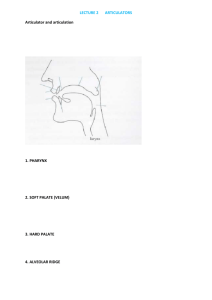
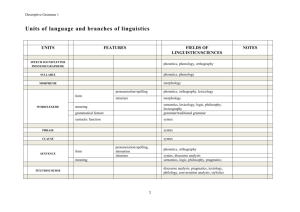
Linguistic program
advertisement

Graduate Institute of Linguistics Ph.D Program Course Map Doctoral Candidate Qualifying Exam Graduate degree:30 credits Required credits (6 credits) Fulfill 30 credits and score at least 80 for each course Qualifying Exam Foundations of Linguistic Theory Data collection Methods Doctoral Dissertation Before qualifying exam: acceptance of two reviewed articles research proposal defense Students should take at least one course each from four areas and choose one major area (at least 9 credits) and one minor area (at least 6 credits) from among the following five areas. Elective credits(24 credits) Students can take courses from other departments or institution with the approval of the supervisor. Phonology and Syntax and Pragmatics and Languages and Phonetics Semantics Sociolinguistics Cognition 學 Course area Courses Foundations of Linguistic Theory Data collection Methods Phonetics (I) (II) Phonology (I). (II) Phonetics Lab (I) (II) Mandarin Phonetics Tonal Analysis Sign Language: Phonology and Morphology Seminar on Sign Language Phonology Advanced Phonology Seminar First area: Phonology Seminar: Syllable Structure Phonology and Phonetics Seminar on Phonology Acquisition (I) (II) Phonology Seminar Seminar on Laboratory Phonology Phonology and the Lexicon Phonology Seminar: Markedness and Frequency Advanced Phonetics Advanced Laboratory Phonology Phonology Seminar: Phonology and Phonetics Phonology Seminar: Prosody Required courses Computational Linguistics and Corpus Linguistics Linguistic Structure of Southern Min: Phonetics and Phonology Mandarin and English Phonetics The Phonetics of Spoken and Signed Languages Semantics Semantics (I)(II) Formal Semantics 2.5 Syntax (II) Morphology Experimental Syntax 2.4 Chinese Grammar Chinese Grammar (I)(II) Verbs and Cognition 2.4 Lexical-Functional Grammar Lexical Semantics Verbal Semantics Syntax and Semantics in Formosan Languages (I) (II) Lexicon and Syntax of Taiwan Sign Language Seminar on Taiwan Sign Language Syntax Semantics and Syntax of Taiwan Sign Language Seminar on classifiers in Spoken and Signed Languages Conceptual Structure and Grammar 2.3.4 Taiwan Sign Language Grammar Advanced Syntax Seminar on Syntax Topics on Syntax-Semantics Interface Seminar on Semantics Seminar on Syntax: Coordination Cognition-based Chinese Grammar (I)(II)2.4 Issues in Minimalist Syntax The Syntax of Complex Predicate Constructions Role and Reference Grammar Cognition-based English Grammar 2.4 Cognition-based Taiwan Sign Language Grammar 2.4 Seminar on Pragmatics :2,3 Austronesian Linguistics 2,3 Taiwan Sign Language Semantics Advanced Seminar on Semantics Comparative Syntax Linguistic Structure of Southern Min: Syntax and Semantics Sign Language: Phonology and Morphology Pragmatics Sociolinguistics Discourse Analysis Second area: Syntax and Semantics Third area: Pragmatics and Sociolinguistics Language Variation and Change Gesture, Facial Expression and Communication 3.4 Conceptual Structure and Grammar 2.3.4 Seminar on Pragmatics 2,3 Language and Culture of Deaf Introduction to Sign Language Research 3,4 Austronesian Linguistics 2,3 Seminar on Sociolinguistics Applied Linguistics 3,4 Gesture, Facial Expression and Communication 3.4 Experimental Syntax 2.4 Verbs and Cognition 2.4 Psycholinguistics Advanced Psycholinguistics Cognitive Linguistics Language and Cognition Categorization and Cognition Categorization and Cognition (I)(II) Conceptual Structure and Grammar 2.3.4 Cognitive Linguistics and Second Language Acquisition(I) (II) Comparative Study of Sign Languages (I)(II) Visual Linguistics Cognitive Linguistics Seminar: Metaphor Language Evolution Fourth area: Linguistic Theory and Sign Language Typology Language and Cognition Competence and Performance Cognition-based Chinese Grammar (I)、(II)2.4 Psycholinguistics Seminar Seminar on Sign Linguistics (I) Cognition-based English Grammar 2.4 Cognition-based Taiwan Sign Language Grammar 2.4 Introduction to Neurolinguistics Clinical Linguistics Language Universality and Innateness Introduction to Sign Language Research 3,4 Language Acquisition, Development and Attrition 3,4 Language and Aging: Comprehension and Production Introduction to Metaphor Applied Linguistics 3,4 Cognitive Neurology and Language Learning Formal Semantics 2.5 Computational Linguistics Computational Linguistics (II) Corpus Linguistics Fifth area: Computational and Corpus Linguistics Mathematical Linguistics: Connectionism Mathematical Linguistics (II) Child Language Corpus(I) Child Language Corpus(II) Mathematical Linguistics Fundamental Issues in Linguistics Field Method Field Method: Thao Studies Field Method: Paiwan Studies Area to be determined by the instructor Miscellaneous Introduction to Formosan Languages Seminar on Taiwan Sign Language Introduction to Sign Language Research Seminar on Child Language Acquisition Introduction to Child Language Acquisition Seminar on Formosan Languages Statistics in Linguistic Studies Advanced Statistics