4NBT.6 Lesson
advertisement

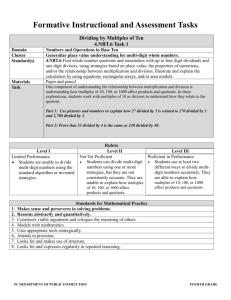
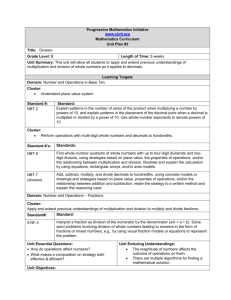
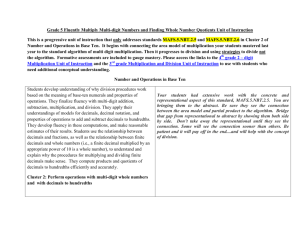
4.NBT.6 2011 Domain: Number and Operations in Base Ten Cluster: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic Standards: Find whole number quotients and remainders with up to four-digit dividends and one-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models. Essential Questions -Why do you have a remainder in division? -Why can’t the remainder be equal to or greater than the divisor? -What are two ways to interpret a remainder? -How can you show different models for division? Content Statements - Students will use basic facts and patterns of zeros to solve division problems with 3-digit dividends and 1-digit divisors. - Students will use compatible numbers and rounding to estimate quotients. - Students will estimate quotients of multi –digit division problems using multiplication facts and Enduring Understandings - Basic Facts and place value patterns can be used to divide multiples of 10 and 100 by 1digit numbers. - There is more than one way to estimate a quotient. Substituting compatible numbers is an efficient technique for estimating quotients. - Mentally multiplying by different powers of ten will help you arrive at an estimate for the quotient of a multi-digit division problem. - The remainder when dividing must be less than the divisor. The nature of the question asked determines how to interpret and use the remainder. - Some real world problems involving joining equal groups, separating equal groups, or comparison can be solved using multiplication; others can be solved using division. Activities, Investigation, and Student Experiences Use base ten blocks or money to create equal groups to illustrate the division process and understand the concept of left over items. Small leveled group work. 4.NBT.6 place-value concepts. - Students will divide whole numbers by 1-digit divisors resulting in quotients with remainders. - Students use words and models to represent multiplication and division problems accurately. - Students will draw pictures and write related number sentences to solve problems. - Students will use repeated subtraction to model division - Students will record division as repeated subtraction -Students will use place value to understand the algorithm of long division - Students will use the standard algorithm to divide a two-digit number by a one-digit number - Students will use the standard algorithm to divide 3-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers. - Students will use the standard algorithm to divide 3 – digit numbers by - Information in a problem can often be shown with a picture or diagram and used to understand and solve the problem. Some problems can be solved by writing and completing a number sentence or equation - Repeated subtraction situations can be modeled and solved using division - Repeated subtractions situations can be solved using a division algorithm different from the standard algorithm - The sharing interpretation of division can be used to model the standard division algorithm - The standard division algorithm breaks the calculation into simpler calculations using basic facts, place-value, the relationship between multiplication and division and estimation. - The standard division algorithm breaks the calculation into simpler calculations using basic facts, place-value, the relationship between multiplication and division, and estimation. - The relationship between multiplication and division and estimation can be used to determine the place value of the 2011 4.NBT.6 1-digit numbers and properly decide where to begin dividing. - Students will estimate and find quotients for 4 – digit dividends and 1-digit divisors. 2011 largest digit in a quotient. - The process for the standard division algorithm with one-digit divisors is the same when extended from 2 – 3 digit dividends to 4-digit dividends Assessments -Series Assessments –Teacher Observation -Teacher made Assessments -Open-ended word problems A 4th grade student bought 4 new pencil boxes. She has 2616 pencils. The student would like to put the same number of pencils in each box. How many pencils are in each box? Equipment Needed: Math manipulatives, available technology, pencil, paper. Teacher Resources: Series Textbook Supplemental Worksheets http://aaaknow.com/div41_x3.htm step by step instructions http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ITloMQvj-lU you tube video showing the traditional algorithm and the inverse operation 4.NBT.6 2011 http://www.mathplayground.com/division02.html interactive math game to practice long division http://studyjams.scholastic.com/studyjams/jams/mat h/index.htm Math Movies http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/ illuminations.nctm.org - look for websites and lesson plans http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/vlibrary.html www.softschools.com http://math.pppst.com/ - Many free Pre-made Power Point Presentations for Math and across the curriculum