WIDS
advertisement

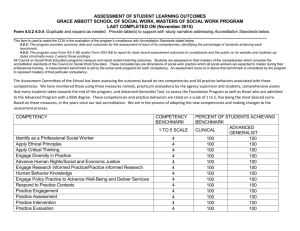
Learning Plan 1 WIDS Model and Performance Based Learning Information Overview When you design learning experiences, you need strategies and tools. The WIDS Model gives you both. WIDS is a performance-based learning model that addresses the WHO, WHAT, WHEN, and HOW of learning and assessment. In this learning plan you will be introduced to the WIDS model and build the foundation for a performance-based learning and assessment plan for your own course offerings. Target Competencies Apply the features of performance-based learning to your specific curriculum development project. Linked Core Abilities Think critically and creatively You will demonstrate your competence: o by constructing a foundation for a performance-based framework that will be filled in throughout this training. Your performance will be successful when: o foundation describes the target population of students. o foundation includes a program map with courses or modules of instruction indicated. o foundation lists the topics included in at least one module or unit of instruction. Learning Objectives a. Examine the WIDS model b. Identify the terminology associated with the WIDS model c. Identify characteristics of the students you expect to enroll in your program d. Identify your strengths and weakness as a teacher in reference to delivering a performancebased learning experience Apply the features of performance based learning to communication with your students Linked Core Abilities Think critically and creatively You will demonstrate your competence: o by writing a short paragraph that explains criterion-based grading using the features of performance-based learning. Your performance will be successful when: o paragraph is brief and easy to understand. o paragraph avoids or explains jargon. o paragraph targets students as the audience. o paragraph explains that students will be given competencies and performance standards at the beginning of the or unit of instruction. o paragraph explains that students are not measured against the performance of other students, but graded according to how well they perform the competencies. o paragraph explains that students must achieve all competencies at a minimum level to pass the course. o paragraph explains that assessment focuses on the competencies. Learning Objectives a. Describe the essential features of performance-based learning b. Identify the advantages and disadvantages of performance-based learning for the student and instructor Learning Activities _____1. _____2. _____3. _____4. _____5. _____6. VIEW the Instructional Design System Overview presentation. COMPLETE the WIDS Bulls-eye VIEW the performance-based learning presentation. FOLLOW ALONG with the information under the first tab of the training manual. CONSIDER your own teaching style. REVIEW the chart on page 3 that compares performance based learning to the traditional model of teaching. COMPLETE the Teaching and Learning Analysis activity sheet. DISCUSS with the group any insights you'd like to share. THINK ABOUT this training and what you would like to achieve from it. COMPLETE the workshop goals activity sheet (Practice Handout 1.1) Assessment Activities _____1. _____2. WRITE a short paragraph to your students explaining criterion-referenced grading. Use Assessment Sheet 1.1 FILL IN information for foundation of framework for description of target population (who are your students), and courses or modules / units that make up your program. Use Assessment Sheet 1.2 Instructional Design System The WIDS Model *What is an Instructional Design System? An instructional design system, or IDS, is a framework to facilitate teaching and learning that can be applied to a body of knowledge or subject area. The system includes everything from the “what” you will be teaching, to the “how” you will teach it, to the how you will “assess” whether learning has happened or not. It is more than just a curriculum. It is a comprehensive system that integrates all aspects of your students’ learning experience to achieve a pre-defined outcome. *What is the WIDS model? The Worldwide Instructional Design System (WIDS) is a model for instructional design that helps you, the teacher or curriculum designer, plan teaching and learning activities that are student-centered, and performance based. It uses the questions of WHO? WHAT? WHEN? and HOW? to outline a uniform, yet flexible, high quality system of instruction and performance assessment. The WIDS model will help you answer…. WHO are my learners? WHAT do they need to learn? WHEN will they, and I, know that they have learned? HOW will I help them learn? Instructional design happens from the inside out—you start with the knowledge of where you want to end up; in other words, with the standards you are teaching to. Instruction happens from the outside in. Learners what to know what they will be learning and what activities will help them learn, and they deserve to have this information from the very start. *What is performance-based teaching and learning? Performance-based teaching and learning is an approach in which results are specified before instruction begins. Results must be demonstrated by the student in order to successfully complete the learning experience. Performance standards or criteria for successful demonstration of results are also specified prior to the beginning of instruction. There are four features that define performance-based teaching and learning. Feature #1: The competencies to be demonstrated are identified and communicated to the student before instruction begins. The competencies are clearly stated in terms of performance. This is the WHAT of the model. All content for the curriculum is based on these competencies. Example: SET UP a personal computer. CONDUCT a client consultation. Feature #2: Assessment of the competency requires the student to perform the competency. This is part of the WHEN. Example: SET UP a personal computer Student must demonstrate they can set up a personal computer. CONDUCT client consultation. Student will demonstrate a client consultation. Feature #3: The performance standards, or the criteria against which performance of the competency will be judged, are stated for each competency and communicated to the student before instruction begins. This is also part of the WHEN. Example: PREPARE a resume. Resume contains clear evidence of skills / training. Resume follows the recommended format (list specs) Resume includes a minimum of three achievements. Resume documents work history. Resume has 100% correct spelling and grammar Resume is prepared on a computer and stored on a flash drive for update and revision. Criteria for acceptable performance must be “criterion-referenced” rather than “norm-referenced.” Criterion referenced means that you set a particular standard or set of conditions that must be met, and ALL students must meet those standards or conditions. Norm-referenced means you evaluate performance in relation to all others being assessed and adjust everyone’s grade according to the highest grade earned; this is often referred to as “grading on the curve.” Feature #4: The learning activities and teaching strategies give the student an opportunity to develop the knowledge, skills, and attitudes necessary for each of the specified competencies. This is the HOW. A variety of learning styles and strategies are incorporated. Learning activities are student-centered. Students are given periodic and detailed feedback. Students must meet the performance standards or criteria for all competencies to achieve the final credential. Here’s how performance-based learning compares to the traditional model of instruction: Component Traditional Instruction WHO WHAT Teacher centered—focuses on what the teacher will do, e.g. what input the teacher will provide? Based on textbooks or faculty Performance-Based Learning expertise WHEN HOW Based on task analysis or established standards Emphasizes facts and information Rarely shares intended outcomes with students before instruction begins Focuses on “covering” material Relies heavily on paper/pencil Focuses assessment on retention of information and facts Is often ambiguous about what will be evaluated Allows for averaging of grades so that unsatisfactory progress in one area is offset by progress in other areas Often based on “seat-time;” students move on once “enough” time has been logged. Primarily teacher instruction Students are passive Little variation in learning style Little feedback provided Lacks connection between learning activities and intended outcomes testing Student-centered—focuses on what the students will learn and do, e.g., what are the student outcomes? Emphasizes application of knowledge, skills, and attitudes States measurable, observable learning targets Shares intended outcomes with students before instruction begins Focuses on what students will be able to DO upon successful completion of learning experiences Relies on demonstration of the application of skills, knowledge and attitudes Measures achievement based on performance standards or criteria that are specified up front and are criterion-referenced Requires the satisfactory performance of each competency Students progress only when competencies are mastered Holds teachers and students responsible for achievement of intended outcomes learning Features student-centered instruction Students have an active role in Varied learning styles are addressed Provides periodic feedback for improvement Clear connections between learning activities and intended outcomes Teaching and Learning Analysis Take this short assessment to gauge your instructional style: Traditional model, or performance-based? Check the box that most closely describes your approach to instruction. Feature #1: The competencies to be demonstrated are identified and communicated to the student before instruction begins. The competencies are clearly stated in terms of performance. Traditional You plan the instruction around information you want to “cover.” You think of your course in terms of “broad goals” you cover over the duration of the course Performance-based You plan the instruction around knowledge, skills, and attitudes the student needs to learn. You identify content and instructional strategies based on the competencies a student needs to demonstrate. Feature #2: Assessment of the competency requires the student to perform the competency. Traditional Assessment requires the memorization of facts and information. Assessment is accomplished primarily through paper / pencil tests. Performance-based Assessment requires the application of what students know. Assessment is accomplished through demonstration of skills. Feature #3: The performance standards, or the criteria against which performance of the competency will be judged, are stated for each competency and communicated to the student before instruction begins. Traditional Grading is done on a “curve.” Grades are the primary source of feedback to the student. Performance-based Grading is done according to pre-set performance standards or criteria that are communicated to the student up-front. Rubrics and checklists are used to communicate expectations and evaluate work. Feature #4: The learning activities and teaching strategies give the student an opportunity to develop the knowledge, skills, and attitudes necessary for each of the specified competencies. Traditional Instruction is organized according to chapters in a text. Most of instructional time is spent lecturing. Performance-based Instruction is organized around specific competencies to be learned. Students are involved in a variety of activities during instructional time. Practice Handout: 1.1 During this training, you will be working on designing learning for one of your own programs or courses of study. I will be working on the following program, course, or module / unit: Think through the features of performance based learning that you will try to incorporate into your course of study. Use the results of the Teaching and Learning Analysis activity to help you think about goals you’d like to achieve during this training related to course development. Goal 1: Goal 2: Goal 3: What will you do to achieve these goals? Assessment Sheet: 1.1 Directions: Imagine you are going to explain to your students the difference between criterion-referenced grading and norm-referenced grading. In plain language, write a short paragraph that explains the difference. Include why criterion-referenced grading is to their advantage. When you are done, use the checklist at the bottom of the page to judge how well you’ve done. Criterion-referenced Assessment explanation… 1. Is brief and easy to understand 2. Avoids or explains jargon 3. Targets students as audience 4. Explains that students will be given the competencies and performance standards at the beginning of the course 5. Explains that students are not measured against performance of other students, but are graded according to how well they perform the competencies 6. Explains that students must achieve all competencies to minimum level to pass the course 7. Explains that assessment focuses on demonstration of the competencies Yes No Assessment Sheet: 1.2 This assessment and many of the assessments in this workshop are designed to help you develop the information needed to complete the documents you will be required to complete and turn in to the state Private Career Schools Office regarding your curriculum. You will not be able to complete all the information required during this workshop; what you do not complete during the training sessions, you can continue to work on back at your school. Your school specialist will help you complete the state documents and can answer any questions you may have. Directions: Describe the characteristics of the student population you expect to enroll in this program. Who are your students and what are they like? What unique qualities do they bring to the educational environment that might have an impact on how you teach, and how they learn? Description of student population… 1. describes age range of students 2. describes educational background of students 3. describes socio-economic conditions of students 4. describes any language barriers students may have due to ethnicity 5. describes range of goals of students who are likely to enroll 6. describes reasons why students are interested in this industry / occupation 7. describes any geographic considerations students have (transportation issues, etc.) 8. describes any other characteristics of the student that may be important to teaching and learning. Yes No Program Map (Assessment Sheet 1.2) Program Title:_______________________________________________________________________ Program Length:____________________________________________________________________ Course Name:__________________________ Course Name:_________________________ Sequence in program:__________________ Sequence in program:_________________ Module / Unit Name:___________________ Module / Unit Name:__________________ Topics & Hours: Topics & Hours: Course Name:_________________________ Course Name:_________________________ Sequence in program__________________ Sequence in program__________________ Modules / Unit_______________________ Modules / Unit_______________________ Topics & Hours: Topics & Hours: Program Map: Page: Course Name:_________________________ Course Name:_________________________ Sequence in program:__________________ Sequence in program:__________________ Module / Unit Name:___________________ Module / Unit Name:___________________ Topics & Hours: Topics & Hours: Course Name:_________________________ Course Name:_________________________ Sequence in program:__________________ Sequence in program:__________________ Module / Unit Name:___________________ Module / Unit Name:___________________ Topics & Hours: Topics & Hours: Program Map: Page: Course Name:_________________________ Course Name:_________________________ Sequence in program:__________________ Sequence in program:_________________ Module / Unit Name:___________________ Module / Unit Name:__________________ Topics & Hours: Topics & Hours: Program Map… 1. includes program title 2. includes duration of program 3. includes program duration also stated in clock hours 4. lists each course that makes up the program 5. indicates the sequence in the program of each course (can be concurrent) 6. lists each module / unit of instruction for each course 7. lists major topics addressed in each course / module / unit of instruction 8. includes clock hours for each topic 9. shows that clock hours for all topics equals total clock hours for program Yes No