49KB - NZQA
advertisement
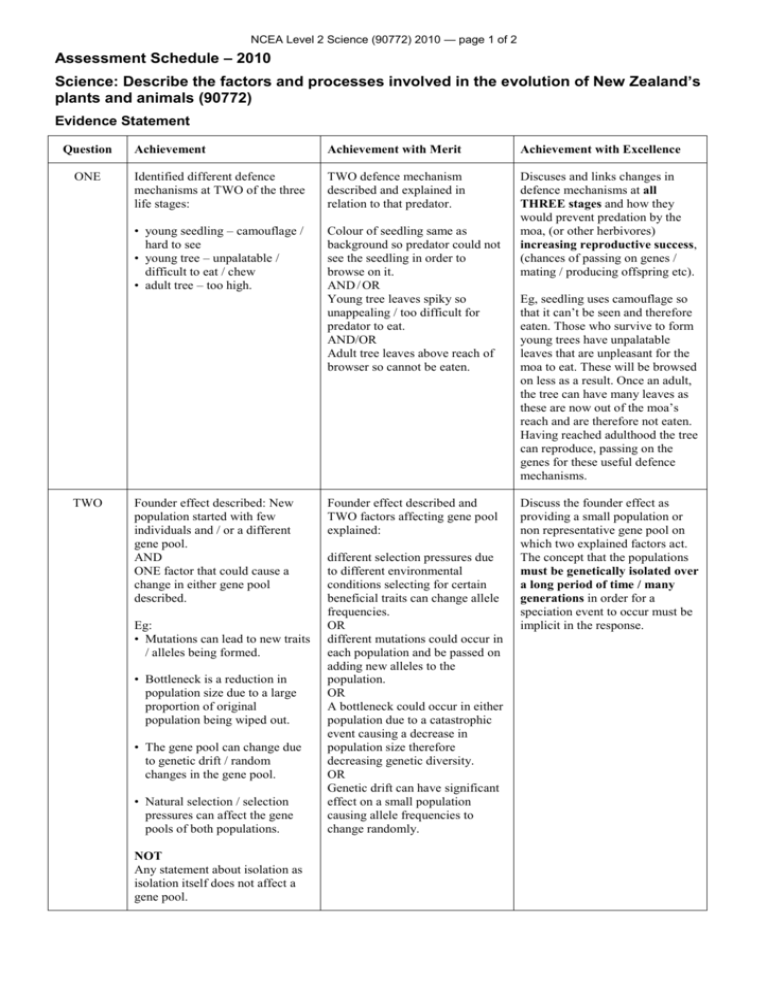
NCEA Level 2 Science (90772) 2010 — page 1 of 2 Assessment Schedule – 2010 Science: Describe the factors and processes involved in the evolution of New Zealand’s plants and animals (90772) Evidence Statement Question ONE TWO Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence Identified different defence mechanisms at TWO of the three life stages: TWO defence mechanism described and explained in relation to that predator. • young seedling – camouflage / hard to see • young tree – unpalatable / difficult to eat / chew • adult tree – too high. Colour of seedling same as background so predator could not see the seedling in order to browse on it. AND / OR Young tree leaves spiky so unappealing / too difficult for predator to eat. AND/OR Adult tree leaves above reach of browser so cannot be eaten. Discuses and links changes in defence mechanisms at all THREE stages and how they would prevent predation by the moa, (or other herbivores) increasing reproductive success, (chances of passing on genes / mating / producing offspring etc). Founder effect described: New population started with few individuals and / or a different gene pool. AND ONE factor that could cause a change in either gene pool described. Eg: • Mutations can lead to new traits / alleles being formed. • Bottleneck is a reduction in population size due to a large proportion of original population being wiped out. • The gene pool can change due to genetic drift / random changes in the gene pool. • Natural selection / selection pressures can affect the gene pools of both populations. NOT Any statement about isolation as isolation itself does not affect a gene pool. Founder effect described and TWO factors affecting gene pool explained: different selection pressures due to different environmental conditions selecting for certain beneficial traits can change allele frequencies. OR different mutations could occur in each population and be passed on adding new alleles to the population. OR A bottleneck could occur in either population due to a catastrophic event causing a decrease in population size therefore decreasing genetic diversity. OR Genetic drift can have significant effect on a small population causing allele frequencies to change randomly. Eg, seedling uses camouflage so that it can’t be seen and therefore eaten. Those who survive to form young trees have unpalatable leaves that are unpleasant for the moa to eat. These will be browsed on less as a result. Once an adult, the tree can have many leaves as these are now out of the moa’s reach and are therefore not eaten. Having reached adulthood the tree can reproduce, passing on the genes for these useful defence mechanisms. Discuss the founder effect as providing a small population or non representative gene pool on which two explained factors act. The concept that the populations must be genetically isolated over a long period of time / many generations in order for a speciation event to occur must be implicit in the response. NCEA Level 2 Science (90772) 2010 — page 2 of 2 THREE Survival of pōhutukawa limited by harsh environmental factors. OR Selection pressures cause some individuals to die out, (or others to survive). OR Selection against certain alleles reduces diversity in gene pool. OR Alleles selected against would be lost from the gene pool Plants that could not tolerate high salt / low fresh water / strong winds and poor soil would not survive. AND their genes could not be passed on to the next generation, (become less common in the gene pool). OR Plants that could tolerate high salt / low fresh water / strong winds and poor soil would survive. AND their genes would be passed on to the next generation, (become more common in the gene pool). Discusses that the gene pool of the pōhutukawa has less diversity due to the action of natural, (directional), selection removing less desirable alleles from the gene pool as a consequence of decreased reproductive success in those individuals. OR Discusses differences or a change in allele frequencies in the gene pool as a result of lost alleles due to selection and gain of alleles due to mutation or selection. FOUR Identifies that: Explains that isolation as a result of the Southern Alps prevents gene flow between populations. OR Explains that different selection pressures on the two populations, isolated by the southern alps, cause distinct gene pools to form. Considers isolation, (and its geological cause), and differing selection pressures causing distinct gene pools and links both merit statements together in a way that explains new species formation. Fault / plate movement causes uplift / mountain building / orogeny, (of Southern Alps). AND Mountains geographically separate populations. AND Isolation leads to speciation. Eg, the Alpine Fault caused uplift / mountain building and the koura was geographically isolated by this formation leading to two different species. Eg, as the Alpine Fault was formed, the Southern Alps were also formed creating geological boundaries that separated the koura. This prevented gene flow. This separation meant two distinct species arose due to the different environmental conditions / selection pressures affecting the gene pools in different ways. Eg, the Alpine Fault formation and the rise of the Southern Alps separated the koura into two areas. Isolation prevents gene flow between populations. So accumulated differences are not shared. Different environmental conditions acted as different selection pressures and so different traits were selected for which led to two different species of koura evolving. Judgement Statement Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence 3A 2M+1A 2E+1A








