ENG
advertisement

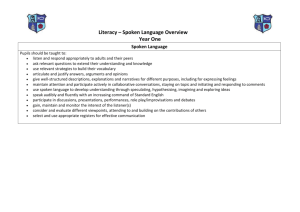
THE HONG KONG INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION Course Outline Programme Title : M.Ed. (English) Course Title : The Grammar of English Speech Department : English Credit Points : Three Contact Hours : 39 Pre-requisite(s) : Nil [If applicable.] Level : [If applicable. For example, for Discipline Studies under the BEd Core Curriculum, there are three levels of modules to reflect the progression of study or the extent of in-depth knowledge.] Synopsis: Much of what we know and teach about English grammar is based on patterns in the written language. This module explores the idea of a related, but distinct, grammar of English speech and its applications to the teaching of English as a second language. Objectives : Upon completion of the module, course participants should be able to: 1. Recognize and explain major grammatical differences between written and spoken English encountered in authentic texts. 2. 3. Make judgements about what is ‘grammatical’ and ‘non-grammatical’ in the context of spoken English. Apply an understanding of the grammatical and lexical features of spoken English to issues of ‘standardness’ in non-native speaker English. Apply this understanding to the design of pedagogical tasks for oral English. Content 1. Differences between spoken and written text. Varieties of spoken text. Features of spoken interaction. 2. Models of grammar and their relationship to writing and speech. 3. Features of the grammar of English speech: (a) linearity, (b) implicitness, (c) interactivity, (d) expressiveness. 4. Lexico-grammatical features: (a) lexical chunks and prefabricated expressions, (b) vernacularity, (d) creativity and word play. 5. Standardness and non-standardness in native and nonnative English speech. 6. Oral English in the curriculum. 1 Assessment 1. A reaction paper on one or more of the recommended readings (2,000-2,500 words) 2. A plan for a lesson or unit of work based on a transcription of an authentic passage of spoken English, to include the transcription, activities based on the transcription and a rationale based on concepts introduced during the module. (2,000-2,500 words) Required Text Burns, A. (2001). Analysing spoken discourse: implications for TESOL. In A. Burns & C. Coffin (eds.) Analysing English in a Global Context (pp. 123-148). London: Routledge. (Pre-course reading). Carter, R. and M. McCarthy. (1995). Grammar and the spoken language. Applied Linguistics 16(2): 141158. Recommended Reading Biber, D., Johansson, S., Leech, G., Conrad, S. & Finegan, E. (1999) Longman Grammar of Spoken and Written English. London: Longman. (Chapter 14: The grammar of conversation. Chapter 13: Lexical expressions in speech and writing). Brazil, D. (1995). A grammar of speech. Oxford University Press, Oxford. Carter, R. (1999) Common language: corpus, creativity and cognition. Language and Literature, 8(3), 195216. < http://lal.sagepub.com/cgi/reprint/8/3/195.pdf> Carter, R. (2004) Language and Creativity: The Art of Common Talk. London: Routledge. Carter, R., Hughes, R. & McCarthy, M. (1998). Telling tails: grammar, the spoken language and materials development. In B. Tomlinson (ed.) Materials Development in Language Teaching. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Carter, R., & McCarthy, M. (1997). Written and spoke vocabulary. In N. Schmitt & M. McCarthy (eds.) Vocabulary: Description, Acquisition, Pedagogy (pp. 20-39). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Carter, R., & McCarthy, M. (2004). Talking, creating: Interactional language, creativity, and context. Applied Linguistics, 25(1), 62-89. Deterding, D. & Kirkpatrick, A. (2006) Intelligibility and an emerging ASEAN English lingua franca. World Englishes, 25(3). Holme, R. (2004) Literacy: An Introduction. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press (Chapters 9 & 10 on differences between speech and writing). Hughes, R. & McCarthy, M. (1998) From sentence to grammar: discourse grammar and English language teaching. TESOL Quarterly, 32(2), 263-287. Leech, G., Rayson, P. & Wilson, A. (2001). Word Frequencies in Written and Spoken English. London: Longman. McCarthy, M. & Carter, R. (2002) Ten criteria for a spoken grammar. In E. Hinkel & S. Fotos (eds.) New perspectives on grammar teaching in second language classrooms (pp. 51-75). Mahwah: NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. Related Websites Nil Related Journals Nil 2