Palaeontology Notes
advertisement

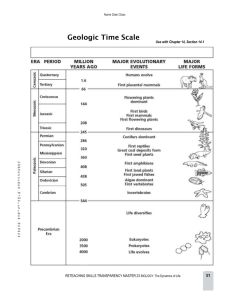
Paleontology & Earth History Notes •The Earth is over years old •This huge amount of time is broken up into smaller ‘chunks’… They are: • : the largest- measure 100’s of millions & billions • : measured in tens of millions of years • : measured in millions of years • are the smallestmeasured in thousands of years How is “Time” recorded? •The divisions are created by what’s found in the rock record- Name this organism: •As one kind of life form ends, adapts or Name the PHYLUM: changes, a of time begins •To understand how life forms are different we look at or the physical structure of that organism •We life based on physiology •The system of classification is called •Organisms are given scientific names based on a system called Taxonomy • • • Name this organism: Name the PHYLUM: • • • • • Domain Simply put: • Name this organism: • Name the PHYLUM: • Kingdoms • (AKA Metazoa; multi-cellular; feed, move, reproduce, eukaryotic; heterotophic) • (specialized eukaryote; heterotophic; necrophyte; multicellular filamentous) • (small, simple; can form chains or mats; prokaryotes (no membrane around nucleus) • (autotrophic; multicellular; specialized eukaryotic cells; no means of locomotion) • (unicellular; large, single eukaryote; some form chains or colonies) Phylum- simplified list • Snails, clams (bivalves), Abalone, squid, octopus, cuttlefish • Corals, sea anemones, jellyfish • Segmented worms (of which there are about 9,000 species) • Means “jointed leg”; Insects (ants, bees, etc.), crustaceans (shrimp); arachnids • Anything with a backbone/ vertebrae; notochord Cnidaria: Hydra, Sea Anemone & Jellyfish Annelida: Leech, Vermiform, Earthworm Arthropoda: Insect, Crustacean, Arachnid Chordata: Sea Lamprey, Ape, Snake Class •There are at least 80 different classes in taxonomy… Human lineage •Kingdom = •Class = •Order = Name this organism: •Family = Name the PHYLUM: •Genus = •Species = Binomial Nomenclature Carolus Linnaeus 23 May - 10 January The of Nomenclature Part I Eon: What is this? Eras: Periods: Precambrian Aeon billion – million years ago •Its name means " " •All geologic time before the beginning of the era •This includes about geologic time % of all Who is this? •Covers the time from the of the earth Hadean Era to million years ago •The Precambrian subdivision of the •This interval predates true time since known on earth of this age are •Formation of the and of •Earth is in a state What is this? •Earth bombarded by /planetesimals •Formation of the •Primal starts to form with organic amino acids • No in the Planetesimal bombardment DNA- Deoxyribonucleic Acid Early Earth: Hadean Era •Our satellite, formed from debris , was •At this time our day was hours long not 24 hours • were constant What is this? -speed winds •The moon was from earth miles •Tides were over 3 billion years ago feet even •The moon is moving away at about inches per year- today it is ~250,000 miles away Archaean Era . to million years ago •Its name means " •The middle " of Precambrian time •Permanent similar to today • First signs of as sediment begin to accumulate in the •Life on earth indicated by the appearance of fossil ( or blue-green algae) in rocks about 3.5 billion years old • , single-celled organisms with no distinct organs are present Cyanobacteria AKA: Blue-Green Algae produces oxygen ( ) Proterozoic Era million – million •Its name means " " •The final era of the Precambrian Aeon •Fossils of primitive •Also more advanced multi-cellular organisms ( latter part of this era ) found in the Other Prokaryotic organisms include and Primitive Prokaryotes eventually adapted into Eukaryotes Sturtian Period million – million •Very little is known about this time •AKA: Period (from Greek cryos “ • ” and genesis “ ”) lasted for the entire period •The name derived from glacial deposits •The Earth suffered the most severe ice ages ever •Glaciers extended to the •Extensive glaciers led to the hypothesis of the deeply-frozen planetary oceans called " " •Boulders dropped by laminated marine sediment in Namibia gives credence to theory into Period million - million years ago •AKA: •The Proterozoic era period of the •Distinguished by representing complex soft-bodied organisms •Mounds of algae form structures called considered to be the first fossils & What are these? • creates oxygen which kills off many early organisms •Some simple fossils •First (Greek for “stinging nettle”) •Cnidarians have stinging cells called •Possibly precursors to first • Possibly some also present What are these? Part II Aeon: Era: Periods: Phanerozoic Aeon million years ago •Means “ ” •Though it only represents about % of earth her/history it is arguably the most interesting •Virtually found during this time Paleozoic Era million – million •The word Paleozoic is from Greek and means “ ” •Fossil shows first shellfish, fish, plants, insects, spiders, amphibians, and reptiles Cambrian Period million – million •AKA: “Age of Marine •It is named after ” , the Roman name for •The •Major formation of period of the Paleozoic era rock Period this depicts? •Continents are & with shallow • climate just about world-wide •“North America” is •Originally thought to be the first ‘explosion’ of •Shelled ( organisms in oceans ) Hallucigenia •Every invertebrate represented •Early sponges called present • are abundant • abundant •First active / •Some (“long foot”) •Simple (“spiny skin”) Name this creature: ancestors of •Possibly some early sea lilies or •Early or snails found (“stomach-foot”) •A few simple like pikaia vertebrates •Mass oldest trilobites including Early Cambrian Earth Cambrian than fiction! - Stranger Hallucigenia sparsa is less than cm long and really bizarre! Phylum: Name this creature: Common early Cambrian predatory invertebrates: A. , ranging from 2.5 to 19 mm long B. , 43 to 70 mm long C. Sidneyia, another Cambrian D. Two species of Anomalocaris; the biggest specimens are estimated to have been nearly 2 ft long – Name this creature: of early Cambrian animals Many of the Paleozoic fossils were discovered by Charles D. March 31, - February 9 in a layer of rock called the Shale near British Columbia, Canada He and four others collected over fossils in Early Archaeocyathid Modern Sponges haven’t much in millions of years Who is this? - Wisconsin’s State Fossil Mass Extinction •Trilobites were quite abundant in the Cambrian and most went •There were by the end of this period mass extinctions in the Cambrian •Several theories try to explain these events •The depletion theory states that cold water from deep in the ocean rose to the upper levels chilling and starving life into extinction •Some global warming phenomenon in the near future warn of the same What is this? Ordovician Period 505 million – 440 million •It is named after a Celtic tribe called the •The second earliest period of the •Seas over era Hemisphere at greatest extent •Rocks are mostly •Mature marine ecosystems develop with some deep-water life but most of life centers around What is this? •Super-continent called Gondwana in southern hemisphere shifts toward south pole •North America, Europe and Africa colliding forming first •Massive glaciers dropped cause mass extinction ; • (“moss-animals”) are present • saw blades - whose fossils look like •Many over 19 ft long present- some •Fish with present (early backbones) • and other sea life widespread •Some plant •Mass extinction of have been found % of all marine invertebrate genera (genus) and all families % of •Possible reasons for extinction are cooling of ocean and/or oxygen depletion •The Ordovician extinction occurred about million years ago What is this? •This extinction is cited as the most devastating extinction to marine communities in earth history •Disappearance of & bryozoan families of all brachiopod •Also numerous groups of , trilobites, and graptolites disappeared from the fossil record •Much of the reef-building decimated was also •In total, more than families of marine invertebrates perished in this extinction •Ordovician life include smaller invertebrates preying on •Cephalopods belong to the phylum What is this? •Some had straight shells and others coiled Silurian Period million – million •It is named after a the Silures tribe called •Earth continues its global temps stabilize •Sea levels climate as to previous levels •Mountains forming in •Most of the world’s deposits occur (halite) What is this? •Proof of earliest •Extensive present • spread rapidly throughout fossil record •First fish with jaws as well as the first What is this? • (sea lilies) abundant • widespread • , conodonts, corals, stromatoporoids and mollusks common •Land being invaded by arthropods like relatives of (arachnids) & centipedes •Earliest plants (plants with xylem and phloem; ferns) found in southern hemisphere •Most common plants belong to genus Cooksonia; Controversial Baragwanathia (type of advanced vascular plant called a ) found in Australia • Modern (ascomycete fossils) and Xylem & Phloem are tubes to carry nutrition and water to the leaves carries water Phloem carries food These are characteristics of plants Devonian Period million – million •Named after Devonshire, •AKA: “Age of dominant life form ” as fish •Extensive U. S. & Canada in eastern •Continents are becoming •Europe and North America near equator •South Pole located in Central • fish (ostracoderms) • Dunklosteous of huge size- like • (a group still around today) What is this? •First (Sarcopterygii) -finned fish •Brachiopods, echinoderms, flourish •Near the end of Devonianfirst • (four legged) on land; closely related to lungfish and amphibians •Psilotophyta (giant southern hemisphere What is this? ) in • plants now in northern hemisphere- only one meter tall •First seed plants ( ) •Mass extinction where nearly % of life disappeared What is this? Why is it important? •The first rays are Chondrichthyes (“cartilaginous fish”) along with sharks and skates • were a major advancement for life on land •They could travel on land but needed to be near What is this? at all times Carboniferous Period million – million •‘Carboniferous’ refers to the large deposits •AKA: “Age of ” •Includes the Mississippian (Lower Carboniferous) & Pennsylvanian (Upper Carboniferous) periods •The earth’s climate is still •Less seasonal variation of •Great earth’s lowlands cover much of What kind of eggs? •Orogeny in eastern US ( ), Texas, Colorado, Britain (Hercynian Mountains), also in Eastern Europe/ Siberia (Ural Mountains) •Laurussia (Europe & North America) collides with Godwanaland (Africa & South America) •Two massive the South Pole cover • number & diversity reach greatest •Giant are diverse •First Carboniferous appear in the late • egg allowed tetrapods to lay eggs away from water •Earliest amniote fossil Hylonomus What is this? -like •Other tetrapods include Amphibiamus (type of Temnospondyl), Anthracosaurs • (includes most reptiles except turtles; dinosaurs; birds) • Dimetrodon) (precursors to mammals, •First land • What kind of egg? are abundant •Great forests of ferns, (seed-bearing plants), horsetails •Freshwater appear •Heavily armored fish from Devonian What is this?