The Grass is Always Greener - Seattle Public Schools Secondary
advertisement

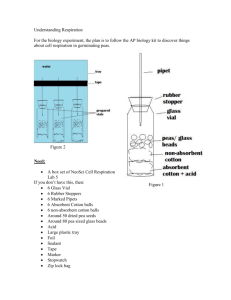
Biology New Procedure Item Template Cellular Respiration in Peas Directions: Use the following information to answer questions 1 through 9. Miguel wanted to find out the difference in the rate of cellular respiration between dry and germinated peas. He had heard the dry peas were alive and wanted to see if they would still carry out cellular respiration. He decided to focus on one component of air: oxygen. He remembered that oxygen was taken in along with glucose during cellular respiration. Remember germinated means that the plant has been soaked in water and is beginning to sprout. Question: What is the difference between the amount of oxygen taken in during cellular respiration between dry and germinated peas? Hypothesis: Germinating pea seeds will take up more oxygen than the dry pea seeds because they are growing and need more energy, which is made through cellular respiration. Materials: Respirometers: Glass vials closed with a stopper that has a pipette inserted through the stopper (see diagram) Germinating pea seeds Dry pea seeds Glass beads Absorbent cotton soaked in KOH ! Dry cotton to protect the seeds Water bath Timer Investigation Setup Diagram: The respirometers are submerged in the water in this beaker to close the system. As the respiring peas use up the oxygen in the respirometer, the water enters the pipettes as indicated by the arrows. Water enters pipette Vial on Left Germinating peas in a closed vial. The KOH will remove the CO2, so the only gas in the vial is O2 Vial on Right Dry peas in a closed vial. The KOH will remove the CO2, so the only gas in the vial is O2 Biology New Procedure Item Template Procedure: 1. Set up the respirometers—as shown in the Investigation Setup diagram by following instructions in #2-8 2. Place one absorbent cotton ball in the bottom of the vial and drop exactly 5 ml of KOH on to the cotton. 3. Place one non-absorbent cotton ball over the KOH cotton ball. The KOH will react with the CO2 and eliminate the CO2 from the vial so you will only focus on Oxygen gas. 4. Place equal volumes of each of the germinated seeds, the dry seeds and the glass beads into each respirometer. 5. Be sure to tightly seal each vial with the cork. The cork as been prepared by inserting a pipette into the hole and sealed tightly. 6. Submerge the vials into a basin of room temperature water so that the water just barely enters the top of the pipette. 7. Record the initial reading where the water level is inside the pipette. 8. Set your timer and take the reading where the water level is inside the pipette at 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes and 20 minutes. 9. Repeat Steps 2-8 at least two more times. Data: The table below shows the change in water level inside the pipette at each time interval for the germinated peas, the dry peas and the beads. Measurement of Oxygen Consumption by germinated peas and dry peas at room temperature Time (min) Amount of water that entered the pipette for each vial (ml) Germinated Peas Dry Peas 5 10 15 20 Graph: The data above was plotted below: .07 .14 .20 .27 .03 .05 .05 .07 Biology New Procedure Item Template INQ-F(1) In the table below list 3 controls in this investigation 2 Why are the vials placed under water creating a closed system? o o o o A. To control the evaporation of water B. To capture the oxygen produced by the peas C. To see if limiting the amount of air affects the rate of cellular respiration D. To prevent atmospheric CO2 from replacing the CO2 removed by KOH 3 Which variable was the manipulated (changed) variable in this investigation? o o o o SYS-B(2) INQ-B(1) A. The presence or absence of oxygen B. The type of “seed” placed in the vial. C. The presence or absence of carbon dioxide D. Whether the plant system was open or closed to the atmosphere 4 Which variable was the responding (dependent) variable in this investigation? Write your answer in this box: INQ-B(1) Biology New Procedure Item Template 5 Write a conclusion for this investigation. In your conclusion, be sure to: Answer the investigative question. What were the Big Ideas (important concepts) from this investigation? o Include supporting data from the Measurement of Oxygen Consumption by germinated peas, dry peas and beads at room temperature table and graph to support each of your big ideas. o Explain how these data support your conclusion. Provide a scientific explanation for the pattern in the data. Question: What is the difference between the amount of oxygen taken in during cellular respiration between dry and germinated plants? Conclusion: INQ-C(1) Biology New Procedure Item Template 6 List the inputs of matter and energy for Cellular Respiration. Use words or chemical symbols. LS1-A(1) Write your answer in this box: 7 List the outputs of matter and energy for Cellular Respiration. Use words or chemical symbols. Write your answer in this box: 8. Miguel’s lab partner, Shawnie asked what might happen if a live cricket were place in the vial instead of peas. Design an experiment to test Shawie’s question. a. Plan a controlled experiment to answer the Shawnies’ question. You may use any materials and equipment in your procedure. Be sure your procedure includes: logical steps to do the experiment two controlled (kept the same) variables one manipulated (independent) variable one responding (dependent) variable how often measurements should be taken and recorded LS1-A(1) Cellular Respiration in Peas – Biology EOC Scenario, Seattle PS Question: What is the effect of placing a live cricket into the vial on the amount of oxygen consumed in the vial? Procedure: Seattle Public Schools October 2012 Cellular Respiration in Peas – Biology EOC Scenario, Seattle PS Seattle Public Schools October 2012