Line Scale - Crescent School
advertisement
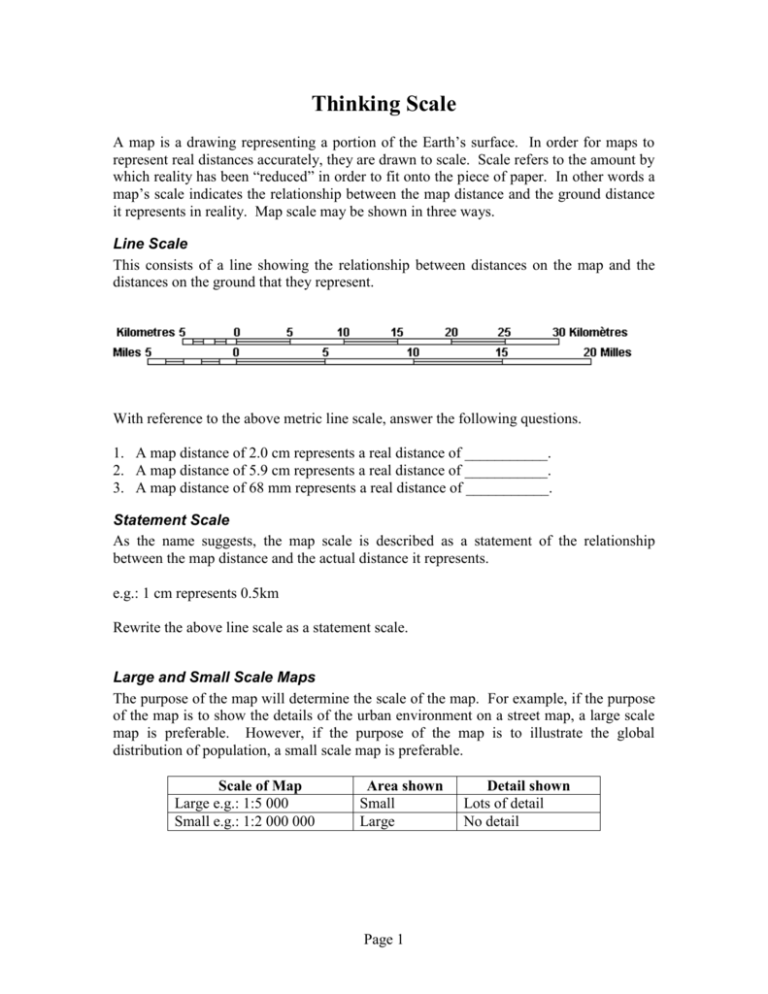
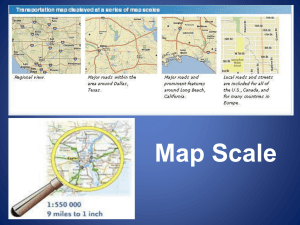
Thinking Scale A map is a drawing representing a portion of the Earth’s surface. In order for maps to represent real distances accurately, they are drawn to scale. Scale refers to the amount by which reality has been “reduced” in order to fit onto the piece of paper. In other words a map’s scale indicates the relationship between the map distance and the ground distance it represents in reality. Map scale may be shown in three ways. Line Scale This consists of a line showing the relationship between distances on the map and the distances on the ground that they represent. With reference to the above metric line scale, answer the following questions. 1. A map distance of 2.0 cm represents a real distance of ___________. 2. A map distance of 5.9 cm represents a real distance of ___________. 3. A map distance of 68 mm represents a real distance of ___________. Statement Scale As the name suggests, the map scale is described as a statement of the relationship between the map distance and the actual distance it represents. e.g.: 1 cm represents 0.5km Rewrite the above line scale as a statement scale. Large and Small Scale Maps The purpose of the map will determine the scale of the map. For example, if the purpose of the map is to show the details of the urban environment on a street map, a large scale map is preferable. However, if the purpose of the map is to illustrate the global distribution of population, a small scale map is preferable. Scale of Map Large e.g.: 1:5 000 Small e.g.: 1:2 000 000 Area shown Small Large Page 1 Detail shown Lots of detail No detail Ratio Scale This consists of a ratio illustrating the relationship between map distance and the actual distance it represents. In what way does the ratio scale differ from the other two scales? The ratio scale or representative fraction indicates by how much reality has been "reduced" in order to fit on the map. I.e.: 1:50 000 (or 1/50 000) indicates that reality has been “reduced” 50 000 times to fit its representation on the page. Using the 1:50 000 map scale as an example, we will learn how to apply this scale to determine the ground distance from the map distance. 1: 50 000 refers to the map distance refers to the ground distance Below are two ways of calculating real life distances using a ratio as a scale: A. It is important to note that the same units are used on both sides of the ratio. For example 1:50 000 could mean 1cm on the map equals 50 000cm in real life. Using cm in real life to measure long distances is not practical. So simple convert the cm into Metres or Kilometres. Use the following to help you: 100cm = 1 metre; 1000m = 1km; therefore 10 000cm = 1 km. So by dividing by 10 000 or moving the decimal to the left 5 spaces - 1cm = 50 000cm becomes 1cm = .5km If you measure on your map a distance of 4.5cm the actual distance is 4.5 x .5 = 2.25km B. Measure the map distance between two points on the map. In order to maintain the same ratio between map and ground distance as expressed in the map scale, apply the distance measured from the map to both the left and right sides of the ratio, by multiplying both sides of the ratio by the map distance. Remember that the ground distance will be in the same units of measurement as the map distance. Usually ground distances are not expressed in centimetres or millimetres but rather in metres and kilometres, so you will have to convert the ground distance answer from cm to km for example. Page 2 e.g.: map scale 1:50 000 map distance measured = 4.5cm Method Write down the map scale Map distance Ground distance 1 : 50 000 Multiply both sides of the ratio by the 1 x 4.5 cm map measurement Write the answer in ratio format 4.5 cm Convert the ground distance into units 4.5 cm that express ground distance better 50 000 x 4.5 cm 225 000 cm 2.25 km OR 2, 250 metres Activity Use an Atlas to complete the following activities. 1. Refer to a map of Taiwan in your atlas. What is the straight line distance in kilometers between Taipei and Kao-hsiung? 2. With reference to a map of Canada’s Political Divisions, describe the map scale used and explain why this map scale was used. Page 3