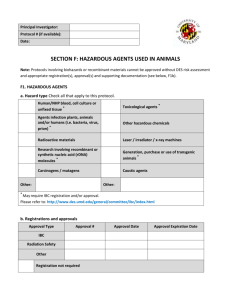
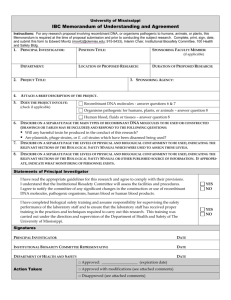
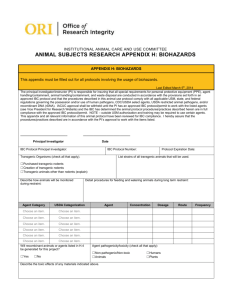
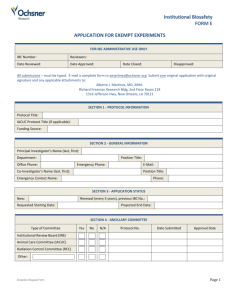
IBC USE ONLY - University of California, Irvine
advertisement

University of California, Irvine Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC) Modification Form IBC USE ONLY Biosafety Level Required: Date Received: IBC Approval # This form is to be used to request approval for modification(s) of previously approved IBC protocols. Modifications include changes in methods or procedures, location of research facilities, personnel, rDNA, or other biological materials. Changes must not be implemented until IBC approval is granted. E-mail the complete application to ibc@uci.edu. Fax or mail a signed copy of the Investigator’s Acknowledgment of Responsibilities to Fax (949) 824-1325 or 4600 Health Sciences Rd ZOT 2725 Principal Investigator: Phone: Fax: IBC Protocol # Project Title: UCI E-mail: MODIFICATIONS: Check all that apply Investigator contact information, Personnel, Location – complete Section A rDNA – complete Section B Generation of transgenic animals (including cross breeding, knock outs, breeding of two different strains) or other genetically animals - complete Section B-1 Generation of transgenic plants- complete Section B-2 Infectious Agents – complete Section C Whole animals (vertebrates vs invertebrates) – complete Section D Human/Primate Materials- complete Section E Biological Toxins – complete Section F Project Description 1. Explain how the requested modification(s) will affect the scope of work: a. In lay language, provide a one paragraph summary of your overall research objectives. b. Summarize the purpose and goals and anticipated outcomes c. Explain why and how specific agents are used. 2. Explain what precautions, decontamination, and disposal methods will be employed as a result of the modification. 3. Why should the new procedure(s) be a modification of the existing project rather than a new protocol submission? 4. Describe how personnel have been (or will be) trained in the handling of the new or changed material. Section A: Contact Information Change only: New Mailing Address: Telephone Last printed June 15, 2016 6:42:00 PM V6 7/09 Fax UCI e-mail address 1 New emergency number Personnel Action Complete the sections below only if you are adding personnel Name: Last, First UCI E-Mail e.g. anteater@uci.edu Position Title e.g. Staff researcher Add Delete Add Delete Add Delete EH&S training completed Bloodborne pathogens (BBP) (required annually) Laboratory Core and Hazardous Waste required every (3 years). Fulfills CalOSHA requirements Select Agents BBP Viral Vectors Hazardous Waste BSL-3 Laboratory Core Other: Select Agents BBP Viral Vectors Hazardous Waste BSL-3 Laboratory Core Other: Select Agents BBP Viral Vectors Hazardous Waste BSL-3 Laboratory Core Other: Add Delete Select Agents Hazardous Waste Other: BBP BSL-3 Viral Vectors Laboratory Core Occupational Health Requirements Check all that apply None Vaccine Hep B Respirator Other: None Vaccine Hep B Respirator Other: None Vaccine Hep B Respirator Other: None Hep B Other: Vaccine Respirator Location of Study Action Building: e.g. Hewitt Hall Room # e.g.103 Shared room or open bench space Add Delete Add Delete Add Delete Add Delete Bench No Yes, PI’s name: Bench No Yes, PI’s name: Bench No Yes, PI’s name: Bench No Yes, PI’s name: Room functions Check all that apply Bench work Agent storage Tissue culture Animal procedure room Other: Other: Bench work Agent storage Tissue culture Animal procedure room Other: Other: Bench work Agent storage Tissue culture Animal procedure room Other: Other: Bench work Agent storage Tissue culture Animal procedure room Other: Other: Aerosol containment control equipment Check all that apply Biosafety Level BSL1, BSL2, BSL2+, BSL3, or ABSL1, 2, 3, Fume hood Cert Date: Biosafety cabinet Cert Date: Glove box Cert Date: Sealed centrifuge cups Sealed rotors on centrifuge Fume hood Cert Date: Biosafety cabinet Cert Date: Glove box Cert Date: Sealed centrifuge cups Sealed rotors on centrifuge Fume hood Cert Date: Biosafety cabinet Cert Date: Glove box Cert Date: Sealed centrifuge cups Sealed rotors on centrifuge Fume hood Cert Date: Biosafety cabinet Cert Date: Glove box Cert Date: Sealed centrifuge cups Sealed rotors on centrifuge Section B rDNA Check one Addition of a new rDNA host – vector system and/or Change(s) to an approved rDNA host-vector system Identify the nature of the DNA sequence, Identify host (s) to be used: Example E. Identify the vector(s) to be used: Examples: coli, S. cerevisiae, human/animal cells, whole animals, humans. Last printed June 15, 2016 6:42:00 PM V6 7/09 Bacterial plasmids, yeast plasmids, cultured cell plasmid vectors, baculoviruses, transforming viruses 2 including the species of origin (i.e., specific gene, promoter, expressed product and function (if known). Will an attempt be made to purify any of the foreign gene product(s)? Yes No If yes, indicate which foreign gene product will be purified and describe the procedures for purification If replication-incompetent vectors will be used, explain how incompetent vectors will be tested for reversion mutations (e.g., endpoint dilution analysis, plaque assay). Change(s) to the experiments covered by NIH guidelines – SUMMARY OF EXPERIMENTS COVERED BY THE “NIH GUIDELINES” The NIH Guidelines can be found at http://oba.od.nih.gov/oba/index.html Mark the appropriate section(s) that describes this project. If experiment does not fall into any of these categories, contact Biosafety Office for assistance at extension 49888 (check all that apply): Appendix B of this application describes Risk Groups (RG). 1. III A....must receive approval from IBC, Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee, and NIH Director before initiation of experiments. III-A-1-a: The deliberate transfer of a drug resistance trait to microorganisms that are not known to acquire the trait naturally if such acquisition could compromise the use of the drug to control disease agents in humans, veterinary medicine, or agriculture. (Note that antibiotic resistance markers used for selecting and propagating plasmids in E. coli are not included.) 2. III B….must receive approval from NIH/OBA and IBC before initiation of experiments. III-B-1: Experiments involving the cloning of toxin molecules with LD50 of <100ng per kg body weight (e.g., microbial toxins such as botulinum toxin, tetanus toxin). 3. III C.....must receive approval from IBC, IRB, and RAC review before research participant enrollment. III-C-1: Experiments involving the deliberate transfer of rDNA, or DNA or RNA derived from rDNA, into one or more human research participants. NOTE: Attach response to Points to Consider under: Appendix M of the NIH Guidelines and submit any supplemental documents such as investigator brochure, clinical study, correspondence with NIH, etc 4. III D....must receive approval from IBC before initiation of experiments. III-D-1 Experiments using Risk Group 2, Risk Group 3, Risk Group 4, or Restricted Agents as host-vector systems III-D-2 Experiments in which DNA or RNA from Risk Group 2, Risk Group 3, Risk Group 4, or Restricted Agents is cloned into nonpathogenic prokaryotic or lower eukaryotic host-vector systems III-D-2-a Experiments in which DNA from RG- 2, RG- 3 agents, or RG-4 agents is transferred into nonpathogenic prokaryotes or lower eukaryotes. III-D-2-b Containment conditions for experiments in which DNA from restricted agents is transferred into nonpathogenic prokaryotes or lower eukaryotes shall be determined by NIH/OBA following a case-by-case review (see Section V-L, Footnotes and References of Sections I-IV). A U.S. Department of Agriculture permit is required for work with plant or animal pathogens (see Section V-G, Footnotes and References of Sections I-IV) III-D-3 Experiments involving the use of infectious DNA or RNA viruses or defective DNA or RNA viruses in the presence of helper virus in tissue culture systems (Section III-D-3) III-D-3-a Use of infectious or defective RG-2 viruses in the presence of helper virus. III-D-3-b Use of infectious or defective RG-3 viruses in the presence of helper virus may be conducted at BL3 containment. III-D-3-d Use of infectious or defective restricted poxviruses in the presence of helper virus shall be determined on a case-bycase basis following NIH/OBA review. A USDA permit is required for work with plant or animal pathogens. III-D-3-e Use of infectious or defective viruses in the presence of helper virus not covered in Sections III-D-3-a through III-D-3-d. Last printed June 15, 2016 6:42:00 PM V6 7/09 3 5. III D 4 III-D-4III-D-4-a III-D-4-b rDNA Involving Whole Animal Experiments involving whole animals in which the animal's genome has been altered by introduction of DNA or RNA into the germ line (transgenic animals) and experiments involving viable recombinant DNA-modified microorganisms tested on whole animals. rDNA, or DNA or RNA molecules derived therefrom, from any source except for greater than two-thirds of eukaryotic viral genome may be transferred to any non-human vertebrate or any invertebrate organism and propagated under conditions of physical containment comparable to BSL1 or BSL1-N and appropriate to the organism under study. Animals that contain sequences from viral vectors, which do not lead to transmissible infection either directly or indirectly as a result of complementation or recombination in animals, may be propagated under conditions of physical containment comparable to BSL1 or BSL1-N and appropriate to the organism under study. Experiments involving the introduction of other sequences from eukaryotic viral genomes into animals are covered under Section III-D-4-b. Investigator must demonstrate that the fraction of the viral genome being utilized does not lead to productive infection. Experiments involving rDNA, or DNA or RNA derived therefrom, involving whole animals, including transgenic animals, and not covered by Sections III-D-1 or III-D-4-a, may be conducted at the appropriate containment determined by the IBC. III-D-4-c-1 Experiments involving the generation of transgenic rodents that require BSL1 containment as described under Section III-E-3 III-D-4-c-2 Purchase or transfer of transgenic rodents that are exempt from the “NIH Guidelines” under Section III-F but must be registered with the IBC (Section III-D-4-c-2) III-D-6 Experiments involving more than 10 liters of culture. (The appropriate containment will be decided by the IBC. Where appropriate, Appendix K of the “NIH Guidelines” will be used to determine containment conditions.) 6. III E – Experiments that require IBC notice prior to initiation III-E-1 Experiments involving the formation of R-DNA molecules containing no more than 2/3 of the genome of any eukaryotic virus (all viruses from a single Family being considered identical) which may be propagated and maintained in cells in tissue culture using BL1 containment? (It must be shown that the cells lack helper virus for the specific Families of defective viruses used. The DNA may contain fragments of the genome of viruses from more than one Family but each fragment shall be less than two-thirds of a genome.) III-E-2-b-5 Experiments with recombinant DNA-modified arthropods or small animals associated with plants, or with arthropods or small animals with recombinant DNA-modified microorganisms associated with them if the recombinant DNA-modified microorganisms have no recognized potential for serious detrimental impact on managed or natural ecosystems. III-E-3 Experiments involving the generation of rodents in which the animal’s genome has been altered by stable introduction of recombinant DNA, or DNA derived therefrom, into the germ-line (transgenic rodents)? (Only experiments that require BL1 containment are covered under this section; experiments that require BL2, BL3, or BL4 containment are covered under Section III-D-4.) 7. III F – Experiments that are exempt from the NIH Guidelines but require submission prior to initiation III-F-1 Recombinant DNA molecules that are not in organisms or viruses III-F-2 Recombinant DNA molecules that consist entirely of DNA segments from a single nonchromosomal or viral DNA source, though one or more of the segments may be a synthetic equivalent III-F-3 Recombinant DNA molecules that consist entirely of DNA from a prokaryotic host including its indigenous plasmids or viruses when propagated only in that host (or a closely related strain of the same species) or when transferred to another host by well established physiological means. III-F-4 Recombinant DNA molecules that consist entirely of DNA from a eukaryotic host including its chloroplasts, mitochondria, or plasmids (but excluding viruses) when propagated only in that host (or closely related strain of the same species). III-F-5 Those that consist entirely of DNA segments from different species that exchange DNA by known physiological processes though one or more of the segments may be a synthetic equivalent. Last printed June 15, 2016 6:42:00 PM V6 7/09 4 III-F-6 Those that do not present a significant risk to health or the environment as determined by the NIH Director, with the advice of the RAC, and following appropriate notice and opportunity for public comment. ADDENDUM B-1 Use and Creation of Transgenic or Genetically Modified Animals 1. Yes No Are you creating a new strain of genetically engineered (e.g transgenic or knock out) animals? This includes cross breeding two strains of genetically engineered animals. 2. If "Yes", please describe (procedure and technique) how the transgenic animal will be created. 2a. If the animal is created by use of viral vectors, describe the vector and promoter. 3. Provide the gene name and function 4. Provide a description of the possible hazards associated with the alteration 5. Yes No Has the source animal already been genetically modified? If yes, describe the genetic modification(s) 6. Yes No Is the transgenic/knockout line created at the UCI Transgenic Core Facility? If no, provide an alternate facility location. 7. Yes followed. No Does the transgenic animal pose a potential hazard to animal caregivers? If yes, describe the precautions that must be ADDENDUM B-2 Use and Creation of Transgenic or Genetically Modified Plants. 1. What is the source of the material: PI laboratory Collaborator at UCI Provide PI name: Outside of UCI: Provide name: 2. Yes No Have you received authorization from the appropriate federal, state, and local regulatory agencies to acquire these materials? 3. List all applicable authorizing agencies: 4. Describe how the transgenic plant is constructed (check and describe all that apply): Yes No Agrobacterium: Yes No Rhizobium: Yes No Electroporation : Yes No Microprojectile bombardment : Yes No Viral directed transformation or viral infection : Yes No Other : SUMMARY OF EXPERIMENTS COVERED BY THE NIH GUIDELINES SECTION VIII FOR RESEARCH INVOLVING RECOMBINANT DNA (rDNA) IN PLANTS Mark the appropriate section(s) that describes this project. III D....must receive approval from IBC before initiation of experiments. III-D-5 Experiments involving whole plants Last printed June 15, 2016 6:42:00 PM V6 7/09 5 III-D-5-a BL3-P (Plants) or BL2-P + biological containment which is recommended for experiments involving most exotic (see Section V-M, Footnotes and References of Sections I-IV) infectious agents with recognized potential for serious detrimental impact on managed or natural ecosystems when recombinant DNA techniques are associated with whole plants (Section III-D-5-a) III-D-5-b BL3-P or BL2-P + biological containment which is recommended for experiments involving plants containing cloned genomes of readily transmissible exotic infectious agents with recognized potential for serious detrimental effects on managed or natural ecosystems in which there exists the possibility of reconstituting the complete and functional genome of the infectious agent by genomic complementation in planta III-D-5-d BL3-P containment is recommended for experiments involving sequences encoding potent vertebrate toxins introduced into plants or associated organisms (also refer to Section III-B-1) III-D-5-e BL3-P or BL2-P + biological containment is recommended for experiments with microbial pathogens of insects or small animals associated with plants if the rDNA-modified organism has a recognized potential for serious detrimental impact on managed or natural ecosystems III E …..Experiments that require IBC notice prior to initiation III-E-2 Experiments involving R-DNA-modified whole plants, and/or experiments involving R-DNA-modified organisms associated with plants, except those that fall under Section III-A, III-B, III-C, III-D, and III-F? (See Section III-E-2 for recommendation of containment levels.) III-E-2-a BL1-P which is recommended for all experiments with recombinant DNA-containing plants and plant-associated microorganisms not covered in Section III-E-2-b or other sections of the NIH Guidelines? Examples of such experiments are those involving recombinant DNA-modified plants that are not noxious weeds or cannot interbreed with noxious weeds in the immediate geographic area, and experiments involving whole plants and recombinant DNA-modified non-exotic (see Section V-M, Footnotes and References of Sections I-IV) microorganisms that have no recognized potential for rapid and widespread dissemination or for serious detrimental impact on managed or natural ecosystems (e.g., Rhizobium spp. and Agrobacterium spp.) III-E-2-b BL2-P or BL1-P + biological containment is recommended for the following experiments: III-E-2-b – (1) Plants modified by rDNA that are noxious weeds or can interbreed with noxious weeds in the immediate geographic area. III-E-2-b – (2) Plants in which the introduced DNA represents the complete genome of a non-exotic infectious agent. III-E-2-b – (3) Plants associated with rDNA-modified non-exotic microorganisms that have a recognized potential for serious detrimental impact on managed or natural ecosystems. III-E-2-b – (4) Plants associated with rDNA-modified exotic microorganisms that have no recognized potential for serious detrimental impact on managed or natural ecosystems Section C Infectious Agents Agent (Adenovirus) Risk Group RG2 Biosafety Level (BSL1-4) BSL2 Building Med Sci C Room Number 123 Room Use (experiment, storage or both) Section D Whole animals (vertebrates vs invertebrates) Biological Materials used (Infectious agents, vectors, or human cell lines used in live animals?) e.g. MLV retrovirus Animal species e.g. Mice Max infectious units/dose e.g.10^8 ml Last printed June 15, 2016 6:42:00 PM V6 7/09 Max dose per animal e.g. 5 Method of delivery: e.g Intravenous, Intranasal, Subcutaneous, Intramuscular 6 Specify route(s) of shedding/excretion of infectious agents: e.g. Urine, Feces, Saliva, Blood, Unknown Please explain the measures your lab will take to prevent accidental exposure to Section E Human Material Material – List each material per line e.g. Established cell line Type e.g. HEK Source e.g. Human Origin of materials Check all that apply Clinical specimens Known Pathogens e.g. None Building e.g. Med Sci Room Number e.g.123 Commercial vendor Clinical specimens Field Primate center None Other Commercial vendor Clinical specimens Field Primate center None Other Commercial vendor Clinical specimen Field Primate center None Other Section F Biological ToxinS Toxin Building Room # Room Used Amount Purchased (experiment, storage, or both) Physical stage of agent Beginning concentration Final concentration use 1. Describe the type of work being done with Toxin(s) listed above (1-2 sentences only) 2. Describe the dilution procedures. 3. Describe safe handling and disposal procedures that will be used for this toxin. Acknowledgement of Responsibilities I attest that the information contained in this IBC modification is accurate and complete. I agree to comply with all requirements pertaining to the use, handling, storage and disposal of biohazardous agents and recombinant DNA molecules as outlined in my approved IBC protocol and this modification request. Typed Name of Principal Investigator Signature of Principal Investigator Approval for inclusion of this modification into the referenced protocol has been granted by the IBC Signature of IBC Chair or designee Last printed June 15, 2016 6:42:00 PM V6 7/09 Date 7 Date