13_light - sacss-science
advertisement

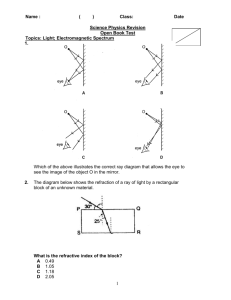
Name: ( ) Class: Date: Sec 4E Topical Revision – Light 1. Which of the above illustrates the correct ray diagram that allows the eye to see the image of the object O in the mirror. ( ) 2. The image produced by a plane mirror is not A B C D 3. laterally inverted. real. the same size as the object. upright. ) An observer looks straight through a rectangular glass block at an object P, as shown below. How does the object appear to the observer? observer A diminished 4. ( 90o P B further C magnified D nearer ( ) ( ) The position of John and an object is as shown in the diagram below. At which point would the object appear to John? A D B C Mirror Object John 1 5. The diagrams show the passage of light through glass blocks. Which diagram is correct? ( 6. An optician’s test card is placed a distance behind a man who is standing 3.5 m away from a plane mirror. The distance from the man’s eyes to the image of the test card is 8.5 m. What is the distance of the test card from the man? A 1.5 m 7. ) B 3.0 m C 3.5 m ( D 5.0 m ) The diagram shows a pin P placed in front of a mirror and its image I. The lines drawn show the reflected rays from the pin. Which one of the lines has been wrongly drawn? I A B P C D ( ) 2 8. Red light travelling in glass strikes a glass-air boundary. Some light is reflected and some is refracted. Which diagram correctly shows the reflection and refraction? ( 9. The number 9 was drawn on a piece of paper which was placed in front of a plane mirror, as shown in the diagram. How would the image seen in the mirror appear? A B 10. 20° B 40° 1.5 x 108 m/s 3.0 x 108 m/s ( ) C 50° D 80° ( ) B D 2.0 x 108 m/s 4.5 x 108 m/s (( )) ( ) An object is placed 50 cm from a converging lens of focal length 20 cm. The image formed by the lens is A real, diminished and inverted. B real, magnified and inverted. 13. D Given that the refractive index of the glass block is 1.5, what is the speed of the light ray as it travels through the glass block? [Given: Speed of light in air = 3 x 108m/s] A C 12. C The figure below shows a ray of light incident on a plane mirror M1 at 40°. What is the angle of reflection, r, at mirror M2? A 11. ) C D virtual, diminished and upright. virtual, magnified and upright. Which of the following device does not make use of electromagnetic waves in its operation ? A. C. A camera A television set B. D. A radio set A loudspeaker ( ) 3 14. Which of the following statement is false about electromagnetic waves? A Only high frequency electromagnetic waves transfer energy from one place to another. B The higher the frequency of a wave, it’s frequency becomes lower. C Electromagnetic waves obey the laws of reflection. D Electromagnetic waves can travel through vacuum. ( ) 15. The ray diagram shows the formation of a real image by a converging lens. lens image object scale 2cm What is the focal length of the lens? A 16. 3 cm 4 cm C 7 cm D 12 cm ( ) The diagram shows the action of a converging lens. Which statement best describes the image formed. A. C. 17. B It is real, erect and magnified. It is real, inverted and magnified. B. D. It is real, erect and diminished. It is virtual, inverted and magnified. ( ) The image of an object formed is smaller than the object when the object is placed 25 cm from a converging lens. Placed at a distance of 23 cm, the image of the object becomes slightly bigger than the object. What is the approximate focal length of the lens? A. 2 cm B. 6 cm C. 12 cm D. 24 cm ( ) 4 18. Infra-red, Ultraviolet and Radiowaves are part of the electromagnetic spectrum. What is the correct order of increasing frequency? Lowest frequency A B C D 19. Infra-red Ultraviolet Infra-red Ultraviolet Radiowaves Radio waves Ultraviolet Infra-red ( ) ( ) Which of the following is correctly matched? A. B. C. D. 20. Ultraviolet Infra-red Radio waves Radio waves highest frequency Shortest wavelength visible light X-rays gamma rays ultraviolet rays Longest wavelength gamma rays ultraviolet rays radio waves infrared radiation Which ray below shown passing through a convex lens is correct? A B C D ( ) 21. The diagram below shows the refraction of a ray of light by a rectangular plastic block. (a) Calculate the (i) refractive index and (ii) critical angle of the glass block. (b) What happens if a ray of light from the glass makes an angle of incidence that is greater than the critical angle? 5 22 (a) The diagram below shows the position I of the image formed by a plane mirror of an object O. Continue the two rays drawn leaving O to show how they would be reflected at the mirror to form the image at I. (b) Is the image produced real or virtual? Explain your answer. …………………………………………………………………………………………………… 23. The figure below shows the scale drawing of an image I found near a converging lens L. F is the focal length of the lens. L F F I On the diagram, draw two rays from the top of the image through the lens. Use the rays to find the position of the object. Draw the object and label it O. 24. An object in the shape of an arrow is 2 cm high is placed 4 cm in front of a converging lens. The focal length of the lens is 6 cm. Draw a full scale diagram (on a separate paper) to show how the image of the object is formed by the lens. 6