215-Direct-Antiglobu.. - The Indian Immunohematology Initiative
advertisement

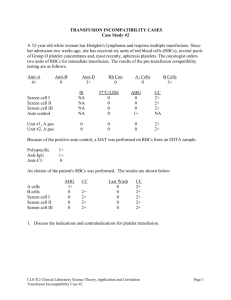
Procedure number: 215 Page 1 of 3 (Blood Bank Name and address) Subject: Direct Antiglobulin Test DIRECT ANTIGLOBULIN TEST PURPOSE To detect IgG or complement components (C') bound to RBCs ("sensitized red cells") in vivo. PRINCIPLE Anti-human globulin serum (AHG) recognizes IgG and/or C' determinates bound to red cells as antigen and agglutinates RBCs sensitized with them. In the direct antiglobulin test washed RBCs are tested against AHG to determine if such sensitization exists. Polyspecific AHG is directed against both human IgG and complement, and is the most sensitive reagent for detecting RBC sensitization. Alternatively, monospecific antisera may be used which detect only IgG or C3. When a DAT is requested, initial testing is with polyspecific AHG. If this is positive it is repeated with both monospecific reagents. In vivo sensitization of red cells by antibody or complement components may occur in the following situations: 1. Hemolytic disease of the fetus or newborn 2. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia or benign autoantibodies 3. Drug-related antibodies sensitizing RBCs 4. Hemolytic transfusion reactions and delayed serologic transfusion reactions 5. Passive transfer of blood group antibodies (e.g. by transfusion of group O platelets to a group A person, maternal RhIG bound to cord RBCs, treatment with IVIG or RhIG for ITP) 6. Passive adsorption of antibody not directed against RBCs in patients with polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia (e.g. patients with renal failure or HIV infection). The presence of human serum in a cell suspension will neutralize the AHG resulting in false negative reactions. Therefore, prior to the addition of AHG, the RBC suspension must be washed repeatedly with saline to remove all serum (see procedure #202). Proper and complete washing is verified by the addition of IgG-coated Coombs control cells ("check cells") to all negative AHG reactions. A DAT is performed when ordered by a physician and as part of cord blood testing (see procedure #224), a transfusion reaction workup, and antibody identification (see procedure #221). POLICY For adult patients, if the DAT is positive with polyspecific AHG, it is repeated with anti-IgG and anti-C3 as a "reflex" test. This is not necessary for positive cord blood DATs. MATERIALS AND SPECIMENS See General Guidelines for serologic testing, procedure # 201 EDTA anticoagulated blood (lavender top) is the preferred specimen for a DAT. However, if the specimen is submitted in a clotted (red top) tube, the DAT can still be performed. In the latter case the reaction with anti=IgG is valid if there is a negative control. Anti-C’3 may produce false-positive reactions due to in vitro complement fixation. Immunohematologic Problem Worksheet, appendix 221.1 or other patient worksheet. Procedure number: 215 Page 2 of 3 (Blood Bank Name and address) Subject: Direct Antiglobulin Test PROCEDURE 1. Prepare a washed 3-5% red cell suspension of the RBCs to be tested. 2. Properly label a 10x75 or l2x75 mm test tube with patient identifier and “DAT”. 3. Add one drop of the cell suspension to the test tube and wash 4 times with saline. 4. Add 1 or 2 drops of polyspecific AHG serum to the test tube according to the manufacturer’s instructions. 5. Mix and centrifuge at the appropriate speed and time for the serofuge in use. 6. Examine the tube for agglutination. If the reaction appears equivocal or mixed field macroscopically, examine it microscopically. Record the results on an appropriate patient worksheet. 7. Add one drop of Coombs control cell (“check cells”) to any tube showing a negative test. Centrifuge at the appropriate speed and time and examine for agglutination. Record the results. 8. If the DAT is positive with polyspecific AHG, for all but cord blood workups, repeat the test with monospecific reagents as below. Procedure using Monospecific Anti-IgG and Anti-C3 1. Properly label 10x75 or l2x75 mm test tubes with patient identifier and "IgG" and "C3". 2. Add one drop of the red cell suspension to each tube and wash 4 times with saline. 3. Add 1 or 2 drops of anti-IgG to the tube marked "IgG" and 1 or 2 drops of anti-C3 to the tube marked "C3" each according to the manufacturer’s instructions. 4. Mix and centrifuge at the appropriate speed and time for the serofuge in use. 5. Examine the tubes for agglutination. If a reaction appears equivocal or mixed field macroscopically, examine it microscopically. Record the results. 6. Add one drop of check cells as appropriate to any tube(s) with a negative reaction. Centrifuge and examine for agglutination. Record the results. Procedure number: 215 Page 3 of 3 (Blood Bank Name and address) Subject: Direct Antiglobulin Test INTERPRETATION A negative DAT is invalid if the Coombs control cells (“check cells”) are non-reactive. Reasons for a negative reaction with check cells include: A. Incomplete washing so that remaining serum neutralized the AHG serum added. B. Failure to add AHG serum to the test. C. Improper function of the AHG serum. POLYSPEC AHG ANTI-IgG ANTI-C3 0 INTERPRETATION Negative (no repeat with monospecific reagents) + + 0 Positive reaction due to IgG coated RBCs. Seen in HDN, WAIHA, some drug antibodies, passively acquired ABO antibodies. + 0 + Positive reaction due to complement coated RBCs. Seen with cold agglutinins (common) and some drug antibodies + + + Positive reaction due to IgG and C' coated RBCs. May be seen in WAIHA and some drug antibodies. mf mf mf or 0 Positive reaction due to IgG coating of one RBC population. Classically associated with a delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction. The investigation of a positive DAT is discussed in procedure #222. Adopted Reviewed Reviewed Reviewed Reviewed Reviewed Reviewed Reviewed Reviewed Reviewed Reviewed Reviewed