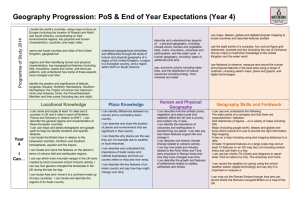
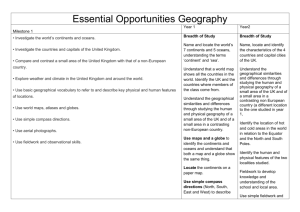
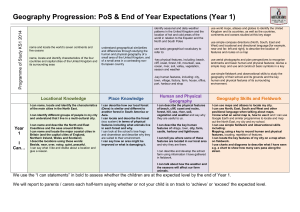
Geography Curriculum Map KS1 learning intentions • Investigate the
advertisement

Geography Curriculum Map KS1 learning intentions • Investigate the world’s continents and oceans. • Investigate the countries and capitals of the United Kingdom. • Compare and contrast a small area of the United Kingdom with that of a non-European country. • Explore weather and climate in the United Kingdom and around the world. • Use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to and describe key physical and human features of locations. • Use world maps, atlases and globes. • Use simple compass directions. • Use aerial photographs. Year 1 • Use fieldwork and observational skills A1 Harvest; To investigate Sp1 Kings & Queens patterns • Identify land use around the school. use simple fieldwork and observational skills to study the geography of their school and its grounds and the key human and physical features of its surrounding environment. Su1 Pirates (Seaside) to investigate places • Use world maps, atlases and globes to identify the United Kingdom and its countries, as well as the countries, continents and oceans studied. • Name and locate the world’s continents and oceans. • Use compass directions (north, south, east and west) and locational language (e.g. near and far) to describe the location of features and routes on a map. name and locate the world’s seven continents and five oceans Geography Curriculum Map A2 Light & Dark Sp2 Countries & Cultures; To investigate patterns • Understand geographical similarities and differences through studying the human and physical geography of a small area of the United Kingdom and of a contrasting nonEuropean country. key physical features, including: beach, cliff, coast, forest, hill, mountain, sea, ocean, river, soil, valley, vegetation, season and weather use simple compass directions (North, South, East and West) and locational and directional language [for example, near and far; left and right], to describe the location of features and routes on a map use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features; devise a simple map; and use and construct basic symbols in a key Su2 Where I live; to investigate places • Ask and answer geographical questions (such as: What is this place like? What or who will I see in this place? What do people do in this place?). • Identify the key features of a location in order to say whether it is a city, town, village, coastal or rural area. • Use simple fieldwork and observational skills to study the geography of the school and the key human and physical features of its surrounding environment. • Use aerial images and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic physical features. • Name, locate and identify characteristics of the four countries and capital cities of the United Kingdom and its surrounding seas. Geography Curriculum Map name, locate and identify characteristics of the four countries and capital cities of the United Kingdom and its surrounding seas key human features, including: city, town, village, factory, farm, house, office, port, harbour and shop use world maps, atlases and globes to identify the United Kingdom and its countries, as well as the countries, continents and oceans studied at this key stage Geography Curriculum Map KS1 learning intentions • Investigate the world’s continents and oceans. • Investigate the countries and capitals of the United Kingdom. • Compare and contrast a small area of the United Kingdom with that of a non-European country. • Explore weather and climate in the United Kingdom and around the world. • Use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to and describe key physical and human features of locations. • Use world maps, atlases and globes. • Use simple compass directions. • Use aerial photographs. Year 2 • Use fieldwork and observational skills A1 Transport; to communicate Sp1 Heroes geographically use simple fieldwork and observational skills to study the geography of their school and its grounds and the key human and physical features of its surrounding environment. • Devise a simple map; and use and construct basic symbols in a key. Use simple grid references (A1, B1). Su1 India? Africa? Countries in the news; to communicate geographically • Use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to: • key physical features, including: beach, coast, forest, hill, mountain, ocean, river, soil, valley, vegetation, season and weather. • key human features, including: city, town, village, factory, farm, house, office and shop. Geography Curriculum Map A2 Animals Sp2 Buildings (Great Fire of London) Su2 Water • Identify seasonal and daily weather patterns in the United Kingdom and the location of hot and cold areas of the world in relation to the Equator and the North and South Poles. Geography Curriculum Map Year 3 learning intentions • Identify key geographical features of the countries of the United Kingdom, and show an understanding of how some of these aspects have changed over time. • Locate the geographic zones of the world. • Understand the significance of the geographic zones of the world. • Understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region or area of the United Kingdom (different from that taught at Key Stage 1). Year 3 A1 The Victorians Sp1 Me and my World; to investigate Su1 The UK (The Great in GB) To places investigate places • An excellent knowledge of • Ask and answer geographical where places are and what questions about the physical and they are like. human characteristics of a location. • Explain own views about locations, giving reasons. • Explain own views about locations, giving reasons. • Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping • Use fieldwork to observe and to locate countries and record the human and physical describe features. features in the local area using a • Name and locate the range of methods including countries of Europe sketch maps, plans and and identify their main graphs and digital technologies. physical and • Use a range of resources to human characteristics. identify the key physical and human features of a location. locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe • Name and locate counties and (including the location of Russia) cities of the United and North and South America, concentrating on their Kingdom, geographical regions environmental regions, key physical and their identifying human and and human characteristics, physical characteristics, including Geography Curriculum Map countries, and major cities hills, mountains, cities, rivers, key topographical features and land-use patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time. name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and landuse patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied A2 Natural Disasters; To communicate geographically • Describe key aspects of: • physical geography, including: rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes and the water cycle. physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes, and the water cycle Sp2 Dinosaurs and Cavemen Su2 Maps; to investigate patterns • Name and locate the Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle and date time zones. Describe some of the characteristics of these geographical areas. • Describe geographical similarities and differences between countries. • Describe how the locality of the Geography Curriculum Map school has changed over time. identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night) use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied use the eight points of a compass, four and six-figure grid references, symbols and key (including the use of Ordnance Survey maps) to build their knowledge of the United Kingdom and the wider world use fieldwork to observe, measure, record and present the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies. Geography Curriculum Map Year 4 learning intentions • Describe and understand key aspects of: • human geography, including: settlements, land use, economic activity including trade links and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water supplies. Year 4 A1 Romans Sp1 Chocolate; to communicate geographically • human geography, including: settlements and land use. • Use the eight points of a compass, four-figure grid references, symbols and key to communicate knowledge of the United Kingdom and the wider world. human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features Su1 Water and rivers Geography Curriculum Map studied . A2 Me and my body Year 5 learning intentions Sp2 Ancient Egypt Su2 Animals around the world • Understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region or area in a European country. • Understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of the human and physical geography of a region or area within North or South America. • Describe and understand key aspects of: • physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, Geography Curriculum Map mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes and the water cycle • Use fieldwork to observe, measure and record the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs and digital technologies. Year 5 A1 Anglo Saxons and Vikings Sp1 Journey into Space Su1 Where animals and plants live; To investigate patterns • Identify and describe the geographical significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, and time zones (including day and night). • Describe and understand key aspects of: • physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes and the water cycle • human geography, including: • Create maps of locations identifying patterns (such as: land use, climate zones, population densities, height of land). A2 Architects and Designers Sp2 Small or Sprawl; To investigate places use the eight points of a compass, four and six-figure grid references, symbols and key • Use different types of (including the use of Ordnance fieldwork sampling (random Survey maps) to build their and systematic) to observe, Su2 Ancient Greece Geography Curriculum Map knowledge of the United Kingdom and the wider world use fieldwork to observe, measure, record and present the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies. measure and record the human and physical features in the local area. Record the results in a range of ways. • Analyse and give views on the effectiveness of different geographical representations of a location (such as aerial images compared with maps and topological maps - as in London’s Tube map). • Name and locate some of the countries and cities of the world and their identifying human and physical characteristics, including hills, mountains, rivers, key topographical features and land-use patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time. Year 6 learning intentions • Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. • Use the eight points of a compass, four-figure grid references, symbols and keys (including the use of Ordnance Survey maps) to build knowledge of the United Kingdom and the world. • Use a wide range of geographical sources in order to investigate places and patterns. • Locate the world’s countries, with a focus on Europe and countries of particular interest to pupils. • Locate the world’s countries, with focus on North and South America and countries of particular interest to pupils. Year 6 A1 Tudors Sp1 World War Two Su1 Food, Fun and Fitness • human geography, including: • Use the eight points of a compass, four-figure grid references, symbols and a key Geography Curriculum Map (that uses standard Ordnance Survey symbols) to communicate knowledge of the United Kingdom and the world. use the eight points of a compass, four and six-figure grid references, symbols and key (including the use of Ordnance Survey maps) to build their knowledge of the United Kingdom and the wider world A2 North or South America; To investigate places • Name and locate the countries of North and South America and identify their main physical and human characteristics. • Collect and analyse statistics and other information in order to draw clear conclusions about locations. • Identify and describe how the physical features affect the human activity within a location. • Use a range of geographical resources to give detailed descriptions Sp2 World War two/Revision Su2 France; To investigate patterns • human geography, including: settlements, land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals, and water supplies. • Understand some of the reasons for geographical similarities and differences between countries. • Describe how locations around the world are changing and explain some of the reasons for change. • Describe geographical diversity across the world. • Describe how countries and geographical regions are Geography Curriculum Map and opinions of the characteristic features of a location. understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the United Kingdom, a region in a European country, and a region within North or South America use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied interconnected and interdependent. understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the United Kingdom, a region in a European country, and a region within North or South America use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied