YouDoNotHaveToHaveHIV
advertisement

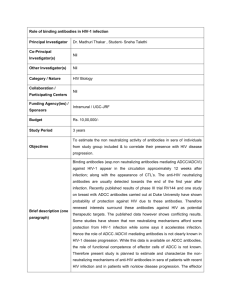
You Don't Need to Have HIV to Test HIV Positive Factors known to cause false-positive HIV antibody test results: Anti-carbohydrate antibodies Naturally-occurring antibodies Passive immunization: receipt of gamma globulin or immune globulin (as prophylaxis against infection which contains antibodies) Leprosy Tuberculosis DID YOU KNOW? Mycobacterium avium Systemic lupus erythematosus No HIV test that Renal (kidney) failure Hemodialysis/renal failure Alpha interferon therapy in hemodialysis patients claims to diagnose Flu actual infection has Flu vaccination ever been approved by Herpes simplex I the FDA. Herpes simplex II Upper respiratory tract infection (cold or flu) No HIV test can Recent viral infection or exposure to viral vaccines determine if you have Pregnancy Malaria HIV specific Hepatitis antibodies or the Blood transfusions actual virus. Normal human ribonucleoproteins Other retroviruses No HIV test has ever Anti-microsomal antibodies been validated by the Stevens-Johnson syndrome High levels of circulating immune complexes direct finding of HIV Hypergammaglobulinemia (high levels of antibodies) in any human being False positives on other tests, including RPR (rapid plasma reagent) test for syphilis Rheumatoid arthritis No exposure to HIV is Hepatitis B vaccination necessary in order to Tetanus vaccination test HIV positive. Organ transplantation Renal transplantation Anti-lymphocyte antibodies Anti-collagen antibodies (found in gay men, hemophiliacs, Africans and people with leprosy) Serum-positive for rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibody (both found in rheumatoid arthritis and other autoantibodies) AntiAutoimmune diseases Malignant neoplasms (cancers) Anti-nuclear antibodies Anti-hepatitis A IgM (antibody) Proteins on the filter paper Anti-Hbc IgM Epstein-Barr virus Administration of human immunoglobulin pooled Visceral leishmaniasis before 1985 Anti-mitochondrial antibodies Hemophilia Hyperbilirubinemia Hematologic malignant disorders and lymphoma Cross reactions in healthy individuals Primary biliary cirrhosis Alcoholic hepatitis/alcoholic liver disease Q-fever with associated hepatitis Primary sclerosing cholangitis Heat-treated specimens "Sticky" blood (in Africans) Lipemic serum (blood with high levels of fat or lipids) Antibodies with a high affinity for polystyrene (used in the test kits) Hemolyzed serum (hemoglobin separated from red Multiple myeloma cells) HLA antibodies (to Class I and II leukocyte antigens) Globulins produced during polyclonal gammopathies in Anti-smooth muscle antibody AIDS risk groups) Anti-parietal cell antibody Non-viral l proteins passed through sexual activity References: http://www.virusmyth.net/aids/data/cjtestfp.htm