Preparation of the Text
advertisement
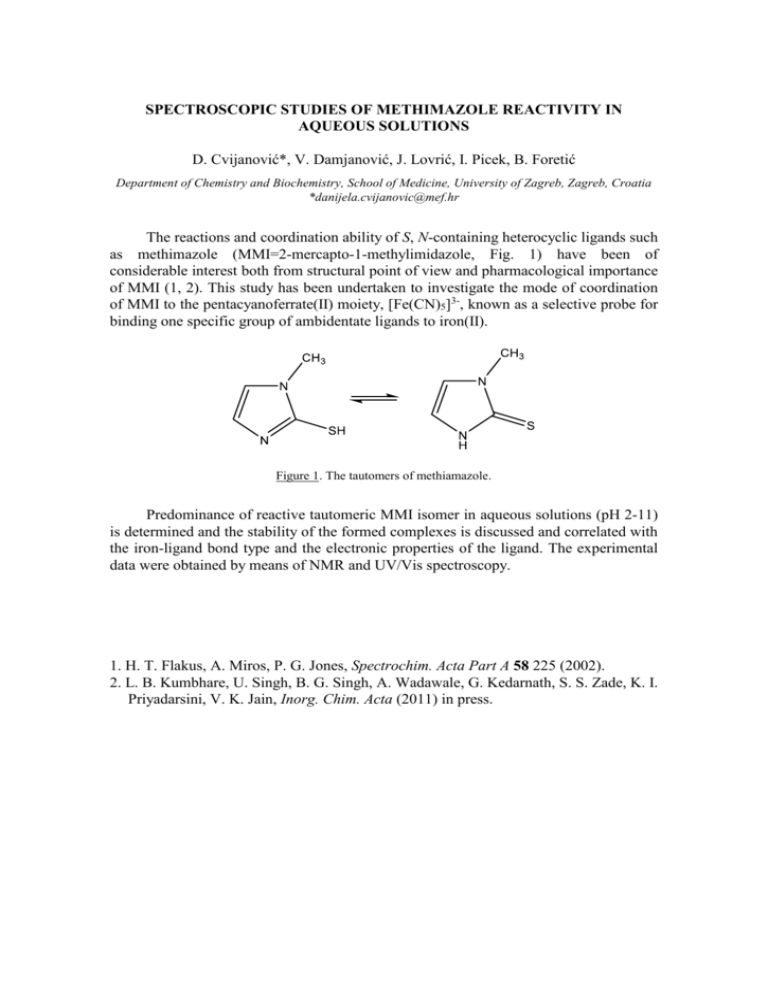
SPECTROSCOPIC STUDIES OF METHIMAZOLE REACTIVITY IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS D. Cvijanović*, V. Damjanović, J. Lovrić, I. Picek, B. Foretić Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, School of Medicine, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia *danijela.cvijanovic@mef.hr The reactions and coordination ability of S, N-containing heterocyclic ligands such as methimazole (MMI=2-mercapto-1-methylimidazole, Fig. 1) have been of considerable interest both from structural point of view and pharmacological importance of MMI (1, 2). This study has been undertaken to investigate the mode of coordination of MMI to the pentacyanoferrate(II) moiety, [Fe(CN)5]3-, known as a selective probe for binding one specific group of ambidentate ligands to iron(II). Figure 1. The tautomers of methiamazole. Predominance of reactive tautomeric MMI isomer in aqueous solutions (pH 2-11) is determined and the stability of the formed complexes is discussed and correlated with the iron-ligand bond type and the electronic properties of the ligand. The experimental data were obtained by means of NMR and UV/Vis spectroscopy. 1. H. T. Flakus, A. Miros, P. G. Jones, Spectrochim. Acta Part A 58 225 (2002). 2. L. B. Kumbhare, U. Singh, B. G. Singh, A. Wadawale, G. Kedarnath, S. S. Zade, K. I. Priyadarsini, V. K. Jain, Inorg. Chim. Acta (2011) in press.











