Learning Guide: Origins of Life
advertisement

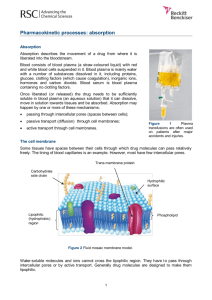
Learning Guide: The Cell Membrane and Passive Transport Bill Activity #24 To Think About: How is growth and dynamic homeostasis maintained by the constant movement of molecules across membranes? 1st Read About: Membrane structure and function Pgs. 125-130 Campbell’s Biology 9th edition (2-sided column notes) Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins o Describe why the cell membrane exhibits selective permeability o Explain why a phospholipid is considered amphipathic (use a sketch in your answer). o Describe the fluidity of cell membranes. o Using the components of the cell membrane, explain why the cell membrane is referred to as a “fluid mosaic model”. Describe how each of the following can affect membrane fluidity: a) decreasing temperature, b) phospholipids with unsaturatured hydrocarbon chains, c) cholesterol o Explain using an example how variations in the cell membrane lipid compositions can be an evolutionary adaptation o Membrane proteins are the mosaic part of the model. Describe each of the two main categories: integral proteins and peripheral proteins. o Membrane carbohydrates are important in cell-cell recognition. What are two examples of this? o Distinguish between glycolipids and glycoproteins. 2nd Interact: Watch Mr. Andersen’s 015 Cell Membranes Video. Take notes in your bill. o In the context of cell membranes, explain why Mr. Andersen uses shampoo as a chemical component in his DNA extraction experiment. 3rd Read About: Membrane structure results in selective permeability o Pgs. 131-135 Campbell’s Biology 9th edition (2-sided column notes) o Explain how the biological membrane is an example of a supramolecular structure. Include an explanation of the cell membrane’s most important function. Sketch a muscle cell and show all of its chemical exchanges with labeled arrows to further enhance your answer. The permeability of the lipid bilayer. o Create the two column table with the headings (material and method). Consider the following materials that must cross the membrane. For each tell how it is accomplished: carbon dioxide, glucose, H+, oxygen, water o Describe the structure and function of transport proteins. Passive transport is diffusion of a substance across a membrane with no energy investment o Define and take notes on the following terms as you read: diffusion, concentration gradient, passive transport o Describe how water diffuses across the membrane. Name this movement. o Sketch animal cells and plant cells in three types of solutions. Label the solution types, and their effects on the cells. Take notes about these cell conditions as you read. o Define osmoregulation and P. caudatum’s evolutionary adaptation. o Define facilitated diffusion. Is it active or passive transport? Cite two examples. 4th Interact: Watch Mr. Andersen’s 016 Transport Across Cell Membranes Video. Take notes on the video . Supplementary Resources: Click the links below for more information to help you learn more about this lesson. BFW Publishers: Principles of Life Chapter 5 Online Resources Crash Course Biology: In Da Club—Membranes and Transport Pearson BioCoach: Membrane Structure and Transport Pearson BioCoach: Membranes and Communication McGraw Hill: Osmosis Georgia State University Hyperphysics: Diffusion and Osmosis (from a physicist’s point of view) Wisc-Online: Passive Transport-Osmosis (simulation) Northland College: Active Transport Animation Learn More: For more information about membrane structure and function, use the links below: OsyOsmosis: A game that allows you to control a character, Osy, by controlling how much water she takes up from her environment Nobel Prize in Chemistry, 2003: Peter Agre and Roderick MacKinnon, “for discoveries concerning channels in cell membranes.”