Word Document - Essentially Education

Air Quality Quick Revision
Which chemicals are in the air?
The Earth’s atmosphere is a mixture of gases:
78% Nitrogen
21% Oxygen
1% Argon
0.04% carbon dioxide
Variable amounts of water vapour
Human activity adds harmful chemicals to the atmosphere.
How do chemical reactions make air pollutants?
Coal is mainly carbon, petrol and diesel are mainly hydrocarbons.
These fossil fuels burn in power stations to generate electricity, and in vehicles like cars and trains.
When fuels burn they react with oxygen from the air, this process is known as combustion.
In all chemicals reactions, the atoms are rearranged, the same atoms are still present in both the reactants and products; they are just combined together in a different way. This is known as conservation of atoms.
An example is, methane reacts with oxygen to make carbon dioxide and water:
CH
4
+ 2O
2
CO
2
+ 2H
2
O
The properties of the reactants are very different from the properties of the products.
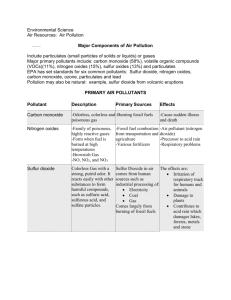
What are the main air pollutants?
These are the main air pollutants, that are polluting our atmosphere:
Sulfur dioxide, SO
2
Nitrogen monoxide, NO
Nitrogen dioxide, NO
2
Carbon monoxide, CO
Carbon dioxide, CO
2
Small particulates of carbon
Where do air pollutants come from?
Fossil fuels burn to make carbon dioxide. Sometimes there is not enough oxygen to convert all the carbon in the fuel to carbon dioxide. This results in incomplete combustion, which makes carbon monoxide and solid carbon particulates.
Some fossil fuels contain sulfur impurities. When the fuel burns, the sulfur reacts with oxygen to make sulfur dioxide.
At high temperatures, inside engines, nitrogen and oxygen from the air react to make nitrogen oxides.
Nitrogen monoxide forms first, this reacts with more oxygen from the air to make nitrogen dioxide
– in other words, nitrogen monoxide is oxidised. Together, NO and NO
2
are called NO x
.
Where do air pollutants go?
Some pollutants harm human directly, others damage the environment, and so harm humans indirectly.
Here are some of the effects that the pollutants have on human health:
Particulate carbon makes surfaces dirty and can cause health problems if breathed in.
Carbon monoxide is poisonous.
Carbon dioxide dissolves in rain water and sea water. Plants use it for photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere contributes to global warming.
Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide react with water and oxygen to make acid rain.
Nitrogen dioxide may increase the risk of asthma attacks.
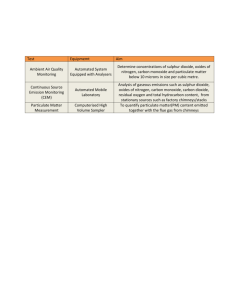
How can we improve air quality?
The only way to make less carbon dioxide is to burn less fossil fuels.
We can reduce air pollution from fossil fuel power stations by:
Using less electricity
Removing sulfur impurities from fossil fuels before burning them
Removing sulfur dioxide and particulates from the gases that power stations emit
We can reduce air pollution from vehicle exhaust gases by:
Developing efficient engines that burn less fuel
Using low-sulfur fuels
Using catalytic converters to convert, nitrogen monoxide to nitrogen and oxygen, and carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide
Using public transport instead of cars
Having legal limits on exhaust emissions