Tetanus Immunisation following Injuries
advertisement

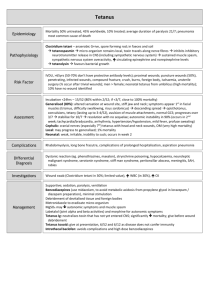
Tetanus Vaccination A course of vaccine consists of three injections, with an interval of four weeks between each dose. A booster dose ten years after the primary course and again ten years later maintains a satisfactory level of protection, probably lifelong.When an adult has received a total of five doses of tetanus (e.g. primary course plus two boosters), no further boosters are recommended except for the treatment of tetanus prone wounds. The following are considered to be tetanus prone wounds: a. Wound or burn sustained more than 6 hours before surgical treatment of same b. Wound or burn which at any interval after injury shows one or more of the following characteristics: 1. Significant degree of devitalised tissue 2. Puncture type wound 3. Contact with soil or manure 4. Clinical evidence of sepsis Thorough surgical toilet of the wound is essential, whatever the tetanus immunisation of the patient. The single antigen tetanus vaccine has now been replaced by the combined tetanus/low dose diphtheria vaccine for adults and adolescents for all routine uses in these age groups. The change was on the advice of the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation, generated by concern at the low levels of immunity to diphtheria in older people in the UK. It brings us into line with recommendations from the World Health Organisation. For tetanus prone wounds, human tetanus immunoglobulin is also used. It is important that it is administered at a different site to the vaccine to avoid interaction. The dose, for most uses, is 250iu by intramuscular injection. If more than 24 hours have elapsed since injury or there is a risk of heavy contamination or following burns, the dose is 500iu. Disease There are 20-60 cases of tetanus annually in the UK. It is rare but the organism (Clostridium tetani) is widespread. The elderly are more vulnerable, although it can also occur in sports players. Signs include painful muscle stiffness, commonly starting in the masseters and neck extensors and later spreading to the trunk and limbs. If the time taken from the first symptom to the establishment of spasms is less than 24 hours, severe disease is likely. Management includes placing the patient in a quiet environment as any external stimuli can trigger spasms. Unnecessary interventions should be avoided. The patient will usually need to be admitted to ICU for intubation and ventilation. Antibiotics are controversial but Penicillin and Metronidazole (Tetracycline in penicillin allergy) may benefit. Diazepam should be used to control spasms and human immunoglobulin should be given. Tetanus Immunisation following Injuries Immunisation status Fully immunised, i.e. has received a total of 5 doses at appropriate intervals as single antigen or in a combined vaccine Primary immunisation complete, boosters incomplete but up to date Primary immunisation incomplete or boosters not up to date Not immunised or immunisation status not known or uncertain Clean wound Vaccine Tetanus prone wound Vaccine None required None required None required (unless next dose due soon and convenient to give it now) A reinforcing dose of combined tetanus/diphtheria vaccine and further doses as required to complete the recommended schedule (to ensure future immunity) An immediate dose of vaccine followed, if records confirm this is needed, by completion of a full 3 dose course of combined tetanus/diphtheria vaccine to ensure future immunity None required (unless next dose due soon and convenient to give it now) A reinforcing dose of combined tetanus/diphtheria vaccine and further doses as required to complete the recommended schedule (to ensure future immunity) An immediate dose of vaccine followed, if records confirm this is needed, by completion of a full 3 dose course of combined tetanus/diphtheria vaccine to ensure future immunity Human tetanus immunoglobulin Only if risk especially high (e.g. contaminated with stable manure Only if risk especially high (see above) Yes: one dose of human tetanus immunoglobulin in a different site Yes: one dose of human tetanus immunoglobulin in a different site