Northern Mountain Rim
advertisement
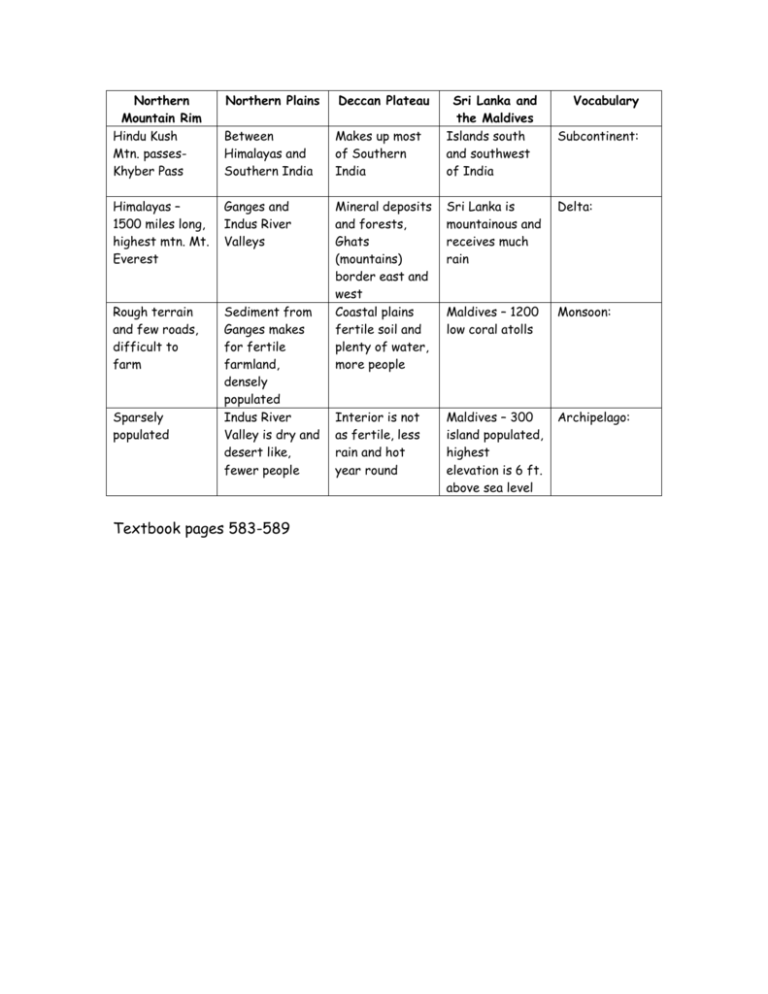
Northern Mountain Rim Hindu Kush Mtn. passesKhyber Pass Northern Plains Deccan Plateau Between Himalayas and Southern India Makes up most of Southern India Himalayas – 1500 miles long, highest mtn. Mt. Everest Ganges and Indus River Valleys Sri Lanka is mountainous and receives much rain Delta: Rough terrain and few roads, difficult to farm Sediment from Ganges makes for fertile farmland, densely populated Indus River Valley is dry and desert like, fewer people Mineral deposits and forests, Ghats (mountains) border east and west Coastal plains fertile soil and plenty of water, more people Maldives – 1200 low coral atolls Monsoon: Interior is not as fertile, less rain and hot year round Maldives – 300 island populated, highest elevation is 6 ft. above sea level Archipelago: Sparsely populated Textbook pages 583-589 Sri Lanka and the Maldives Islands south and southwest of India Vocabulary Subcontinent: