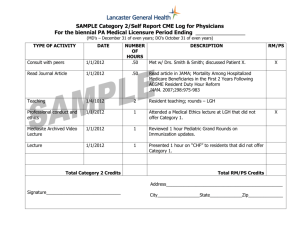
INPATIENT WARDS – RENAL-RHEUMATOLOGY
advertisement
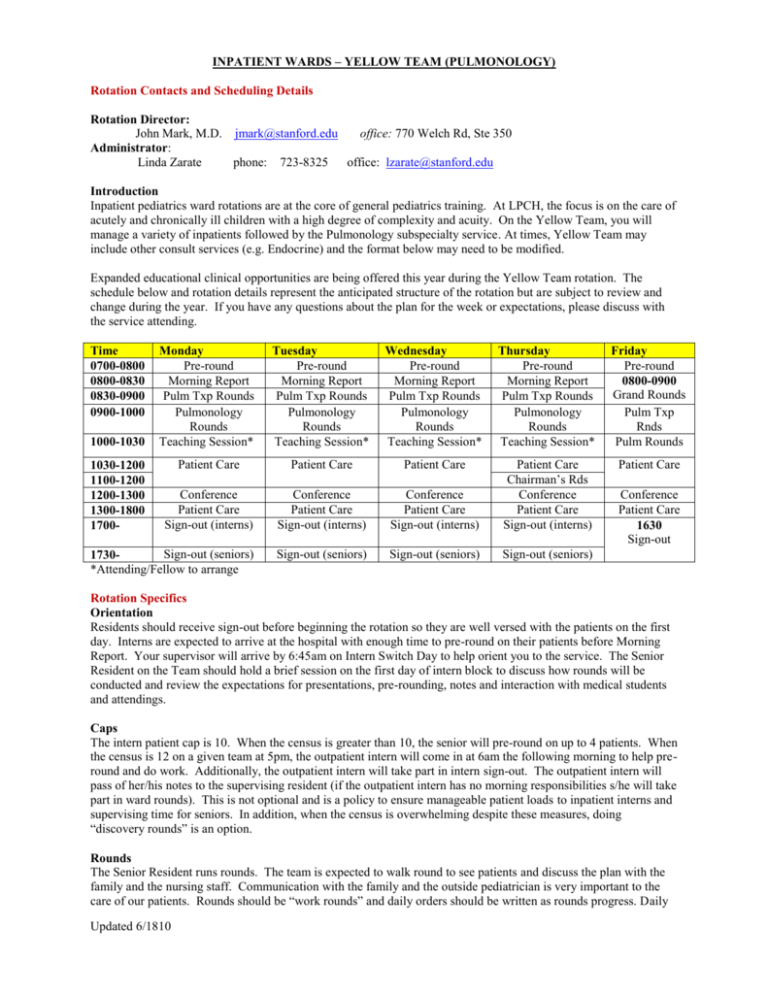
INPATIENT WARDS – YELLOW TEAM (PULMONOLOGY) Rotation Contacts and Scheduling Details Rotation Director: John Mark, M.D. jmark@stanford.edu office: 770 Welch Rd, Ste 350 Administrator: Linda Zarate phone: 723-8325 office: lzarate@stanford.edu Introduction Inpatient pediatrics ward rotations are at the core of general pediatrics training. At LPCH, the focus is on the care of acutely and chronically ill children with a high degree of complexity and acuity. On the Yellow Team, you will manage a variety of inpatients followed by the Pulmonology subspecialty service. At times, Yellow Team may include other consult services (e.g. Endocrine) and the format below may need to be modified. Expanded educational clinical opportunities are being offered this year during the Yellow Team rotation. The schedule below and rotation details represent the anticipated structure of the rotation but are subject to review and change during the year. If you have any questions about the plan for the week or expectations, please discuss with the service attending. Time 0700-0800 0800-0830 0830-0900 0900-1000 Monday Pre-round Morning Report Pulm Txp Rounds Pulmonology Rounds Teaching Session* Tuesday Pre-round Morning Report Pulm Txp Rounds Pulmonology Rounds Teaching Session* Wednesday Pre-round Morning Report Pulm Txp Rounds Pulmonology Rounds Teaching Session* Thursday Pre-round Morning Report Pulm Txp Rounds Pulmonology Rounds Teaching Session* Friday Pre-round 0800-0900 Grand Rounds Pulm Txp Rnds Pulm Rounds Patient Care Patient Care Patient Care Patient Care Conference Patient Care Sign-out (interns) Conference Patient Care Sign-out (interns) Conference Patient Care Sign-out (interns) Patient Care Chairman’s Rds Conference Patient Care Sign-out (interns) Sign-out (seniors) 1730*Attending/Fellow to arrange Sign-out (seniors) Sign-out (seniors) Sign-out (seniors) 1000-1030 1030-1200 1100-1200 1200-1300 1300-1800 1700- Conference Patient Care 1630 Sign-out Rotation Specifics Orientation Residents should receive sign-out before beginning the rotation so they are well versed with the patients on the first day. Interns are expected to arrive at the hospital with enough time to pre-round on their patients before Morning Report. Your supervisor will arrive by 6:45am on Intern Switch Day to help orient you to the service. The Senior Resident on the Team should hold a brief session on the first day of intern block to discuss how rounds will be conducted and review the expectations for presentations, pre-rounding, notes and interaction with medical students and attendings. Caps The intern patient cap is 10. When the census is greater than 10, the senior will pre-round on up to 4 patients. When the census is 12 on a given team at 5pm, the outpatient intern will come in at 6am the following morning to help preround and do work. Additionally, the outpatient intern will take part in intern sign-out. The outpatient intern will pass of her/his notes to the supervising resident (if the outpatient intern has no morning responsibilities s/he will take part in ward rounds). This is not optional and is a policy to ensure manageable patient loads to inpatient interns and supervising time for seniors. In addition, when the census is overwhelming despite these measures, doing “discovery rounds” is an option. Rounds The Senior Resident runs rounds. The team is expected to walk round to see patients and discuss the plan with the family and the nursing staff. Communication with the family and the outside pediatrician is very important to the care of our patients. Rounds should be “work rounds” and daily orders should be written as rounds progress. Daily Updated 6/1810 discharges after rounds should be given priority. Teaching sessions will be held in the mornings with a variable format including didactic, case based, bedside and experiential. The teaching sessions will be determined by the Attending/Fellow each week. Pagers The Yellow Team will have a team text pager to facilitate communication. Interns will be the primary team member to carry the pager, except when in Continuity Clinic or after signing out to the Blue/Yellow night float resident. Yellow Team Call Schedule Fridays Interns on the outpatient services will come to sign-out on weeks 1 and 3 to be aware of the services they will pre-round for and then cover on Sunday from 6A-5P. Interns on the primary inpatient service will take overnight call with help from one of the 2 Senior NF supervisors who has been covering in an every-other-night fashion all week with her counterpart, and so therefore knows the children well. Interns on call on Friday night will pre-round on their primary week-day service early on Saturday morning, with support from the NF supervisor, who is not needed for rounds on Saturday morning. Saturdays Post-call interns complete their work with the help of the NF supervisor who was on-call with them the prior night. This supervisor facilitates any necessary hand-offs to the on-call team, and gives the intern’s notes to the day-time supervisor for Yellow Team rounds. The post-call interns leave within 27 hours of their arrival the prior day, likely without actually attending rounds. Rounds are run by the day-time supervisors, who are also the seniors on the teams during the week. One senior will round with Blue/Yellow, and one senior will round with Red/Green. The on-call interns for these services will be present with each senior, but the senior will report the data (and ideally examine on rounds) the children seen by the post-call intern who should be gone by rounds. The NF supervisor is able to stay to join rounds on the children who were examined by the post-call intern, and ideally has some sense of their course and their exam findings as well. The NF supervisor does not need to be back in the hospital until 5PM on Monday night, so duty hours restrictions are not as big of a concern with this person. Sundays During Intern Week 1, the outpatient Yellow and outpatient Green interns will come in for a day shift until 5pm. They will do the pre-rounding, rounding, and patient care. They should have some sense of the patients since they came to sign-out on Friday night, and they have the supervision of senior residents who are on the regular day-time teams. At 5pm, the Night Float interns come to take over. During Intern Week 2, the 2nd and last week of Night Float for the Night Float Interns, the Night Float Interns come in on Sunday for a 24-hour call. This ensures a golden weekend for the color-team residents, while also granting the Night Float interns only one 24-hour Sunday without the need for reversal back to night-time hours on Monday as the rotation is then over. Rounds will again be run by two separate day-time seniors who are on the primary, week-day teams: Blue/Yellow will be run by one senior (either the week-day Blue or Yellow senior) and Red/Green rounds will be run by the other day-time senior (either the week-day Red or Green senior). Sign-out Sign-out should take place as follows: Prior to 5 pm, supervisors determine order of team sign-out and update LINKS On the first day of the rotation, the day senior will sign out to the night intern and night senior while the day intern observes On following days, the day intern will sign out to the night intern then the day senior will sign out to the night senior (day seniors should observe intern sign-out and day interns should observe supervisor sign-out as time allows. In such cases the day senior listens carefully adding any missed details, teaches intern about sign-out strategies, and answers pages as needed). Updated 6/1810 Sign-out consists of a brief one-liner about the patient, significant PMHx, reason for admission, and current status. Then either problem-based or systems-based sign-out should include current exam, tasks to be done overnight for that system or problem, contingency planning (what could go wrong and what the team should do about it), and “what worked” (highlight of problems that have arisen and what worked to solve them) As the rotation progresses, Night Teams will know the service better. Therefore, sign-out should be relatively quick and concise—focusing on new admissions and new developments for existing patients. Sign-out will not include pulmonary consult patients even if resident supervisor or intern participate in the evaluation of the pulmonary consult patient. During their weekday calls, the Night Team is only responsible for pre-rounding on and writing notes for the new patients who they admitted during the previous night (progress notes needed on all admissions prior to midnight). Between 6:45 and 7:00 each morning (Monday through Friday) supervisors from each team will meet with the Night Team supervisor to sign out new patients and important overnight events (the night team must be out of the hospital by 7:30. If the day team arrives too late, this on time departure cannot happen). Interns should provide written signout to the daytime teams and give verbal sign out to the daytime interns about new admissions and significant overnight events. In addition, the Night Team will communicate any questions regarding their management overnight and the day team will provide feedback on those issues the following night. Evening Report (when working overnight shift) As part of our educational curriculum, there is an Evening Report held each night in the Housestaff Lounge. These reports, led by overnight pediatric hospitalists, focus on acute ‘on call’ issues. The sessions will be very flexible and will include bedside teaching, practical skills, and physical exam rounds. It is the responsibility of the night float supervisor to contact the hospitalist to arrange the most convenient times for these educational sessions. Resident Roles and Responsibilities Intern: • Performs the primary patient care role • Pre-rounds on patients and writes daily progress notes and orders • Presents patients on rounds and takes care of daily work associated with patient care • Performs dictated history and physicals on new patients • Plans discharges and does paperwork. • Takes call on weekends • Supervises medical students caring for your patients. Supervising Resident: • Supervises interns and medical students • Starts day at 6:45-7:00 am • Examines new and sick patients, check labs and films – prior to Morning Rounds • Discusses overnight events with the Night Team and receives sign-out • Runs rounds and makes management decisions with the input of the team and attendings • Follows-up on daily patient work to ensure the plan is carried out appropriately • Contacts the private pediatricians with an update on their patient • Takes responsibility for the care of all patients on the team • Conducts efficient walk/work rounds • Helps organize/facilitate morning teaching sessions with the Attending/Fellow Evaluation and Feedback The methods of evaluation for the Yellow Team Ward Rotation will consist of: MedHub Resident Evaluations, Faculty Evaluations, Rotation Evaluations Feedback should be provided by the supervisor to intern on a regular basis, but at least weekly. The supervisor should also request feedback from the intern. This is a professional expectation. The focus of feedback will be on competency-based goals and objectives. Feedback to the supervisor should be provided by the service attendings on a weekly basis focusing on competency-based goals and objectives and leadership of a patient care team. It is the responsibility of the resident to solicit attending feedback. At the end of the rotation an end-of-rotation feedback session will be conducted by the supervising resident and subspecialty attending. Updated 6/1810 ACGME Competency-based Goals and Objectives Goal 1. Demonstrate competency in caring for patients with complicated pneumonia Resident Objectives Instructional Strategies Assessment of Competence 1. Select appropriate imaging modalities Patient care MedHub evaluation (done by to clarify diagnosis Teaching on rounds pulmonary service attending) Teaching Module: Active observation by service X-ray “Complicated Pneumonia” attending of patient care CT Review and discussion with US resident imaging results Laryngoscopy Bronchoscopy (PGY 1, 3) 2. Selected appropriate antibiotic Patient care MedHub evaluation (done by coverage when indicated Teaching on rounds pulmonary group) (PGY 1, 3) Teaching Module: Active observation by service “Complicated Pneumonia” attending of patient encounter 3. Recognize when acceleration or Patient care MedHub evaluation (done by alteration of care indicated for Teaching on rounds pulmonary group) inadequate response to therapy and Teaching Module: Active observation by service initiate consultation or additional care “Complicated Pneumonia” attending of patient encounter IR Chest tube VATS (PGY 3) ACGME Competency Goals MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and apply this knowledge to patient care PC—Provide effective health care services SBP - Incorporate considerations of cost awareness and risk-benefit analysis in patient and or population-based care as appropriate MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and apply this knowledge to patient care PC—Provide effective health care services MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and apply this knowledge to patient care PC—Provide effective health care services ICS—(a)Communicate effectively with physicians, other health professionals, and health related agencies; (b)Work effectively as a member or leader of a health care team SBP - Work in inter-professional teams to enhance patient safety and improve patient care Goal 2. Demonstrate competency in caring for patients with neuromuscular disorders with pulmonary compromise Resident Objectives 1. Identify the physical examination findings that reflect pulmonary compromise in setting of neuromuscular weakness syndromes (PGY 1, 3) 2. Discuss and demonstrate participation in the multi-disciplinary approach to the care of a patient with neuromuscular disease Nutrition services Respiratory therapy Social services Updated 6/1810 Instructional Strategies Patient care Teaching on rounds Patient care Teaching on rounds Assessment of Competence Active observation by service attending of physical examination or repeat of exam ACGME Competency Goals PC—Provide effective health care Services MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and apply this knowledge to patient care MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and apply this knowledge to patient care PC—Provide effective health care services SBP—(a )Know how to work with other health professionals and health related agencies (b) Assist patients in dealing with system complexities ICS – Work effectively with others as a member or leader Patient-centered discussion with faculty Faculty observation during patient care conferences of a health care team or other professional group Nursing (PGY 1, 3) Goal 3. Demonstrate competency in caring for patients with exacerbation of cystic fibrosis requiring hospitalization Resident Objectives: Instructional Strategies Assessment of Competence ACGME Competency Goals 1. List the signs and symptoms of cystic Reading materials Patient-centered discussion with MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and fibrosis exacerbation warranting Clinical encounters faculty apply this knowledge to patient care hospitalization PC—Provide effective health care services (PGY 1, 3) 2. Initiate care for patient with cystic Reading materials Patient-centered discussion with MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and fibrosis exacerbation Clinical encounters faculty apply this knowledge to patient care Review of orders by attending PC—Provide effective health care services Selection of appropriate antibiotics Selection of appropriate airway clearance techniques Selection of appropriate nutritional support Initiate appropriate infection control measures (PGY 1, 3) 3. Discuss and demonstrate participation Patient care Patient-centered discussion with MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and in the multi-disciplinary approach to the Teaching on rounds faculty apply this knowledge to patient care care of a patient with cystic fibrosis Faculty observation during patient PC—Provide effective health care services care conferences SBP—(a )Know how to work with other health Nutrition services professionals and health related agencies (b) Assist Respiratory therapy patients in dealing with system complexities Social services ICS – Work effectively with others as a member or leader Nursing of a health care team or other professional group (PGY 1, 3) 4. Describe the roles of commonly used Reading materials Patient-centered discussion with MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and medications in the management of a CF Clinical encounters faculty apply this knowledge to patient care exacerbation Review of orders by attending PC—Provide effective health care services Anti-inflammatories (e.g., azithromycin) Mucolytics (e.g., dornase alpha, Nactyl cysteine, hypertonic saline) Bronchodilators (e.g., albuterol) Pancreatic enzymes (PGY 3) Updated 6/1810 5. Reflect in rounds presentations Reading materials Patient-centered discussion with MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and (including care plan) consideration of Clinical encounters faculty apply this knowledge to patient care extrapulmonary manifestations of cystic MedHub evaluation PC—Provide effective health care services fibrosis ICS—(a)Communicate effectively with physicians, other health professionals, and health related agencies; Pancreatic insufficiency (fat (b)Work effectively as a member or leader of a health malabsorption, insulin intolerance) care team Hepatic dysfunction Nutritional deficiencies (PGY 1, 3) Goal 4: Demonstrate understanding of the care of a child with pulmonary disease in the setting of an immunocompromised state Resident Objectives: Instructional Strategies Assessment of Competence ACGME Competency Goals 1. Recognize signs and symptoms of Patient care Discussions around patient care PC—Provide effective health care services rejection versus infection in an Reading materials MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and immunocompromised patient (e.g., s/p apply this knowledge to patient care lung transplant) (PGY 3) Goal 5. Demonstrate proficiency in use and titration of various devices for respiratory support Resident Objectives: Instructional Strategies Assessment of Competence ACGME Competency Goals 1. Experiment with and differentiate Respiratory therapy Direct input from respiratory MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and between various respiratory support collaboration therapist apply this knowledge to patient care devices Independent reading PC—Provide effective health care services ICS—(a)Communicate effectively with physicians, other Oxygen delivery modalities (e.g., health professionals, and health related agencies; nasal cannula, various face masks) (b)Work effectively as a member or leader of a health CPAP/BiPAP care team (PGY 1, 3) 2. Experiment with and differentiate Respiratory therapy Direct input from respiratory MK—Demonstrate knowledge evolving sciences and between various airway clearance collaboration therapist apply this knowledge to patient care devices Independent reading PC—Provide effective health care services ICS—(a)Communicate effectively with physicians, other VEST health professionals, and health related agencies; IPV (b)Work effectively as a member or leader of a health Cough assist care team Acapella/Flutter device (+ pressure) (PGY 1, 3) PBLI = practice based learning and improvement ICS = interpersonal and communication skills P = professionalism MK = medical knowledge PC = patient care SBP = systems based practice Updated 6/1810