Fatigue Pathway
advertisement
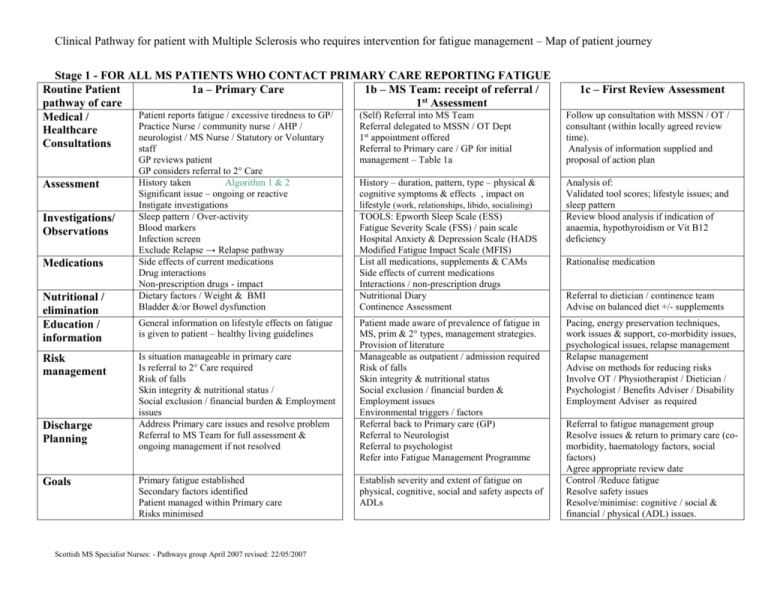
Clinical Pathway for patient with Multiple Sclerosis who requires intervention for fatigue management – Map of patient journey Stage 1 - FOR ALL MS PATIENTS WHO CONTACT PRIMARY CARE REPORTING FATIGUE Routine Patient 1a – Primary Care 1b – MS Team: receipt of referral / pathway of care 1st Assessment Patient reports fatigue / excessive tiredness to GP/ (Self) Referral into MS Team Medical / Practice Nurse / community nurse / AHP / Referral delegated to MSSN / OT Dept Healthcare neurologist / MS Nurse / Statutory or Voluntary 1st appointment offered Consultations staff Referral to Primary care / GP for initial Assessment Investigations/ Observations Medications Nutritional / elimination Education / information Risk management Discharge Planning Goals 1c – First Review Assessment Follow up consultation with MSSN / OT / consultant (within locally agreed review time). Analysis of information supplied and proposal of action plan GP reviews patient GP considers referral to 2° Care History taken Algorithm 1 & 2 Significant issue – ongoing or reactive Instigate investigations Sleep pattern / Over-activity Blood markers Infection screen Exclude Relapse → Relapse pathway Side effects of current medications Drug interactions Non-prescription drugs - impact Dietary factors / Weight & BMI Bladder &/or Bowel dysfunction management – Table 1a History – duration, pattern, type – physical & cognitive symptoms & effects , impact on lifestyle (work, relationships, libido, socialising) TOOLS: Epworth Sleep Scale (ESS) Fatigue Severity Scale (FSS) / pain scale Hospital Anxiety & Depression Scale (HADS Modified Fatigue Impact Scale (MFIS) List all medications, supplements & CAMs Side effects of current medications Interactions / non-prescription drugs Nutritional Diary Continence Assessment Analysis of: Validated tool scores; lifestyle issues; and sleep pattern Review blood analysis if indication of anaemia, hypothyroidism or Vit B12 deficiency General information on lifestyle effects on fatigue is given to patient – healthy living guidelines Patient made aware of prevalence of fatigue in MS, prim & 2° types, management strategies. Provision of literature Manageable as outpatient / admission required Risk of falls Skin integrity & nutritional status Social exclusion / financial burden & Employment issues Environmental triggers / factors Referral back to Primary care (GP) Referral to Neurologist Referral to psychologist Refer into Fatigue Management Programme Pacing, energy preservation techniques, work issues & support, co-morbidity issues, psychological issues, relapse management Relapse management Advise on methods for reducing risks Involve OT / Physiotherapist / Dietician / Psychologist / Benefits Adviser / Disability Employment Adviser as required Is situation manageable in primary care Is referral to 2° Care required Risk of falls Skin integrity & nutritional status / Social exclusion / financial burden & Employment issues Address Primary care issues and resolve problem Referral to MS Team for full assessment & ongoing management if not resolved Primary fatigue established Secondary factors identified Patient managed within Primary care Risks minimised Scottish MS Specialist Nurses: - Pathways group April 2007 revised: 22/05/2007 Establish severity and extent of fatigue on physical, cognitive, social and safety aspects of ADLs Rationalise medication Referral to dietician / continence team Advise on balanced diet +/- supplements Referral to fatigue management group Resolve issues & return to primary care (comorbidity, haematology factors, social factors) Agree appropriate review date Control /Reduce fatigue Resolve safety issues Resolve/minimise: cognitive / social & financial / physical (ADL) issues. Clinical Pathway for patient with Multiple Sclerosis who requires intervention for fatigue management – Map of patient journey Stage 2 – Managing Multiple Sclerosis related fatigue within the MS Team Routine Patient pathway of care Secondary factors Sleep 2a – individual management Manage contributory underlying conditions identified on assessment (pain, spasticity, anaemia, etc) using local or national guidelines Rationalise contributory medications Sleep hygiene – set goals for improving sleep pattern Lifestyle Agree individual interventions / goals: Activity, rest & pacing at work & home Planning & prioritising activities Top Tips for fatigue management Nutrition Advise on balanced diet – healthy eating guidelines , eating routines, fluid intake Elimination Cognitive Advice on diet/fluids, voiding techniques, timing , medication Counselling / relaxation / advise on or referral for management of external stressors (relationship, financial, work, etc) / mood, memory & concentration strategies / medication Environmental Advise or onward referral for: Temperature management Access issues, & ergonomics Set realistic individual timescales for review Measure by repeated use of validated tools Onward referral where required Set SMART goals for each factor identified above Reduce fatigue on validated scoring Establish if need for medication if no improvement in validated scores (Suggest fatigue medications – e.g. Amantadine, Provigil, Fluoxetine, etc) Discharge Planning Goals Scottish MS Specialist Nurses: - Pathways group April 2007 revised: 22/05/2007 2b – group management Set aims and objectives for group – diaries Overview of fatigue in MS Deliver overview of contributory underlying conditions & medication impacts Discuss & review impact of sleep hygiene Contrast / compare tiredness & fatigue Advise / discuss : Planning & prioritising activities Pacing / energy conservation Benefits of exercise / complimentary approaches Top Tips for fatigue management Dietician / team member gives advice on balanced diet – healthy eating guidelines , eating routines, fluid intake Advice / discussion on good bladder & bowel habits Discuss impact of anxiety on symptom experience Recognising and managing low mood Introduction to stress management & coping strategies Relaxation techniques & complimentary approaches Memory & focussing strategies Discuss management of environmental triggers & issues: Top Tips for fatigue management Course evaluation & end of group Refer onto individual management if required Deliver overview of pharmaceutical interventions Individual SMART goals set in relation to programme Involvement of relative / friend / carer to improve understanding of impact of fatigue. Who / where







