2008 Directed Reading B
advertisement

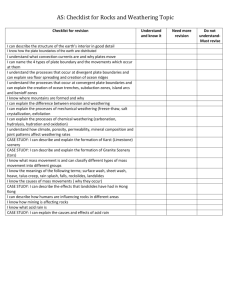
Name ______________________________ Class __________________ Date __________________ Directed Reading Chapter 10 section 1: Weathering Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. What is the process by which rocks are broken down physically or chemically called? a. abrasion b. frost action c. weathering d. .ice wedging MECHANICAL WEATHERING 2. What is it called when rocks are broken into smaller pieces by physical means? a. mechanical weathering b. oxidation c. habitation d. acid precipitation 3. Which of the following is an agent of mechanical weathering? a. air b. oxidation c. weak acids d. gravity Ice 4. What is the alternate freezing and thawing of soil and rock called? a. frost action b. ice weathering c. abrasion d. chemical weathering 5. What type of frost action occurs when a crack in a rock widens from the freezing and thawing of water? a. chemical weathering b. ice wedging c. oxidation d. abrasion Abrasion 6. What is the grinding and wearing away of rock by other rocks or sand called? a. precipitation b. chemical weathering c. abrasion d. oxidation Wind, Water, and Gravity 7. What causes abrasions of rocks and pebbles in fast-flowing streams? a. gravity 8. b. water c. acid precipitation d. wind What causes abrasion when one rock falls off a mountainside onto another rock? a. gravity b. water c. acid precipitation d. wind Plants 9. Which is an example of a plant causing mechanical weathering of a rock? a. acid from lichen breaking down a rock c. a tree root causing a rock to crack b. gophers burrowing in the ground d. rocks washing away in a rain storm Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Science and Technology 11 Weathering and Soil Formation Name ______________________________ Class __________________ Date __________________ Animals 10. How can animals that live in soil cause mechanical weathering? a. by causing oxidation b.drinking water c. by eating plants d. by burrowing Chemical weathering 11. What is it called when rocks break down due to chemical reactions? a. ice wedging b.mechanical weathering c. burrowing d. chemical weathering 12. Which of the following is a common agent of chemical weathering? a. wind b. weak acids c. gravity d. ice Water 13.What kind of weathering takes place when a sugar cube dissolves in water? a. differential weathering c. mechanical weathering b. chemical weathering d. desertification Acid Precipitation 14.What is rain, sleet, or snow that contains a lot of acid called? a. chemical weathering b. acidity c. acid precipitation d. fossil fuel c. burrowing animals d. falling rocks 15.Which of the following can cause acid precipitation? a. burning fossil fuels b. rusting iron Acids in Groundwater 16. What can result from acids in groundwater coming into contact with limestone? a. lichens b. karst features c. oxidation d. acid precipitation Acids in Living Things 17. What kind of organisms produce acids that slowly break down the rocks they live on? a. ferns b. lichens c. orchids d. wasps Air 18. When oxygen in the air reacts with iron, what substance is formed? a. abrasion b.mechanical weathering c. acid precipitation d. rust 19. What is it called when an element combines with oxygen to form an oxide? a. abrasion b.mechanical weathering c. acid precipitation d. oxidation Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Science and Technology 12 Weathering and Soil Formation Name ______________________________ Class __________________ Date __________________ Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Science and Technology 13 Weathering and Soil Formation Name ______________________________ Class __________________ Date __________________ Directed Reading B continued Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Science and Technology 14 Weathering and Soil Formation Name ______________________________ Class __________________ Date __________________ Directed Reading B continued Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Science and Technology 15 Weathering and Soil Formation