Literary Devices: Definitions & Examples
advertisement

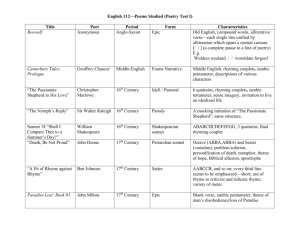
Assonance – the repetition of vowel sounds within nonrhyming words. An example of assonance is the repetition of the u sound in the following line: Only their usual maneuvers, dear -W.H. Auden, “O What Is That Sound” Alliteration – the repetition of consonant sounds at the beginning of words. Note the repetition of d in the following: Deep into that darkness peering, long I stood there wondering, fearing, Doubting, dreaming dreams no mortal ever dared to dream before -Edgar Allan Poe, “The Raven” Rhythm – the pattern or flow of sound created by the arrangement of stressed and unstressed syllables, used to bring out a musical quality in language. Iambic pentameter – a pattern of poetic meter made up of 5 units, each unit made up of 2 syllables, the first unstressed and the second stressed. But soft! What light through yonder window breaks? It is the East, and Juliet is the sun! - William Shakespeare, Romeo and Juliet Sonnet – a 14-line lyric poem, commonly written in iambic pentameter - Petrarchan sonnet 1st 8 lines (octave) presents a problem or raises a question abba, abba rhyme scheme end 6 lines (sestet) resolves or comments on the problem cdecde or cdcdcd rhyme scheme - Shakespearean sonnet 3 sets of 4 lines (quatrain) abab, cdcd, efef scheme 1 pair of rhyming lines (couplet) gg rhyme scheme Personification – a figure of speech in which human qualities are given to an object, animal, or idea. The grey-eyed morn smiles on the frowning night - William Shakespeare, Romeo and Juliet Metaphor – a figure of speech that makes a comparison between two things that are basically unlike but have something in common. Unlike similes, metaphors do not contain the word like or as. Simile – a figure of speech that makes a comparison between two unlike things, using the word like or as. Idiom – a common figure of speech whose meaning is different from the literal meaning of its words. For example, “raining cats and dogs.” Oxymoron – a special kind of concise paradox that brings together two contradictory terms. For example, “bright smoke” or “feather of lead.” Paradox – a seemingly contradictory or absurd statement that may nonetheless suggest an important truth.