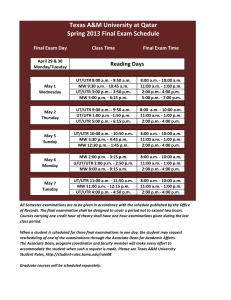
Online Supplement
advertisement

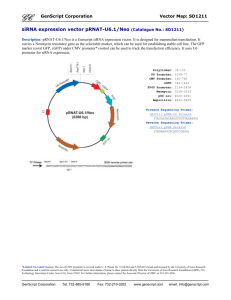
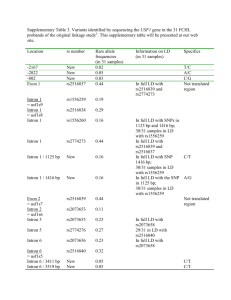
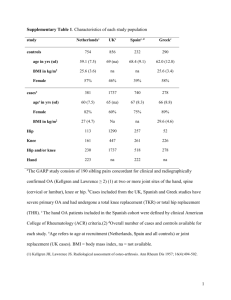
GSNO Reductase and 2 Adrenergic Receptor Gene-gene Interaction: Bronchodilator Responsiveness to Albuterol †* Shweta Choudhry, Ph.D., M.Sc.1, *Loretta G. Que, M.D.2 Zhonghui Yang, Ph.D.2, Limin Liu, Ph.D.3, Celeste Eng, B.S.1, Sung O. Kim, Ph.D.4, Gunjan Kumar, B.S.1, Shannon Thyne, M.D.1, Rocio Chapela, M.D.5, Jose R. Rodriguez-Santana, M.D.6, William Rodriguez-Cintron, M.D.7, Pedro C. Avila, M.D.8, Jonathan S. Stamler, M.D.2, and Esteban G. Burchard, M.D., M.P.H.1,9 * These authors contributed equally to this manuscript 1 Lung Biology Center and Institute for Human Genetics, University of California, San Francisco, CA 2 Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC 3 Microbiology and Immunology, University of California, San Francisco, CA 4 Bipion Co. LTD, Seoul, Republic of Korea 5 Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias, Mexico City, Mexico 6 Centro de Neumologia Pediatrica, CSP, San Juan, PR 7 Veterans Caribbean Health Care System, San Juan, PR 8 Division of Allergy-Immunology, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL 9 Department of Biopharmaceutical Sciences, University of California, San Francisco, CA †Correspondence and reprint requests: Shweta Choudhry, Ph.D. UCSF/Lung Biology Center, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, California 94143-2911; telephone: 415-5149927, fax: 415-514-4365, e-mail: shweta.choudhry@ucsf.edu Running Title: GSNOR-2AR interaction in bronchodilator response 1 Supported By: This work was supported by National Institutes of Health (HL078885, HL088133, U19 AI077439, ES015794), Flight Attendant Medical Research Institute (FAMRI), and the RWJ Amos Medical Faculty Development Award to EGB), HL086887 to LGQ, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences 5U19-ES012496 and NHLBI R01HL96673-01 to JSS, American Thoracic Society “Breakthrough Opportunities in Lung Disease” (BOLD) Award and Tobacco-Related Disease Research Program New Investigator Award (15KT-0008) to SC, the Ernest S. Bazley Grant to PCA, and the Sandler Center for Basic Research in Asthma and the Sandler Family Supporting Foundation. 2 Genotyping Five GSNOR SNPs, +3207 in the potential promoter region and +16701, +16777, +17059 and +17250 in the 3’UTR region were genotyped in the entire GALA cohort. We selected these five SNPs for genotyping based on their allele frequency (minor allele frequency > 5%), location (exonic or in potential promoter region) and the haplotype structure of the GSNOR gene. All five SNPs were genotyped using the AcycloPrime-FPTM (PerkinElmer) method.(1) The PCR cocktail included: 2.4-4.0 ng genomic DNA, 0.1-0.2 µM primers, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 50 µM dNTPs, 6 µl volume with Platinum Taq PCR buffer and 0.1-0.2 units Platinum Taq (Invitrogen) plus 1 µl extra water to counteract evaporation. PCR cycling conditions were as follows: 95°C for 2 minutes, 35 cycles of 92°C for 10 seconds, 58°C for 20 seconds, 68°C for 30 seconds, and final extension at 68°C for 10 minutes. We used AcycloPrime-FP kits for enzymatic cleanup and single base extension genotyping reactions. Plates were read on an EnVision fluorescence polarization plate reader (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA). Constructs and Cell Transfections Luciferase reporter gene constructs The full length GSNOR 3’UTR was amplified from human cDNA. The resulting PCR products were digested using proper restriction enzymes and cloned into both forward (F) and reverse (R) orientations in the pGL3 plasmid containing an SV40 promoter upstream of the firefly luciferase gene (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI). Site directed mutagenesis Site directed mutagenesis of the 3’UTR was performed using QuikChange® II XL Site Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Stratagene, CA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Individual mutants 3 mimicking the SNPs associated with asthma in our patient population were generated by substituting C+16701→T, A+17059→C and T+17250→C (data not shown). Another mutant was created containing the three individual mutants to mimic the GSNOR haplotype associated with asthma. The mutated fragments were amplified using the forward primer: TAATTCAAAAGAGAAAAATAATGTCCATCC and the reverse primer: ATGTGACTACATTAAAACTTTATTCAAC, then ligated into the pGL3 promoter vector. All constructs used in this study were restriction-mapped and sequenced to confirm authenticity and correct orientation in the vector. Transfection experiments and Luciferase assay The luciferase reporter gene constructs were transiently transfected into HEK293 cells with Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen; Carlsbad CA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Approximately 1x106 HEK293 cells were seeded on each well of a 6-well tissue culture plate and transfected with each plasmid construct (0.2 g). Co-transfection with the pRL vector (9 ng) containing the Renilla luciferase gene allowed monitoring of transfection efficiencies. HEK293 cells were chosen because they are of human origin, have high transfection efficiency, and also express the 2AR. Cells were incubated for 48 hours and harvested by adding 500 l of reporter lysis buffer. Specific substrates were used to measure the activities of the firefly and Renilla luciferase with a TD-20/20 luminometer (Turner Designs, Sunnyvale, CA). Firefly luminescence was normalized to Renilla luminescence and reported as relative luciferase units (RLU). All experiments were done in duplicate and independently performed at least three times. Differences among cell transfection groups were evaluated using a student’s t-test. A p value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. 4 References for online supplement 1. Chen X, Levine L, Kwok PY. Fluorescence polarization in homogeneous nucleic acid analysis. Genome Research 1999;9:492-498. 5 Table 1S. SNPs identified in resequencing of the GSNOR exons, exon-intron boundaries and potential promoter regions in Mexican and Puerto Rican subjects with asthma. Frequency SNP bp position* rs number -749 SNP location Alleles Reference Allele Mexicans (n = 24) Puerto Ricans (n = 24) Promoter 1 CAAA/- - 0.02 0.02 Amino Acid change -745 rs3974877 Promoter 1 -/GAAA GAAA 0.17 0.27 -421 rs17216887 Promoter 1 G/C C 0.02 0.02 Promoter 2 C/T T 0.02 0.02 Promoter 2 C/T T 0.12 0.24 +6494 Intron 2 T/C C 0.0 0.02 +6519 Intron 2 T/C C 0.08 0.08 +6551 Intron 2 T/A A 0.02 0.02 +6564 Intron 2 G/A A 0.0 0.02 +7205 Intron 3 T/- - 0.06 0.08 +11651 Intron 4 A/G G 0.0 0.02 +12207 Exon 6 T/C C I --> T 0.0 0.02 +12216 Exon 6 G/A A C --> Y 0.02 0.0 +12443 Intron 6 G/T T 0.0 0.04 +13597 Intron 6 TTG/- - 0.08 0.08 +3003 +3207 rs1154410 6 Frequency SNP bp position* rs number SNP location Alleles Reference Allele Mexicans (n = 24) Puerto Ricans (n = 24) Intron 7 T/C C 0.03 0.0 Intron 7 C/A A 0.09 0.06 +16019 Exon 8 T/C C 0.02 0.02 +16166 Intron 8 G/A A 0.02 0.02 +16354 Exon 9 G/A A 0.02 0.02 +13816 +15983 rs17595424 Amino Acid change Syn (L) +16476 rs12697 3' UTR T/C C 0.11 0.11 +16502 rs12106 3' UTR T/C C 0.11 0.11 +16701 rs1803037 3' UTR G/A A 0.08 0.08 3' UTR T/C C 0.02 0.0 +16770 +16777 rs13832 3' UTR T/G G 0.21 0.29 +16858 rs6827292 3' UTR A/G G 0.02 0.02 +16999 rs1061187 3’ UTR C/T T 0.08 0.08 +17059 rs11547772 3’ UTR T/G G 0.08 0.08 +17200 3’ UTR C/T T 0.02 0.02 +17201 3’ UTR G/T T 0.02 0.02 3’ UTR A/G G 0.10 0.10 +17250 rs7669660 *The bp position of the SNP is calculated with reference to ATG with A as bp 7 African Americans Figure 1S. Pair wise linkage disequilibrium (LD) as estimated by r2 statistic for the SNPs in the GSNOR (ADH5) gene with > 5% frequency in Mexican and Puerto Rican subjects with asthma. r2 statistic of 0 means no LD and 1 means complete LD. Puerto Ricans Mexican 8