System level indicators (inputs)
advertisement
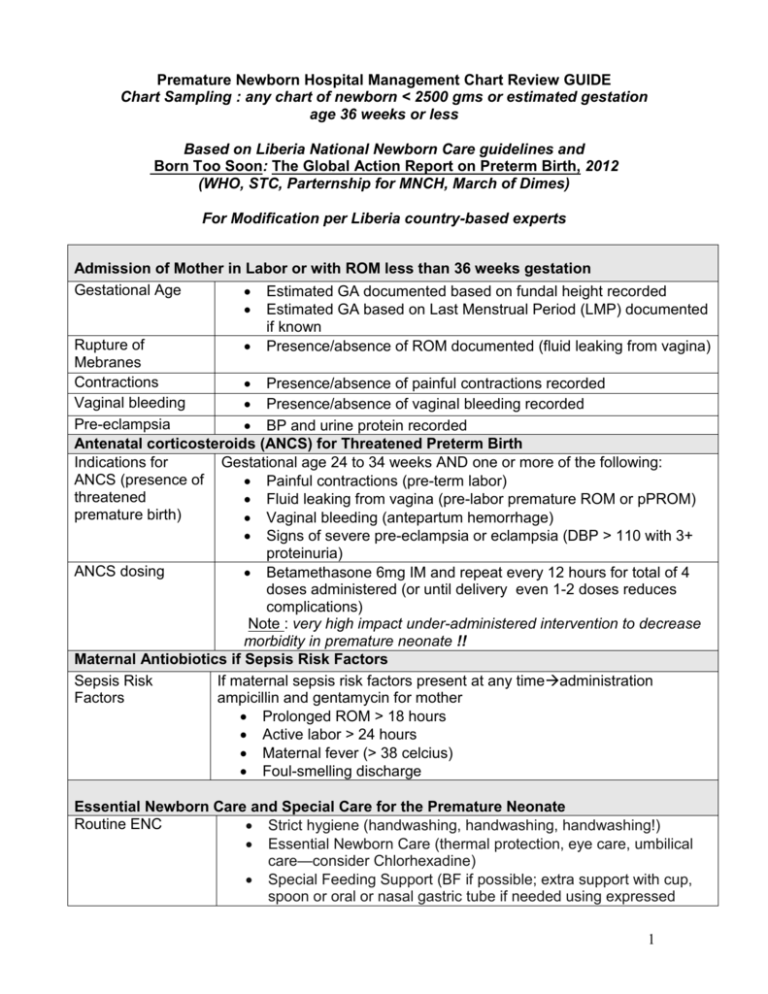
Premature Newborn Hospital Management Chart Review GUIDE Chart Sampling : any chart of newborn < 2500 gms or estimated gestation age 36 weeks or less Based on Liberia National Newborn Care guidelines and Born Too Soon: The Global Action Report on Preterm Birth, 2012 (WHO, STC, Parternship for MNCH, March of Dimes) For Modification per Liberia country-based experts Admission of Mother in Labor or with ROM less than 36 weeks gestation Gestational Age Estimated GA documented based on fundal height recorded Estimated GA based on Last Menstrual Period (LMP) documented if known Rupture of Presence/absence of ROM documented (fluid leaking from vagina) Mebranes Contractions Presence/absence of painful contractions recorded Vaginal bleeding Presence/absence of vaginal bleeding recorded Pre-eclampsia BP and urine protein recorded Antenatal corticosteroids (ANCS) for Threatened Preterm Birth Indications for Gestational age 24 to 34 weeks AND one or more of the following: ANCS (presence of Painful contractions (pre-term labor) threatened Fluid leaking from vagina (pre-labor premature ROM or pPROM) premature birth) Vaginal bleeding (antepartum hemorrhage) Signs of severe pre-eclampsia or eclampsia (DBP > 110 with 3+ proteinuria) ANCS dosing Betamethasone 6mg IM and repeat every 12 hours for total of 4 doses administered (or until delivery even 1-2 doses reduces complications) Note : very high impact under-administered intervention to decrease morbidity in premature neonate !! Maternal Antiobiotics if Sepsis Risk Factors Sepsis Risk If maternal sepsis risk factors present at any timeadministration Factors ampicillin and gentamycin for mother Prolonged ROM > 18 hours Active labor > 24 hours Maternal fever (> 38 celcius) Foul-smelling discharge Essential Newborn Care and Special Care for the Premature Neonate Routine ENC Strict hygiene (handwashing, handwashing, handwashing!) Essential Newborn Care (thermal protection, eye care, umbilical care—consider Chlorhexadine) Special Feeding Support (BF if possible; extra support with cup, spoon or oral or nasal gastric tube if needed using expressed 1 breastmilk if possible) Begin Kangaroo Mother Care (KMC) as quickly as possible after birth (skin to skin contact between baby and mother’s--or other adult’s—chest with baby’s head covered, pre-warmed shirt open to front and socks) Care of Resuscitation if no spontaneous breathing in first golden minute of Complications in delivery (see resuscitation review guide) Neonate Antibiotics if any sepsis risk factors or signs of sepsis (see newborn sepsis guide: 5 mg/kg once daily if > 2 kg; 4 mg/kh once daily if < 2 mg/kg) Supplemental oxygen if signs of Respiratory Distress Syndrome AND if trained provider available to monitor with mandatory use of pulsoximetry (CPAP and surfactant if high-level NICU with trained experienced providers and nursing staff) Monitoring for jaundice with treatment for hyperbilirubinemia if detected Monitoring of Premature Newborn Weight recorded daily Temperature recorded at least once daily RR recorded at least once daily Respiratory status recorded daily Feeding status (nutrition source, quantity and frequency) recorded daily (Breastmilk is best). Absence/presence of jaundice recorded at least one daily Discharge Discharge deferred until normal temperature (> 35< 38 celcius),. demonstrated weight gain and feeding well (at least every 2-3 hours) Documentation of normal physical exam at discharge Documentation of normal feeding status (BF or formula at least every 2-3 hours) at discharge Counseling documented for prematurity care, danger signs and care-seeking Follow up specified ; home-based support if possible Note: Although there has historically been some debate about the gestational age parameters for which ANCS should be administered for threatened premature labor, recommendations issued by WHO at the April 2013 Global Newborn Conference are for administration of ANCS for any threatened preterm labor between 24-36 weeks gestational age based on the four risk factors detailed in table for ACNS indications. Given the challenges with accurate estimation of gestational age in low-resource settings (unless high-quality first trimester sonogram), gestational age should be based on fundal height (# of cm=# of weeks gestational age). This recommendation is based on the very strong evidence that ANCS reduces the incidence and severity of lung problems, especially RDS, a leading cause of premature infant morbidity and mortality. Although 4 doses of ACNS over 48 hours before delivery is ideal, even 1-2 doses can reduce complications. The UN Commission on Lifesaving 2 Commodities for Women and Children has recommended that Betamethasone (the ANCS of choice) be part of every country’s essential drug list. 3







