Biological Literature Miner:
advertisement

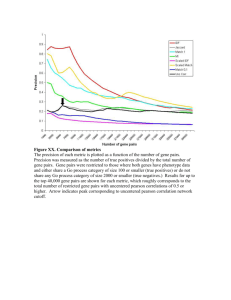
Biological Literature Miner: Gene Mention Recognition and Protein-Protein Interaction Pair Extraction CHEN Yifei ABSTRACT +++++++++ In this dissertation we describe a machine learning-based text mining system to extract automatically useful information from the biological literature: Biological Literature Miner (BioLMiner). BioLMiner is designed, implemented and tuned in collaboration with Feng Liu and includes four subsystems: a Gene Mention Recognizer (GMRer), a Gene Normalizer (GNer), an Interaction Article Classifier (IACer) and a Protein-Protein Interaction Pair Extractor (PPIEor). The two subsystems GMRer and PPIEor are the topic of this dissertation and they are based on Support Vector Machines (SVMs) and Conditional Random Fields (CRFs). GMRer is the first subsystem in BioLMiner and solves the task of recognizing gene mentions, i.e. gene and protein names, in the biological literature. This is a very important step for the next subsystems that are using these extracted gene mentions in order to extract further information. In GMRer both a sequence labeling-based model using CRFs and two classification-based models using forward SVMs and backward SVMs are used, respectively. To improve the performance further, a hybrid model is proposed that fuses, using voting rules, the outputs of the three individual models. PPIEor is the last subsystem of BioLMiner and its purpose is to automatically extract protein-protein interaction (PPI) pairs from the biological literature. Finding these interactions is one of the most pressing problems in the biological domain. During the preprocessing phase, PPIEor transforms the sentence-based articles into clause-based ones and the candidate PPI pairs are distilled. A binary SVM classifier is proposed to predict whether the candidate PPI pairs are correct or not. Finally, a post-processor recovers some self-interaction proteins which cannot be identified by the SVM model.