Expt
advertisement

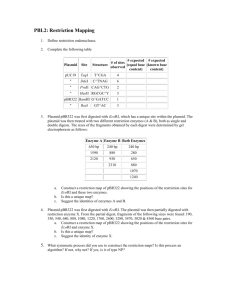
Expt. 5 Restriction Enzyme Mapping of a Circular Plasmid Background & Objective: Effective use of a vector in molecular biology experiments requires that all restriction endonuclease sites in that vector be accurately determined in relation to the genes of interest that are necessary for plasmid function. Digestion of the plasmid DNA with the restriction enzymes of interest in order to “map” their location is a standard step in cloning procedures. Restriction mapping may also be done as the first step in characterizing a DNA fragment that has been isolated prior to sequencing. The plasmid, pBR322, is a bacterial circular plasmid as opposed to the linear bacteriophage λ DNA. The goal of this laboratory exercise is to determine the number and relative location of three restriction endonuclease sites (EcoRI, PvuII, and HincII) on the cloning vector pBR322. . Procedures: Restriction Digestions 1. Label 3 microfuge tubes, one with EcoRI, one with PvuII, and one with HincII. 2. Use the table below to set up the reactions. pBR322 DNA (0.5 μg/μl) 10X Restriction Buffer B Restriction Enzyme Sterile water Total Volume 1 μl 2 μl 1 μl 16 μl 20 μl 3. Label 3 microfuge tubes, one with EcoRI/PvuII, one with PvuII/HincII, and one with HincII/EcoRI. 4. Use the table below to set up the reactions. pBR322 DNA (0.5 μg/μl) 10X Restriction Buffer B Restriction Enzyme 1 Restriction Enzyme 2 Sterile water Total Volume 1 μl 2 μl 1 μl 1 μl 15 μl 20 μl 5. Label 1 microfuge tube with EcoRI/ PvuII/HincII. 6. Use the table below to set up the reactions. pBR322 DNA (0.5 μg/μl) 10X Restriction Buffer B Restriction Enzyme 1 Restriction Enzyme 2 Restriction Enzyme 3 Sterile water Total Volume 1 μl 2 μl 1 μl 1 μl 1 μl 14 μl 20 μl 7. Mix the reactions and centrifuge briefly. 8. Incubate the reaction tubes in the 37C water bath for 1 hour. Pouring an Agarose Gel (1%) 1. Seal the ends of the gel-casting tray with the rubber seals and place it in the electrophoresis unit to create a seal. 2. Dilute 50 mls of 10X TBE with deionized, distilled water to 1X TBE. 3. Weigh 0.5 grams of molecular grade agarose and suspend in 50 mls of 1 TBE in a 300 ml Erlenmeyer flask. 4. Microwave the agarose solution on high power for 1 minute. CAREFULLY, mix the solution, keeping the flask opening pointed away from anyone. Microwave two more times at 15 seconds, carefully mixing in between. The agarose should be completely melted. 5. When the agarose has cooled to below 60C, add 3 μl of ethidium bromide (10 mg/ml) to the agarose solution and gently swirl. 6. Pour the agarose into the casting tray and insert the well-forming comb. 7. When the gel has solidified, about 20-30 minutes, remove the comb, turn the gel tray 90 degrees, and fill the electrophoresis chamber with 1X TBE buffer until just above the gel. Gel Electrophoresis 1. Remove the reactions from the 37C water bath and centrifuge briefly. 2. Add the appropriate amount of 6X loading dye to each reaction (1 μl of loading dye for every 5 μl of reaction mix). 3. Thaw one 12 ul aliquot of the λ HindIII standard. 4. Load the wells of the gel making sure to record the order in your notebook. 5. Electrophorese the gel at 110-120V for 1 hour. 6. Photograph the gel on a UV transilluminator using the Kodak software. 7. Print a copy of your gel for your notebook.