Biology Inheritance Patterns Practice Test - High School
advertisement

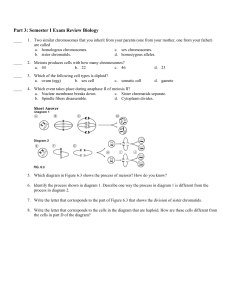
Biology - Unit 9: Inheritance Patterns PRACTICE TEST ____ 1. Two similar chromosomes that you inherit from your parents (one from your mother, one from your father) are called a. homologous chromosomes. c. sex chromosomes. b. sister chromatids. d. homozygous alleles. ____ 2. Meiosis produces cells with how many chromosomes? a. 44 b. 22 c. 46 d. 23 3. Which of the following cell types is diploid? a. ovum b. sex cell d. gamete ____ ____ ____ 4. A distinguishing characteristic that can be inherited is a(n) a. cross. b. allele. c. gene. d. trait. 5. Which of the following phrases describes the Punnett square in Figure 6.1? a. 1/4 probability of heterozygous offspring b. 3/4 probability that dominant trait is expressed ____ c. somatic cell 6. Homozygous alleles are_______ a. always inherited together. b. different forms of the same trait. c. 3/4 probability of homozygous offspring d. heterozygous-heterozygous cross c. d. identical forms of the same gene. identical forms of two different genes. ____ 7. Mendel knew that the variations in the offspring generations resulted from his experiments because he a. allowed plants to cross-pollinate. c. controlled the fertilization process. b. ensured that plants self-pollinated. d. changed the growing conditions. ____ 8. Which pair of genes in Figure 6.2 would be most likely to be inherited together? a. A and B ____ b. A and C c. A and D d. A and E 9. Which event takes place during anaphase II of meiosis II? a. Nuclear membrane breaks down. c. Sister chromatids separate. b. Spindle fibers disassemble. d. Cytoplasm divides. ____ 10. Recessive alleles may not be expressed because they are a. masked by a dominant allele. c. the most common allele in a population. b. the least common allele in a population. d. less likely to have crossing over. ____ 11. Mendel's second law of genetics, the law of independent assortment, is one explanation of the a. random fertilization of gametes. c. greater strength of dominant alleles. b. genetic variation within species. d. final stages of gametogenesis. ____ 12. Which of the following events is an important factor in increasing variety among sexually reproducing organisms? a. testcross b. gene linkage c. crossing over d. mitosis ____ 13. Imagine two heterozygous parents. Each has a dominant allele B for brown eyes and a recessive allele b for blue eyes. The phenotypic ratio for brown:blue eyes in their children is a. 1:2:1. b. 3:1. c. 9:3:3:1. d. 1:3:1. ____ 14. A person who has a disorder caused by a recessive allele is a. considered a carrier of the disorder. c. unable to pass the allele to offspring. b. homozygous for the recessive allele. d. certain to have offspring with the disorder. ____ 15. The Punnett square in Figure 7.1 shows a cross between two parents who have the genotype Ss for a genetic disorder caused by a recessive allele. Which of the following will have the genetic disorder? a. Ss parent b. Ss offspring c. SS offspring d. ss offspring ____ 16. Two parents have the genotype Gg for a genetic disorder caused by a dominant allele. What is the chance that any of their children will inherit the disorder? a. 25% b. 50% c. 75% d. 100% ____ 17. Human height occurs in a continuous range because it is affected by the interaction of several genes, making it a a. autosomal trait. b. sex-linked trait. c. polygenic trait. d. codominant trait. ____ 18. A female is born with attached earlobes, which is a recessive phenotype. Which of the following genotypes could her parents have? a. RR and RR b. Rr and RR c. Rr and rr d. RR and rr ____ 19. What is the main reason that sex-linked disorders are most often observed in males? a. The X chromosome only has genes for genetic disorders. b. The Y chromosome cannot have genes that cause genetic disorders. c. The Y chromosome cannot mask alleles on the X chromosome. d. The X chromosome has genes only for sex determination. Short Answer 20. Which type of interaction is shown by the alleles for flower color? 21. Suppose the first generation pea plants had flowers that were partly red and partly white instead of all pink. What type of relationship between alleles would this be? Write one statement to support your answer. Use the word phenotype in your answer. Short Answer 22. Which diagram in Figure 6.3 shows the process of meiosis? How do you know? 23. Write the letter that corresponds to the cells in the diagram that are haploid. How are these cells different from the cells in part D of the diagram? Use the exhibit to answer the questions that follow. 24. In this plant species, the allele for purple flowers is dominant and the allele for white flowers is recessive. Write the genotype for the offspring that have white flowers. 25. Write the genotype for the offspring that have purple flowers. 26. What is the genotype of the unknown parent? Biology - Unit 9: Inheritance Patterns PRACTICE TEST Answer Section 1. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_14 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 2. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_22 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.16 | FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.17 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 3. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_30 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 4. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_38 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 5. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_46 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.N.1.1.6 | FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.1 | FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.2 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 6. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_54 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.2 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 7. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_79 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.17 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 8. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_70 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.15.15 | FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.17 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 9. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_87 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.16 | FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.17 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 10. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_95 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.2 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 11. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_103 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 12. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_111 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 13. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_127 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.N.1.1.6 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 14. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e110_194 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.2 TOP: Ch 7 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 15. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e110_210 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.N.1.1.6 | FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.1 | FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.2 TOP: Ch 7 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 16. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e110_223 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.N.1.1.6 | FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.2 TOP: Ch 7 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 17. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e110_240 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.2 TOP: Ch 7 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 18. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e110_280 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.2 | FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.4 TOP: Ch 7 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 19. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e110_312 TOP: Ch 7 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 20. ANS: 1 = C1C1, 2 = C1C2, 3 = C1C2, 4 = C2C2; incomplete dominance PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e110_354 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.2 TOP: Ch 7 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 21. ANS: Codominance. The phenotypes of both parents are expressed fully and separately in the offspring. PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e110_362 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.2 TOP: Ch 7 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 22. ANS: Diagram 2 Sample answer: in diagram 2, there are two cell divisions, so this process is meiosis. In diagram 1, there is only one cell division. PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_144 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.16 | FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.17 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 23. ANS: J. Sample answer: The cells in part J of the diagram have fewer chromosomes. The cells in part D of the diagram have more chromosomes. PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: act0976aaf18007e102_156 STA: FL.NGSSS.SCI.08.9-12.SC.912.L.16.16 TOP: Ch 6 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 24. ANS: ff PTS: 1 DIF: Level A TOP: Ch 6 Test - A 25. ANS: Ff REF: act0976aaf18007e102_176 NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 PTS: 1 DIF: Level A TOP: Ch 6 Test - A 26. ANS: Ff REF: act0976aaf18007e102_180 NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 PTS: 1