyes and must also meet the mirror at its bottom. Also, a ray that leaves her hair must be reflected straight back to her head at the top of the mirror. Therefore, due to geometry, the mirror must be half of the woman’s height for this to occur, or 2.5ft tall, regardless of distance. 4.23 A Pechan prism has the following side view: a)Determine the handedness of the image and indicate whether or not the image is inverted The image is inverted because with the odd number of bounces ( 5 bounces) the handedness is left handed. Input: Output: b) Draw the Tunnel diagram (unfold the prism) Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 12 The tunnel diagram is shown below. This is drawn by unfolding the prism system at each reflecting surface c) Can you see any applications for this prism? Applications for a prism that inverts an image, but has zero angular deviation, may be for rifle scopes to flip the image. There is a niche market of these prisms to guards who practice a rare form of yoga where they do headstands for extended periods of time, but must maintain a clear, upright view from the guard station in order to fulfill their watch duties. Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 13 4.24 Plot the deviation angle () versus incidence angle (I1) for a prism with an apex angle of 50, made of NBK7 glass, using d-light. At what angle does the minimum deviation occur? (degrees) 0 deviation -10 0 20 40 60 80 100 -20 -30 -40 -50 incident angle Minimum deviation occurs about 20 degrees incident 4.25 A prism with an apex angle of 90 is shown in the figure below. A ray enters this prism at 30 and exits at 50. What is the index of refraction of the prism? Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 14 4.26 Given a prism with an apex angle A = 6.3 and an Ohara Glass number of S-FPL51, what is the angle of minimum deviation, min, for C, d, and F-light? 4.27 Plot the index of refraction vs. wavelength (F, d, C only) for NBK7, N-FK5, and F5 glasses. Plot all points on the same graph and use wavelength in nm. Use the equation K1 K2 2 for NBK7 and solve for K1 and K2. Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 15 4.28 Describe the dispersion for the following glasses as either higher or lower than KF3 glass. (KF3 glass has an Abbe # of about 55). Classify each type as a crown or a flint: a. b. c. d. 4.29 N-FK5 NBK7 F5 N-LaSF45 For a prism made of F4 glass with an apex angle of 25, plot the deviation angle () versus incidence angle (I) using d-wavelength light, C-light and F-light. a. What is the angular spread of C to F light rays for an incident angle of 35? Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 16 b. c. d. What is the angular spread of d to F light rays for an incident angle of 35? What is the minimum deviation for d light? What is the minimum deviation for d light if we assume a thin lens? Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 17 Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 18 4.30 For a 3" prism made of NBK7, with a 3” base and height of 4”, compare the dispersion at F, C and d light. (Hint: Use K2 from problem 4.27). Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 19 4.31 For the following deviating prisms, draw the correct orientation of the object, R. 4.32 The index of refraction for a glass at three different wavelengths is shown is below: a. b. λ (nm) n 486.1 587.6 656.3 1.525 1.517 1.514 What is the Abbe #? What is the glass number? Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 20 4.33 Given a right-angle prism with an apex angle of 7, what is the angle of deviation for a prism made from: a. b. c. NBK7 F4 NSF57 δ = -A( n-1 ) a) N-BK7 b) F4 c) N-SF57 Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 A= 7o = 0.122 rad n = 1.5168 n = 1.6166 n = 1.847 δ = 0.630 rad , 3.612 deg δ = 0.753 rad , 4.316 deg δ = 0.103 rad , 5.929 deg 21 4.34 4.35 This prism stack is used to focus optical radiation onto a solar cell, which is 2 mm diameter (assume rotational symmetry). Where should the solar cell be located from the reference surface to achieve maximum signal if : a. All of the prisms are made of n = 1.5 glass, and: (1) Prism 1 has an apex angle of 5 (2) Prism 2 has an apex angle of 3 (3) Prism 3 has an apex angle of 1 b. All of the prisms have an apex angle of 5, but each prism has a different index: (1) Prism 1 (nd =1.477) (2) Prism 2 (nd = 1.286) (3) Prism 3 (nd = 1.0955) For the following prism types, what is the parity (odd or even)? Make an unfolded (Tunnel) diagram: a. b. c. Penta Prism Porro Pair Prisms Abbe Prism Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 22 Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 23 4.36 The index of refraction for sapphire (Al2O3) for the ordinary and extraordinary rays is ( in micrometers): no 2 1 ne 2 1 a. b. 1.4313493 2 0.65054713 2 5.3414021 2 2 0.00528 2 0.014238 2 325.0178 1.5039759 2 0.55069141 2 6.5927379 2 2 0.005480263 2 0.014802 2 402.8951 Plot the index versus wavelength from 400 nm to 5 μm in wavelength. Over this range, what wavelength has the greatest index difference? Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 24 4.37 A pulse of white light which is 1ps wide incidence of a glass fiber optic (nF = 1.6, nd = 1.55, nC = 1.5). The output pulse needs to have the red light (C) separated from the blue light (F) by 1 ns. How long must the fiber be made? The problem sets up a situation where light is normally incident on a piece of glass and the dispersion of the glass will cause the light to “smear” out 1000 times its incident width. Since blue light sees a higher n, it will trail red light by 1 nanosecond. Setting up the expression to find this distance, all we need is the OPD between red and blue and divide by the speed of light to get the optical time difference. Chapter 4 Solutions 2/16/2016 25