Practice it
advertisement
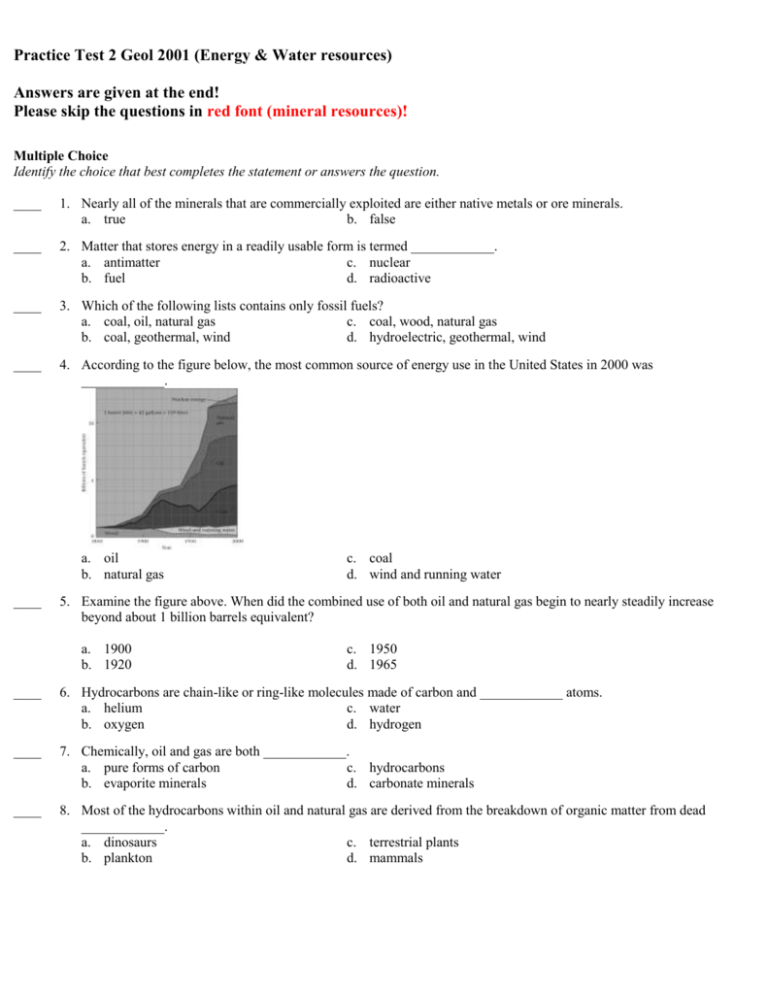
Practice Test 2 Geol 2001 (Energy & Water resources) Answers are given at the end! Please skip the questions in red font (mineral resources)! Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Nearly all of the minerals that are commercially exploited are either native metals or ore minerals. a. true b. false ____ 2. Matter that stores energy in a readily usable form is termed ____________. a. antimatter c. nuclear b. fuel d. radioactive ____ 3. Which of the following lists contains only fossil fuels? a. coal, oil, natural gas c. coal, wood, natural gas b. coal, geothermal, wind d. hydroelectric, geothermal, wind ____ 4. According to the figure below, the most common source of energy use in the United States in 2000 was ____________. a. oil b. natural gas ____ c. coal d. wind and running water 5. Examine the figure above. When did the combined use of both oil and natural gas begin to nearly steadily increase beyond about 1 billion barrels equivalent? a. 1900 b. 1920 c. 1950 d. 1965 ____ 6. Hydrocarbons are chain-like or ring-like molecules made of carbon and ____________ atoms. a. helium c. water b. oxygen d. hydrogen ____ 7. Chemically, oil and gas are both ____________. a. pure forms of carbon c. hydrocarbons b. evaporite minerals d. carbonate minerals ____ 8. Most of the hydrocarbons within oil and natural gas are derived from the breakdown of organic matter from dead ____________. a. dinosaurs c. terrestrial plants b. plankton d. mammals ____ 9. According to this figure below, the greatest depth at which oil is found is ____________. a. about 4 km below the surface b. about 6 km below the surface c. about 9 km below the surface d. at the base of the lithosphere ____ 10. Organic matter builds up evenly in sediments over the entire ocean floor. a. true b. false ____ 11. Examine the table below. Which nation is consuming the greatest fraction of its oil reserves each year? a. Saudi Arabia b. China c. Qatar d. the United States ____ 12. A body of rock in which oil is formed is termed a ____________. a. reservoir rock c. source rock b. seal rock ____ 13. The oil window (temperature range wherein organic matter is converted to petroleum hydrocarbon without destroying it) lies between ____________. a. 30°C and 60°C c. 90°C and 160°C b. 100°C and 250°C d. 200°C and 350°C ____ 14. Look at the figure below. Which of the following would NOT result from increased burial temperature of hydrocarbon molecules? a. causing molecules to react and become larger b. causing molecules to contain fewer atoms c. eventually destroying them, leaving only carbon d. driving all the Hydrogen off, eventually leaving only carbon ____ 15. What effect would the intrusion of a magma body have on the depth to the “oil window”, and why? a. None. b. The depth to the oil window should increase because the magma is migrating upward and thereby decreasing crustal pressures c. The depth to the oil window should decrease because the magma is bringing heat closer to Earth’s surface. d. The depth to the oil window should increase because the water in the magma will cool the nearby rock. ____ 16. A permeable and porous rock, regardless of lithology, is a good candidate to serve as a ____________ in an oilproducing scenario. a. reservoir rock c. source rock b. seal rock ____ 17. An impermeable rock is most likely to be which of these? a. reservoir rock c. source rock b. seal rock ____ 18. Which of the following is NOT an important type of oil trap? a. salt dome c. stratigraphic b. syncline d. anticline ____ 19. A commercially viable oil deposit must include a source rock, a reservoir rock, a seal rock, and a ____________. a. fracture system connecting the reservoir rock to the Earth’s surface so that the oil can move freely upward b. filter rock, between the source and the reservoir rock, to remove impurities c. heater rock, beneath the source rock, to heat the oil and give it buoyancy d. trap that prevents the oil from reaching the Earth’s surface ____ 20. A black, organic-rich shale could likely serve as either of which two necessary types of rocks within oil fields? a. source rock or seal rock c. source rock or reservoir rock b. reservoir rock or seal rock ____ 21. Hydrocarbons consisting of short carbon chains are ____________. a. more volatile than hydrocarbons with longer chains b. more viscous than hydrocarbons with longer chains c. typically stable in a solid state at room temperatures d. All of the above are correct. ____ 22. The figure below shows close-up views of two sand deposits that have differing degrees of cementation. Which explanation about how increased cementation of the clasts would affect the ability of oil to flow to a well does NOT make sense? a. It would slow down the flow of oil to the well because the passages are on average less connected. b. It would slow down the flow of oil to the well because the passages are on average narrower. c. It would have no effect if there are sufficient, interconnected fractures in the rock (though not visible in the figures). d. It would speed up the flow of oil to the well because flow through narrower passages will generate more friction and thereby heat the oil and decrease its viscosity. ____ 23. Is oil or natural gas more likely to be present at the greatest depths within Earth, and why? a. oil, because it is more stable at high temperatures b. oil, because it is more stable at low pressures c. gas, because it is more stable at high temperatures d. gas, because it is more stable at low pressures ____ 24. If a sedimentary basin is tectonically subsiding, how would the depth of the oil window be affected, and why? a. The depth of the oil window would decrease because hot fluids produced from diagenesis of basin sediments would increase hydrocarbon temperatures. b. The depth of the oil window would increase because fluids produced from diagenesis of basin sediments would prevent or buffer any rise of hydrocarbon temperatures. c. The depth of the oil window would decrease because the basin bottom would be closer to the mantle and heat of Earth’s outer core. d. The depth of the oil window would increase because the geothermal gradient in the subsiding basin would lead to cooler rocks being found at greater depths. ____ 25. If drilling encounters both oil and natural gas within a single interval, the ____________. a. gas will float on top of the oil b. oil will float on top of the gas c. gas and oil will be thoroughly mixed together d. gas will exist in a dissolved state within the oil ____ 26. Shale, salt, and fine-grained limestone that are unfractured are all good candidates for ____________. a. reservoir rocks c. source rocks b. seal rocks d. either source rocks or reservoir rocks ____ 27. Graphite forms from natural gas as well as coal when temperatures rise. What does this imply? a. Coal and natural gas molecules decompose to carbon and other matter when temperature rises. b. Coal and natural gas molecules are transformed by neutron bombardment into carbon. c. The precursors of natural gas and coal were graphite or other pure carbon. d. Coal and natural gas must be less dense than graphite. ____ 28. ____________ create(s) an easy route for oil or gas to travel to a well. a. Hydrofracturing c. Drilling mud b. Seismic-reflection d. Pumps ____ 29. The primary reasons that no more than 30% of the oil contained within most reservoirs is recovered are the viscosity of the oil and “patchy” (irregular) or low permeability. Which pair of techniques listed below would probably best increase the percentage of oil recoverable from a reservoir? a. injecting water into the reservoir, and hydraulically fracturing it b. adding weight to the ground surface to compress the reservoir, and applying greater suction to the pumps on the oil wells c. applying greater suction to the pumps on the oil wells and fracturing the reservoir d. hydraulically fracturing the reservoir and injecting steam into it ____ 30. ____________ is/are an example of alternative hydrocarbon sources. a. Gas hydrate c. Oil shale b. Tar sands d. All of the above are correct. ____ 31. Tar has a lower viscosity than gasoline. a. true b. false ____ 32. In tar sand, microbes have biodegraded larger molecules, leaving smaller molecules. a. true b. false ____ 33. Which organic substance is produced by black organic shales at temperatures below the oil window? a. natural gas c. kerogen b. coal d. keratin ____ 34. Natural gas ____________. a. consists of longer carbon chains as compared to oil b. is less common than oil at higher temperatures c. is produced at higher temperatures than oil d. is produced at higher temperatures than graphite ____ 35. Most of the world’s coal was deposited in coal swamps during the ____________. a. Cretaceous c. Carboniferous b. Ordovician d. Jurassic ____ 36. Coal is the altered remains of ancient ____________. a. dinosaurs c. terrestrial plants b. plankton d. mammals ____ 37. ____________ are NOT an example of alternative hydrocarbon sources. a. Methane hydrates c. Oil shales b. Peat bogs d. Tar sands ____ 38. Most coal forms in ____________, which develop and preserve the thick sedimentary sequences necessary for deep burial. a. domes c. shields b. basins d. active margins ____ 39. Which sequence of coal ranks is listed in order from lowest to highest energy content? a. anthracite, bituminous, lignite c. bituminous, lignite, anthracite b. lignite, bituminous, anthracite d. bituminous, anthracite, lignite ____ 40. Coal and metal ore deposits deeper than 100 m below the ground surface are usually mined with which technique? a. underground mining b. strip mining ____ 41. The “energy footprint” and annual CO2 emission of building, power plants, and other infrastructure are normally estimated only for the lifetime of operation, and do not include the cost of building and later removing (or recycling) the building, power plant, and so on. If the cost to construct and remove/recycle such facilities were also included in estimating the “energy footprint” and annual CO2 emissions of a proposed nuclear power, which of these factors would NOT change the resulting calculation? a. mining, refining, and transporting uranium ore to the plant each time the core ‘bundle’ needed change-out b. emissions and energy consumption of the plant during the period of its operation c. the cost to deconstruct, haul away, or decontaminate and recycle the materials of the power station after it had been shutdown d. the cost to manage, haul away, and safely store or recycle the used reactor core rods. ____ 42. U-235, the isotope of uranium that is essential for operating nuclear power plants, is ____________. a. the most common of the naturally occurring isotopes of uranium b. heavier than the other well-known isotope of uranium c. so rare even in uranium oxide deposits that uranium ore must be processed to enrich the proportion of U-235 to all uranium d. created by “breeder reactors” as well as produced during nuclear (atomic bomb) explosions ____ 43. ____________ is/are harnessed from the potential energy of water. a. Hydroelectric power c. Biofuels b. Solar energy d. Hydrologic energy ____ 44. Which of the following is a renewable resource? a. coal c. wind b. oil d. natural gas ____ 45. Look at the figure below. What problem might occur during the long-term operation of a geothermal power plant? a. The groundwater flowing to the geothermal well would dissolve rock, creating solution features within the bedrock. b. The groundwater flowing to the geothermal well would deposit-out (precipitate) minerals, decrease the permeability of the rock formation, and decrease the flow of water to the well. c. The groundwater flowing to the geothermal well would fill the well with placer deposits. d. The groundwater available to flow to the geothermal well would eventually be used up, and the geothermal well would cease providing hot water to the plant ____ 46. According to the table below, the world’s oil reserves are likely to be depleted in about ____________ years. a. 10 b. 40 c. 4,000 d. 600,000 ____ 47. Which of the factors listed below does NOT hinder using geothermal energy to provide most of society’s electrical needs? a. b. c. d. N Groundwater is not available in all places, to capture and carry heat to the surface. Magma is found in the shallow crust in only limited areas of the planet. Rocks rarely have sufficient permeability to allow flow of groundwater. Electrical transmission lines cannot carry electricity generated at geothermal power plants. NOTE: The mineral resources questions below written in red font are not covered in the class. They will not appear in the exam! SKIP these to the Groundwater questions! ____ 48. There are no significant mineral reserves within sedimentary rocks. a. true b. false ____ 49. The first ores that were widely smelted by humans to produce metal were those of ____________. a. bronze c. gold b. copper d. iron ____ 50. The stereotypical gold rush prospector panning for gold in streambeds is mining ________. a. magmatic deposits c. residual mineral deposits b. placer deposits d. sedimentary deposits ____ 51. In what kind of terrain would you expect to find a placer deposit? a. dry lake bed b. mountain peak c. ocean floor d. streambed ____ 52. Which type of ore is most commonly concentrated in magmatic deposits? a. oxides c. native metals b. sulfides d. copper ores ____ 53. Mineral-rich veins within or near plutons, deposited in fractures by hot groundwater, characterize ____________. a. hydrothermal deposits c. residual mineral deposits b. placer deposits d. sedimentary deposits ____ 54. MVT (Mississippi Valley-type) deposits are secondary enrichments primarily of ____________ and ____________. a. gold; silver c. copper; bronze b. tin; aluminum d. lead; zinc ____ 55. Aluminum is made by processing material excavated from____________ deposits. a. residual mineral c. hydrothermal b. placer d. magmatic ____ 56. Which of these geologic phenomena would a modern mineral prospector use to search for a large deposit of sulfide or minerals within a magmatic body? a. areas of earthquake wave attenuation b. the concentration of aluminum in soils of the area c. indications of recent hydrothermal activity d. locally stronger gravity because of denser minerals ____ 57. Which property of magmatic ore deposits causes them to be concentrated by magmas? a. low temperatures of crystallization c. low density b. high temperatures of crystallization d. high density ____ 58. Which ore minerals are abundant in sedimentary rocks that are approximately two billion years old? a. copper sulfides c. iron oxides b. aluminum oxides d. copper oxides ____ 59. In the figure below, why would the densest clasts probably be at the bottom of the river channel? a. b. c. Denser clasts are larger and are therefore found at the river bottom. Denser clasts roll (due to landslides, etc.) further into the river and so are most common in the middle of the channel. Denser clasts require more energy to move and so are deposited first, into flood-scoured channels when waters begin to slow. d. Denser clasts are more magnetic and weak molecular forces cause them to “stick” to water molecules. ____ 60. Which of these materials is used in making glass? a. salt c. limestone b. granite d. sand ____ 61. Blocks of rock used in construction are termed ____________. a. dimension stone c. ore b. gemstone d. lodestone ____ 62. Stone is typically broken into slabs and blocks through the use of ____________. a. mechanical splitting and chiseling c. heat b. abrasion d. All of the above are correct. ____ 63. Which mineral is used in making cement? a. sulfur b. gypsum c. zinc d. limestone ____ 64. Concrete is ____________. a. synonymous with the term cement b. synonymous with the term Portland cement c. a combination of cement, sand, and gravel d. powdered rock of any lithology mixed with water and allowed to set overnight ____ 65. If additional ore resources are not discovered and rates of ore consumption remain the same, in about how many years will most of the resources listed here be exhausted? a. 10 to 20 years b. 30 to 80 years c. 80 to 200 years d. more than 200 years from now ____ 66. Which mineral resources are considered renewable? a. base metals only c. iron and aluminum ores b. nonmetallic minerals only d. No mineral resources are renewable. ____ 67. Mining metallic minerals usually produces sulfur-rich acidic wastes. You learned earlier in this course that calcite (CaCO3) reacts with acids to neutralize them. Based on this, what material could you apply to the acidic surface or groundwater drainage near a metallic ore body or mine, to neutralize its acidity? a. gypsum c. salt b. limestone or marble d. any foliated metamorphic rock ____ 68. The United States government tracks the consumption of metals deemed “strategic” to our society, industry, and defense, and compares their consumption against the resources of those ores within the United States. Based on the chart below, what resources should U.S. geologists be exploring for? a. b. c. d. iron and lead iron, copper, and lead zinc and gold platinum, nickel, cobalt, manganese, and chromium ____ 69. A drawback to mining sulfides is the risk of ____________. a. underground fires c. “rock bursts” b. tunnel collapse d. acid mine runoff Groundwater questions ____ 70. In the figure below, which is NOT a reason for the oil to migrate to the Earth’s surface? a. b. c. d. It is hot and flows upward because of its temperature. It is lighter than any groundwater, and so it will rise through groundwater. There is nothing that looks like a trap rock above it, to prevent it from rising. It is under pressure and migrates upward toward lower pressure. ____ 71. Sinkholes are a concern primarily for residents whose dwellings are constructed atop ____________. a. sandstone c. limestone b. shale d. granite ____ 72. The majority of liquid freshwater within Earth exists in ____________. a. lakes c. pores within rock and sediment b. rivers and streams d. atmospheric clouds ____ 73. Material through which water readily flows is termed ____________. a. fluent c. permeable b. porous ____ 74. Groundwater ____________. a. does not affect the porosity of the rock and sediment through which it flows b. uniformly increases porosity due to dissolution of grains c. uniformly decreases porosity due to deposition of minerals into pores d. may increase or decrease porosity through dissolution or deposition ____ 75. In the figure below, the flecked material to the right of the fault would be considered a(n) ____________. a. aquifer b. aquitard c. artesian well d. perched aquifer ____ 76. Primary porosity may be reduced by ____________. a. compaction of grains c. Both a and b are correct. b. cementation of grains d. None of the above is correct. ____ 77. Dissolution of rock produces ____________. a. primary porosity b. primary permeability c. secondary porosity d. a reduction in primary porosity ____ 78. Unconsolidated sediment typically has greater porosity than lithified rock which it forms. a. true b. false ____ 79. In unfractured rock and sediment, water molecules usually take a ____________. a. straight path c. circular path b. wandering path ____ 80. If a material is porous, it ____________. a. will be permeable as well b. will be impermeable c. may be permeable or impermeable ____ 81. An impermeable layer of rock or sediment is termed a(n) ____________ in hydrogeologic contexts. a. aquitard c. unconfined aquifer b. confined aquifer d. unsaturated zone ____ 82. An aquifer that is isolated from Earth’s surface by an aquitard is ____________. a. supersaturated c. unconfined b. confined aquifer d. unsaturated zone ____ 83. A body of permeable, saturated rock or sediment into which water can percolate directly from the ground surface is termed a(n) ____________. a. aquitard c. unconfined aquifer b. confined aquifer d. unsaturated zone ____ 84. Unless it has recently rained, there is no water within pores in the unsaturated zone. a. true b. false ____ 85. Freshwater lakes are always discharge areas. a. true b. false ____ 86. Rock or sediment between the water table and the land surface represents a(n) ____________. a. aquitard c. unconfined aquifer b. confined aquifer d. unsaturated zone ____ 87. In a humid climate, the topography of the water table ____________. a. is unaffected by local surface topography b. precisely mimics the topography of the ground surface c. is a subdued (less steeply sloping) mimic of surface topography d. is an exaggerated (more steeply sloping) mimic of surface topography ____ 88. Perched water tables occur ____________. a. above the regional water table, within permeable rock or sediment b. above the regional water table, within impermeable rock or sediment c. below the regional water table, within impermeable rock or sediment d. below the regional water table, within permeable rock or sediment ____ 89. Which list correctly orders the three types of subsurface water from shallowest to deepest? a. groundwater, soil moisture, vadose zone water b. soil moisture, groundwater, vadose zone water c. groundwater, vadose zone water, soil moisture d. soil moisture, vadose zone water, groundwater ____ 90. Why will the sandstone shown in the figure below probably not be permeable? a. b. c. d. There isn’t enough pore space. The pore spaces are too small for water to flow through. The pore spaces are not connected enough Both a and b are correct. ____ 91. A well-sorted sediment will have ____________ porosity than a poorly sorted sediment. a. greater c. approximately the same b. less ____ 92. A bedrock that has no intergranular porosity, but that has extensive interconnected fractures, ____________. a. is impermeable c. has secondary porosity b. is probably permeable d. Both b and c are correct. ____ 93. The relationship governing the rate of groundwater flux was discovered by ____________. a. Alfred Wegener c. Henri Darcy b. Isaac Newton d. Charles Richter ____ 94. The elevation of the water table ____________. a. is a constant for a given area as long as the topography remains the same b. may rise during times of drought and sink during rainy periods c. may rise during rainy periods and sink during droughts ____ 95. As a rule, groundwater always flows from areas ____________. a. of greater elevation to those of lesser elevation b. of greater water pressure to those of lesser water pressure c. of greater hydraulic head to those of lesser hydraulic head d. near streams to areas beneath mountain ranges ____ 96. Which statement about recharge areas is NOT true? a. Recharge areas typically are elevated with respect to neighboring areas. b. Recharge areas are regions of relatively high precipitation. c. Recharge areas are the same as discharge areas. d. Recharge areas are areas where water infiltrates the sediment from above. ____ 97. You are in charge of putting in water well for a large farm. Unfortunately, there has been a lot of groundwater pollution in the area since it became industrialized almost 200 years ago. Referring to the figure below, how far down should you install the openings of the well in order to have the best chance of getting uncontaminated water? a. to A b. to B c. to C ____ 98. The rate of groundwater flow per unit area through a body of rock or sediment depends ____________. a. only on the slope of the water table locally b. only on the porosity of the rock or sediment c. on the slope of the water table and the porosity of the rock or sediment d. on the slope of the water table and the permeability of the rock or sediment ____ 99. A dry well will always result whenever the base of the well is above the water table. a. true b. false ____ 100. An artesian well is one that ____________. a. discharges groundwater at ground surface without pumping b. has its intake sited within the saturated zone of an unconfined aquifer c. has intake sited within the unsaturated zone of an unconfined aquifer d. has its recharge area at an elevation below sea level ____ 101. Any place where groundwater naturally flows out of the surface of Earth is termed a ____________. a. flowing artesian well c. spring b. geyser d. recharge area ____ 102. An ordinary (water-producing) well is likely to result when the base of the well extends below the water table. a. true b. false ____ 103. Which factor listed here would not affect the flow of water at a spring? a. the concentrations of various ions and man-made pollutants b. conditions of either drought or heavy rainfall at the recharge area c. the interconnectedness of fractures or pore spaces leading to the spring d. a decline in the water table in the direction from which groundwater feeds the spring ____ 104. A periodic explosive eruption of steam and water from within the ground up through the surface is termed a ____________. a. flowing artesian well c. spring b. geyser d. recharge area ____ 105. Water flowing from hot springs ____________. a. contains more dissolved minerals than water emanating from cool springs b. contains less dissolved minerals than water emanating from cool springs c. is never hotter than 40°C, so it is always safe to bathe in d. only occurs in regions of active volcanic eruption ____ 106. You operate a geothermal power plant here. After several years, the wells that have produced hot water and steam are beginning to run dry. If you want to install injection wells (wells that you can pump water into), so that you could recharge the groundwater circulation system and preserve the flow of hot water to your production well, where would you drill them? (Note: Lines are red (dark grey) at the end with the arrowhead and blue (light grey) nearer the ends without arrowheads.) a. by the blue arrows b. by the red arrows c. in between the blue and red arrows d. at both the blue and red arrows ____ 107. Arsenic can be naturally occurring in groundwater. a. true b. false ____ 108. Extensive pumping of fresh groundwater from wells near a seacoast is most likely to induce ____________. a. saline intrusion; with time the well will start to deliver saline water b. saline expulsion; with time the freshwater/saline water interface within the aquifer will be pushed downward and seaward c. mineral deposition of salts within the aquifer ____ 109. Neither methane nor hydrogen sulfide is naturally-occurring in well-water. a. true b. false ____ 110. Venice, Italy, has largely subsided beneath sea-level because of ____________. a. polar ice caps melting due to global warming b. extensive nearby groundwater mining and sediment compaction c. tectonic forces related to the gradual, ongoing collision of Africa and Europe d. None of the above are correct; Venice was built underwater during the Middle Ages. ____ 111. Pumping vast quantities of water locally ____________. a. raises the local water table b. lowers the local water table, forming a cone-shaped depression c. lowers the local water table, forming a cylindrical depression d. does not affect the water table ____ 112. Groundwater mining refers to ____________. a. acid drainage from mines polluting groundwater b. legal squabbling over groundwater rights (“It’s mine!”) c. pumping out water faster than it can be replenished by recharge d. prospecting an area to find a suitable spot for a well ____ 113. Hard water results from relatively high concentrations of dissolved ____________. a. calcium and magnesium c. sodium b. francium and cesium d. potassium ____ 114. Groundwater ____________. a. rarely, if ever, contains dissolved ions b. dissolves calcite and limestone c. can contain dissolved minerals but can never precipitate minerals out of solution d. can precipitate minerals but only if the ions that would form the mineral in question are undersaturated in the water ____ 115. Bioremediation of contaminated groundwater involves ____________. a. introduction of laboratory-cultured viruses that can dissolve the plume b. pumping nutrients into a contaminant plume to help local bacteria metabolize the plume c. pumping out the contaminated groundwater and using it to irrigate genetically modified crops ____ 116. The well shown in this figure has become “contaminated” with naturally occurring salt water, drawn toward it because too much water was pumped from it for too long. What would be an easy way to restore the aquifer, that is, to push the saline groundwater back toward the ocean? a. Cover the near-shore sea bottom with heavy plastic and concrete to prevent more seawater from entering the aquifer. b. Install a line of wells between your “contaminated” well and the coast, and place desalination equipment in each one, to remove salinity from the aquifer. c. Convert your “contaminated” well into an injection well and begin to pump freshwater into the aquifer through it. d. Increase the amount of rainfall that occurs just inland from your “contaminated” well. ____ 117. Topography dominated by depressions formed by the collapse of caves is termed ____________. a. valley and ridge c. horst and graben b. karst ____ 118. Most large cave and karst systems have resulted from ____________ dissolving ____________. a. carbonic acid; limestone c. phosphoric acid; shale b. ascorbic acid; dolostone d. seawater; rock salt ____ 119. Besides its immense size, what else is unusual about Carlsbad Caverns in southeastern New Mexico? a. Geologists think the system was produced by sulfuric acid rather than carbonic acid. b. The caverns are within a deposit of rock salt rather than limestone. c. The caverns were formed within the span of just a few days in 1937. d. Although there are conduits to the surface, the caverns do not host a population of bats. ____ 120. Most dissolution of bedrock to form caves takes place ____________. a. above the water table b. just below the water table c. greater than 10 m below the water table ____ 121. If the cross-section shown here were typical of the main channel of a long river, would you expect the river to dry up as you followed it downstream? a. b. c. d. Yes, because the water is contaminated. Not if there were additional tributaries entering it downstream. Yes, because it is in a desert. No. ____ 122. Which of the following is not evidence for karst topography? a. salt beds c. limestones b. sinkholes d. disappearing streams ____ 123. You find a huge new cave system and discover it has multiple, extensive levels, each about 500 ft below the one above it. What can you infer about the water table in the region? a. It used to be higher. b. It periodically dropped further and further. c. It lies beneath an aquitard d. Both a and b are correct. ____ 124. Land subsidence is likely when ____________. a. groundwater recharge occurs b. the Ca and Mg content of groundwater increases c. the water table changes d. discharge lowers the water table Practice Test 2 Geol 2001 Summer Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: TOP: 2. ANS: TOP: 3. ANS: TOP: 4. ANS: TOP: 5. ANS: TOP: 6. ANS: TOP: 7. ANS: TOP: 8. ANS: TOP: 9. ANS: TOP: 10. ANS: TOP: 11. ANS: TOP: 12. ANS: TOP: 13. ANS: TOP: 14. ANS: TOP: 15. ANS: TOP: 16. ANS: TOP: 17. ANS: TOP: 18. ANS: TOP: 19. ANS: TOP: 20. ANS: TOP: 21. ANS: TOP: 22. ANS: B X B II A II A II B II D III.A C III.B B III.C B III.C B III.C D III.A C III.C C III.C A III.C C III.C A III.D B III.E B III.E D III.E A III A III.A D PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: 1 Factual 1 Factual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Factual 1 Factual 1 Factual 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Factual 1 Factual 1 Conceptual 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 DIF: Medium REF: 12.1 DIF: Easy REF: 12.2 DIF: Medium REF: 12.2 DIF: Medium REF: 12.2 DIF: Medium REF: 12.2 DIF: Easy REF: 12.3 DIF: Easy REF: 12.3 DIF: Easy REF: 12.3 DIF: Easy REF: 12.3 DIF: Easy REF: 12.3 DIF: Medium REF: 12.3 DIF: Medium REF: 12.3 DIF: Medium REF: 12.3 DIF: Medium REF: 12.3 DIF: Medium REF: 12.3 DIF: Medium REF: 12.3 DIF: Medium REF: 12.3 DIF: Medium REF: 12.3 DIF: Medium REF: 12.3 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.3 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.3 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.3 TOP: 23. ANS: TOP: 24. ANS: TOP: 25. ANS: TOP: 26. ANS: TOP: 27. ANS: TOP: 28. ANS: TOP: 29. ANS: TOP: 30. ANS: TOP: 31. ANS: TOP: 32. ANS: TOP: 33. ANS: TOP: 34. ANS: TOP: 35. ANS: TOP: 36. ANS: TOP: 37. ANS: TOP: 38. ANS: TOP: 39. ANS: TOP: 40. ANS: TOP: 41. ANS: TOP: 42. ANS: TOP: 43. ANS: TOP: 44. ANS: TOP: 45. ANS: TOP: 46. ANS: TOP: III.A C III.C D III.C A III.D B III.E A III.C | VI.B A IV.C D IV.C D V B V.B B V.B C V.C C V.A C III.D C IV.A B VI.A B VI.B B VI.B A VI.C | XII B VII.C C VII.B A VIII.C C VIII.C B VIII.B B VIII.A MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: Conceptual 1 Conceptual 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Factual 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Factual 1 Applied 1 Factual 1 Factual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Conceptual 1 Factual DIF: Difficult REF: 12.3 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.3 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.3 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.3 DIF: Medium REF: 12.3 | 12.6 DIF: Easy REF: 12.4 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.4 DIF: Medium REF: 12.5 DIF: Medium REF: 12.5 DIF: Medium REF: 12.5 DIF: Medium REF: 12.5 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.5 DIF: Easy REF: 12.6 DIF: Easy REF: 12.6 DIF: Medium REF: 12.6 DIF: Medium REF: 12.6 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.6 DIF: Medium REF: 12.6 | 12.12 DIF: Medium REF: 12.7 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.7 DIF: Easy REF: 12.8 DIF: Easy REF: 12.8 DIF: Medium REF: 12.8 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.8 47. ANS: TOP: 48. ANS: TOP: 49. ANS: TOP: 50. ANS: TOP: 51. ANS: TOP: 52. ANS: TOP: 53. ANS: TOP: 54. ANS: TOP: 55. ANS: TOP: 56. ANS: TOP: 57. ANS: TOP: 58. ANS: TOP: 59. ANS: TOP: 60. ANS: TOP: 61. ANS: TOP: 62. ANS: TOP: 63. ANS: TOP: 64. ANS: TOP: 65. ANS: TOP: 66. ANS: TOP: 67. ANS: TOP: 68. ANS: TOP: 69. ANS: TOP: B VIII.B B X B XI.A B XI.C.vii D XI.C.vii B XI.C.i A XI.C.ii D XI.C.iv A XI.C.vi D XI.C D XI.C.i C XI.C.v C XI.C.vii D XIII A XIII.A D XIII.A D XIII.B C XII.B B XIV.A D XIV.A B XIV D XIV.A D XIV.B PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Factual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Factual 1 Factual 1 Factual 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Factual 1 Factual 1 Applied 1 Factual 1 Applied 1 Factual 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Conceptual 1 Applied DIF: Difficult REF: 12.8 DIF: Easy REF: 12.10 DIF: Easy REF: 12.11 DIF: Easy REF: 12.11 DIF: Easy REF: 12.11 DIF: Medium REF: 12.11 DIF: Medium REF: 12.11 DIF: Medium REF: 12.11 DIF: Medium REF: 12.11 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.11 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.11 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.11 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.11 DIF: Easy REF: 12.13 DIF: Easy REF: 12.13 DIF: Easy REF: 12.13 DIF: Easy REF: 12.13 DIF: Medium REF: 12.13 DIF: Easy REF: 12.14 DIF: Easy REF: 12.14 DIF: Medium REF: 12.14 DIF: Medium REF: 12.14 DIF: Medium REF: 12.14 70. ANS: TOP: 71. ANS: TOP: 72. ANS: TOP: 73. ANS: TOP: 74. ANS: TOP: 75. ANS: TOP: 76. ANS: TOP: 77. ANS: TOP: 78. ANS: TOP: 79. ANS: TOP: 80. ANS: TOP: 81. ANS: TOP: 82. ANS: TOP: 83. ANS: TOP: 84. ANS: TOP: 85. ANS: TOP: 86. ANS: TOP: 87. ANS: TOP: 88. ANS: TOP: 89. ANS: TOP: 90. ANS: TOP: 91. ANS: TOP: 92. ANS: TOP: 93. ANS: TOP: 94. ANS: A XIV.B C I C I C II.C D II B II C II.B C II.B A II.B B II.C C II.C A II.D B II.D C II.D B II.E B II.E D II.E C II.E A II.F D II C II.B A II.C D II.E C II.B C PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Conceptual 1 Conceptual 1 Factual 1 DIF: Difficult REF: 12.14 DIF: Medium REF: 16.1 DIF: Medium REF: 16.1 DIF: Easy REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Medium REF: 16.2 DIF: Difficult REF: 16.2 DIF: Difficult REF: 16.2 DIF: Difficult REF: 16.2 DIF: Difficult REF: 16.2 DIF: Easy REF: 16.3 DIF: Medium REF: 16.3 TOP: 95. ANS: TOP: 96. ANS: TOP: 97. ANS: TOP: 98. ANS: TOP: 99. ANS: TOP: 100. ANS: TOP: 101. ANS: TOP: 102. ANS: TOP: 103. ANS: TOP: 104. ANS: TOP: 105. ANS: TOP: 106. ANS: TOP: 107. ANS: TOP: 108. ANS: TOP: 109. ANS: TOP: 110. ANS: TOP: 111. ANS: TOP: 112. ANS: TOP: 113. ANS: TOP: 114. ANS: TOP: 115. ANS: TOP: 116. ANS: TOP: 117. ANS: TOP: 118. ANS: TOP: II.E C III.A C III.A C III.A D III.B A IV.A A IV.A C IV.A A IV.B A IV.B B V A V A V A VI.B A VI B VI B VI B VI.A C VI.A A VI.B B VI.B B VI.C C VI.B B VII.D A VII.A MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Conceptual 1 Factual 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Factual 1 Applied DIF: Medium REF: 16.3 DIF: Medium REF: 16.3 DIF: Difficult REF: 16.3 DIF: Difficult REF: 16.3 DIF: Medium REF: 16.4 DIF: Medium REF: 16.4 DIF: Medium REF: 16.4 DIF: Medium REF: 16.4 DIF: Difficult REF: 16.4 DIF: Medium REF: 16.5 DIF: Medium REF: 16.5 DIF: Difficult REF: 16.5 DIF: Easy REF: 16.6 DIF: Medium REF: 16.6 DIF: Medium REF: 16.6 DIF: Medium REF: 16.6 DIF: Medium REF: 16.6 DIF: Medium REF: 16.6 DIF: Medium REF: 16.6 DIF: Medium REF: 16.6 DIF: Medium REF: 16.6 DIF: Difficult REF: 16.6 DIF: Easy REF: 16.7 DIF: Medium REF: 16.7 119. ANS: TOP: 120. ANS: TOP: 121. ANS: TOP: 122. ANS: TOP: 123. ANS: TOP: 124. ANS: TOP: A VII.A B VII.A B VII.A A VII.D D VII.A D VI.A PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: PTS: MSC: 1 Applied 1 Applied 1 Conceptual 1 Conceptual 1 Conceptual 1 Applied DIF: Medium REF: 16.7 DIF: Medium REF: 16.7 DIF: Medium REF: 16.7 DIF: Medium REF: 16.7 DIF: Difficult REF: 16.7 DIF: Medium REF: 16.8









