The current status of mineral resources in Moldova
advertisement

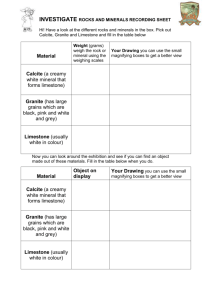
1.4.2. Mineral resources According to the latest statistical data concerning the mineral resources,, there are 313 mineral deposits in the Republic of Moldova, out of which 126 are being exploited. About 900 quarries are used for extraction of non-iron minerals (mainly construction materials); the underground waters are being used through 6600 boreholes and 132,000 shallow wells as well as through a large number of deep and shallow wells which, for the time being, are not officially taken into account. The most frequently used mineral resources are the following: - Inferior Sarmatian and Badenian carbonates, used in the building industry, for cement production, sugar purification, road construction, as fodder additive, etc.; - silica rocks (silicon limestone, diatomite, tripoli), in the food industry, leather industry, paper industry, production of electro-termic materials, etc.; - clayey rocks (argillaceous schists, clay, bentonite clay), serving for the production of cement, bricks, tile, etc; - sands and gravel , for glass production, concrete production, in building industry, road construction; - gypsum, used in construction, and pharmaceutical industry; - crystalline rocks (gabbro, granite), production of ferro-concrete, and in road construction; - oil, natural gas, brown coal,, the reserves are insignificant (Valeni, Victorovca, Vladiceni). The current status of mineral resources in Moldova Most of the mineral resources in Moldova are exploited through quarries, and only certain varieties of limestone are extracted through galleries. The open extraction of minerals (through quarries) is usually associated with the destruction of soils and vegetation, and is leading to the accumulation of important quantities of mining waste, which is quite often spread out by the wind, being a pollution and nuisance factor for adjacent areas.