STANDARD II:
advertisement

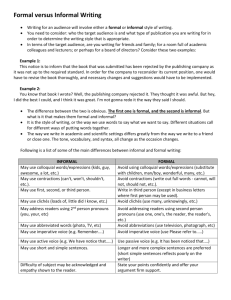
STANDARD II: The student will demonstrate appropriate word choice. OBJECTIVE 2: Use formal and informal language appropriately. ELIGIBLE CONTENT: Informal language. Formal language. (Note: Formal language should avoid slang, contractions, second person, and jargon.) Prerequisites: Teachers should explain the difference between formal and informal language. Lesson/Teaching Strategies: Getting Started: As students talk with each other, they frequently use terms familiar to their age group and often to the community in which they live. This language is sometimes different from the language students hear from others and from the written language they see. The language students use in their daily lives that has meaning to their group is called informal language. The language students see in school textbooks and hear in class is called formal language. Students must learn the difference between formal and informal language and know when to use each appropriately. Activity 1 Materials Needed: Procedure: Contemporary song, radio, overhead projector, transparency with the song’s lyrics, classroom set of the song. (Note: Tape the radio version of the song.) 1. 2. 3. 4. Play the contemporary song for the students. Display the words of the song on the overhead and play the song again. As a class, translate the first two lines of the song into formal language. Divide the class into groups of two students and have each group translate the remaining lyrics into sentences using formal language. 5. Encourage groups to discuss their translations and emphasize the differences between versions. Activity 2 Procedure: Have students create a slang dictionary. Ask students to write at least 30 words that are considered slang. To develop a "Teen's Language Dictionary," have students translate their 30 words into words representing formal language. Examples: C chill–to relax crib–home H honey–a girlfriend Activity 3 Procedure: Have each student create a poem or prose using slang. Have each student translate his or her poem or prose into formal language. Note: The eligible content for this standard warns against the use of slang and contractions in formal language. Students may benefit from writing poems or prose in informal language and then changing that to standard expression. Examples: Informal I was sittin' at the crib watching the tube when my boys came over to chill. Formal I was sitting at home watching T.V. when my friends came over to visit and to relax. Activity 4 Procedure: Listen and record sentences of students as they talk. Write several formal sentences and alternate between formal and informal sentences. Ask students to distinguish between formal and informal language by writing the appropriate descriptor (formal or informal) after each sentence. For each informal sentence, have students translate it into formal language. Extend the lesson by creating more sentences. Example: A person should always try to do their best because you never know who is watching. (informal) A person should always try to do his or her best because one never knows who is watching. (formal)