mec13126-sup-0001-FigS1
advertisement

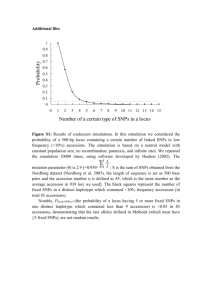
Supplementary Figure legends: Figure S1 – Genotypes and pairwise linkage disequilibrium between all pairs of sexlinked SNPs in reference genome v2.2. A) VG2 plot generated at the SeattleSNPs Variation Resource website (http://pga.gs.washington.edu/VG2.html) for the T52 mapping population. B) VG2 plot for the BT68 mapping population. In A and B, accessions are represented in rows and SNPs in columns. Correspondence between SNP numbers in the figure and SNP location can be found in Table S2. MT indicates male P. trichocarpa accessions, FT female P. trichocarpa accessions, MB male P. balsamifera accessions and FB female P. balsamifera accessions. Text on top of the figure indicates the genomic region where each group of SNPs is mapped. C) Histograms of pairwise linkage disequilibrium (r2) in T52 between all 623 SNPs significant associated with sex in the top panel, only significant SNPs in the same region (as defined in Table 2) in the middle panel and only significant SNPs in different regions (as defined in Table 2) in the bottom panel. Pairwise LD was calculated in the SeattleSNPs Variation Resource website (http://pga.gs.washington.edu/VG2.html). Pairwise LD estimates are available at Dryad. Figure S2 - Phylogenies of regions significantly associated with gender. For each phylogeny, only male accessions were used. X and Y alleles were PCR amplified, cloned and one random clone was Sanger sequenced with allele specific primers. For P. tremuloides, the primers did not produce allele specific amplification. PCR products were cloned and several clones were Sanger sequenced. Y chromosome alleles are indicated with a Y and X chromosome alleles with an X at the beginning of the sequence name. These are followed with Trich, for P. trichocarpa accessions, Balsam for P. balsamifera accessions, Delt, for P. deltoides accessions, Nigra, for P. nigra accessions and Trem_Clone for P. tremuloides. Maximum Likelihood phylogenies were estimated in MEGA5, with Tamura-Nei distance and complete deletion of all positions with missing data and alignment gaps. For each phylogeny we also included the P. trichocarpa reference sequence from genome assembly v2.2 (indicated as POPTR_0009s08410 and POPTR_00019s00240) and the reference sequence from genome assembly v2.2 of the paralogue arising from the Salicoid whole genome duplication (indicated as POPTR_0001s29310 and POPTR_0004s14140. Only bootstrap support values higher than 80 (from 500 replicates of each tree) are shown. a) Phylogeny of Chr9 region (Amplicon1:Chr9:7690067, SI) with a total of 358 positions, b) Schematic representation of gene POPTR_009s08419 (v2.2 of the genome assembly), detailing the position of Amplicon1:Chr09:7690067. Exons are indicated as blue boxes and introns as blue lines, start codon with a green triangle and stop codon with a red triangle. c) Phylogeny of Chr19 Amplicon1:Chr19:40024 (SI) with a total of 1231 positions, d) Phylogeny of Chr19 Amplicon2:Chr19:41515 (SI) with a total of 1291 positions, e) Phylogeny of Chr19 Amplicon3:Chr19:44107 (SI) with a total of 1165 positions. f) Schematic representation of gene POPTR_019s00240 (v2.2 of the genome assembly), detailing the position of the three amplicons. Exons are indicated as blue boxes and introns as blue lines, start codon with a green triangle and stop codon with a red triangle. Figure S3- Manhattan plots all SNPs mapped to the 19 chromosomes in v3.0 (a) and v1.1 (b) of the P. trichocarpa reference genome. The horizontal red line indicates the –log10(p value) corresponding to <0.05 after Bonferroni correction for multiple testing. From top to bottom, population T52, 34 female and 18 male P. trichocarpa accessions, population B34, 18 female and 16 male P. balsamifera accessions and population BT68, 36 female and 32 male accessions, where half the samples of each gender are P. trichocarpa and the other half are P. balsamifera Figure S1 (A) 7" $"#" ! "#" (" &"'" )" %" %) "*+, - ./ 01" %) "2.3401" 56%" ! " ! #$ % & % '$ Figure S1 (B) B FT FB MT MB 1 9 19 proximal 19 distal 2 6 1 Figure S1 (C) 60000 20000 0 Frequency All significant SNPs 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 40000 20000 0 Frequency Significant SNPs in the same region 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 30000 0 10000 Frequency Significant SNPs not in the same region 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 r2 0.8 0.9 1.0 Figure S2 Figure S3 a) b) Genome assembly v3.0 Genome assembly v1.0 T52 T52 12 10 10 8 -log10(p) -log10(p) 12 6 4 8 6 4 2 2 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 7 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 1 19 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1718 19 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1718 19 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1718 19 B34 B34 12 12 10 -log10(p) -log10(p) 10 8 6 4 8 6 4 2 2 0 0 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 2 3 4 5 6 7 BT68 BT68 -log10(p) 12 10 -log10(p) 12 10 8 6 4 8 6 4 2 2 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 19 9 10 Chromosome 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Chromosome