INFLAMMATORY DISEASES OF FEMALE GENITALS
advertisement

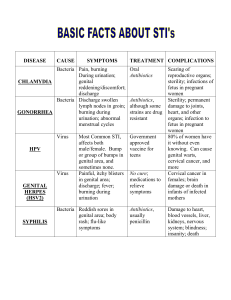
SPECIFIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASES (Sexually transmitted diseases) To specific inflammatory diseases of the female reproductive organs belong tuberculosis and sexually transmitted diseases. According to the WHO's classification, there are 21 such diseases. Their frequency has been risen for the last years. Gonorrhea Gonorrhea is a contagious disease caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Among the specific inflammatory diseases of the female genital tract gonorrhea takes the second place and is in 5-25% of cases of all STDs. Etiology and pathogenesis. Gonorrhea is caused by Neisseria gonorrhea. The causative agent was found in 1879 by A. Neisser. Gram-negative N. gonorrhea is not stable in the outer surrounding and dies quickly at the influence of antiseptic solutions, boiling, drying, but it is rather stabile in human organism. In uncomfortable conditions they transform into L-forms, which can transform into the usual form in the favourable conditions. In case of chronic gonorrhea, N. gonorrhoeae are situated mostly in leukocytes and out of the cells, in case of the acutening of the process they are found in the leukocytes. N. gonorrhea affects mostly those parts of urogenital tract, that are covered with cylindric epithelium: mucosa of urethra, cervical canal, Bartholin's glands ducts, mucosa of uterine cavity, uterine tubes, ovarian epithelium, peritoneum. During the pregnancy, childhood and menopausal period there can be gonorrheal vaginitis. The source of infection is a person with gonorrhea. Ways of infecting: the disease is sexually transmitted homosexual contacts, orogenital contacts very rarely through sponges, towels, underwear during labour from mother (infected eyes, vagina in girls) Incubational period lasts for 3-7 days, sometimes for 2-3 weeks. According to the stage of spreading the process the gonorrhea of lower part of genital organs (gonorrheal urethritis, endocervicitis, Bartholinitis, vulvovaginitis) and gonorrhea of upper parts — gonorrhea ascendens (endometritis, salpingitis, pelvioperitonitis) is classified. According to duration there are such forms of gonorrhea: fresh gonorrheal infection with acute, subacute, torpid passing, which lasts less than two months chronic gonorrheal infection, lasting more than two months latent gonorrheal infection In women the clinic of gonorrhea depends on the localization of the process, virulency of causative agent, age of woman, organism's reactivity, stage of the disease (chronic, acute). Fresh gonorrhea in acute forms has expressed clinical manifestations. Subacute form is characterized by subfebrile condition, sometimes by expressed clinical symptoms, which appeared two weeks before. Torpid gonorrhea in acute form has mild clinical manifestations or is asymptomatic, but N. gonorrhoeae are found in the patient. Latent form is diagnosed when there is no bacteriologic and bacterioscopic confirment, no symptoms, but person is a source of infection. Chronic gonorrhea lasts for more than 2 months, or without establishing of the beginning. Gonococcal urethritis. Clinical manifestation appears within 3-5 days after infection and is characterized by dysuria. Variable degrees of edema and erythema of the urethral meatus, purulent or mucopurulent discharge are present. Gonococcal Bartholinitis. It may occur when N. gonorrhea with vaginal discharge infects the Bartholin's gland. It is manifested by edema, erythema around the duct's os. When the occlusion occurs, pseudoabscess or Bartholin's abscess which are accompanied by purulent process symptoms can develop. Gonococcal endocervicitis. Inflammatory process develops in mucosal layer of the cervical canal. Examination reveals edema and erythema of vagina and part of the cervix. There is a red crown around the cervical os and a mucopurulent cervical discharge. Gonococcal proctitis occurs very rarely. Rectum is involved into the process in the result of contamination with the infected genital discharge. Clinic includes tenesmus and rectal pain. Gonococcal endometritis is the first stage of the ascendant gonorrhea with infection of basal and functional layer of endometrium. It is manifested by lower abdominal pain, high body temperature, sometimes nausea, vomiting. Pain often has spasmatic character. Discharge is sanguine-purulent or mucopurulent. Uterus is painful at palpation. Chronic endometritis is characterized by menstrual disorders. Gonococcal salpingitis is the infection of the fallopian tubes, mostly bilateral. In acute stage the pain in lower part of abdomen is common. It becomes stronger, motion, nausea, vomiting. Menstrual disorders can occur. Gonococcal pelviperitonitis — a specific inflammation of pelvic peritoneum and is a sequel of salpongoophoritis. The onset is acute. Severe lower abdominal pain, peritoneal irritation symptoms, vomiting, meteorism, constipation, high body temperature can be found. Gonococcal inflammation is characterized by the tendency to adhesion process, that leads to localization of inflammation in pelvis. Gonorrhea during pregnancy is often asymptomatic. It can lead to complication of pregnancy, labor and is a risk factor both for the fetus and for the newborn. Possible complications for mother (chorioamnionitis, subevolution of uterus, endometritis) and fetus (premature delivery, unophthalmia, intrauterine sepsis, death) can occur. Artificial abortion is dangerous because of possibility of the uterus, ovaries, tubes infection and other complications. Gonorrhea in children. Mechanism of infection: during delivery when a child passes through infected birth canal, or intrauterine through amnionic fluid, and from ill mother to child while looking after it. Elder children may be infected while using common toilet, sponge, bath. Gonorrhea in girls is acute with the expressed edema and erythema of mucosal membrane, mucopurulent discharge, frequent and painful urination, itching. There can be high body temperature. In girls gonorrhea causes the same complications as in women. Peculiarities of the gonococcal infection: increasing of quantity of capsular and L-forms of N. gonorrhea decreasing of sensitivity to penicillin antibiotics large percentage of asymptomatic and torpid forms reinfection frequent relapsing as a sequele of inadequate treatment urogenital infection is often mixed (Gonococci, Chlamidias, Trichomonades, Mycoplasmas, Candides) This should be taken into account during treatment. Diagnosis of the process is based on the data of complex examination. The disease is characterized by urethritis, bartholinitis, endocervicitis, bilateral salpingitis, proctitis, pelviperitonitis. But diagnosis of gonorrhea can't be confirmed without laboratory tests. Diagnosis of gonorrhea is confirmed by positive results of bacterioscopic and bacteriologic tests of cervical, vaginal, urethral discharge. To acuten the chronic process the so-called "provocation" is conducted: 1. 0,25% solution of argentum nitrici on mucosal membrane of the cervix, vagina and urethra is applied 2. introducing of gonovaccine, pyrogenal, prodigiozan 3. diathermy Smears must be taken on the 2-4th day of the menstrual cycle and after provocation in 24, 48, 72 hours, that allows to reveal N. gonorrhea. Treatment is provided in special clinic. Sometimes the patient is treated by the venerologist in ambulatory. To reveal another sexually transmitted diseases clinical and laboratory examination must be performed. While prescnbing medicines the clinical form, complications and seventy of the process should be taken into consideration The mam medicines in gonorrhea treatment are antibiotics Gonococcal infection very often is accompanied with trichomoniasis, chlamidiasis, candidiasis, mycoplasmosis. Antibiotics that have influence on the following agents such as: Ciprofloxacin, Doxycychn, Trobicyn, Sumamed, Cephtnaxon, Afloxacin m combination with Metronidazol, Tiberal, Naxogyn should be prescribed The dose of antibiotics is taken according to the methodical instructions of the Ukraine MHP and annotation of medicines. Gonovaccme is used after ineffective antibiotic treatment and relapse in the latent fresh torpid and chronic form of the disease (200-300 mln. of microbe bodies, in 2-3 days intramuscularly). During pregnancy immunotherapy and antibiotics with negative influence on a fetus are not used. For toilet of external genital organs 0,002% solution of Chlorhexidme, Re-cutan, Bahz-2 are prescribed Local treatment of chronic gonorrhea is conducted after disappearing of the signs of acute inflammation In chronic and subacute stages physiotherapeutic methods are used, laser radiation, paraffinotherapy, mud-cure, diathermy, inductothermy, U H F-therapy The control of the results of treatment: disappearing of subjective signs and microbe agents in all the infected organs and discharge. On the 7-10th day after medical therapy the bacterioscopic and bacteriologic methods are used to confirm the results of treatment. If there is no N. gonorrhea in the material, then the combined provocation is conducted injection of Gonovaccme (500 mln of microbe bodies), instillation of 1% Lugol's solution in urethra, 0,5% solution of Argentum Nitrate into cervical canal Discharge from this organ should be examined during 3 days. Smears are taken during menstruation and then after provocation in 24, 48, 72 hours. Such examinations are provided during 2-3 menstrual cycles. Women which have contacts or work with children are not allowed to work. Prophylaxis. Using of condom is the most effective prevention method If the sexual intercourse has happened without it, then the external genital organs should be washed with water and soap, and after urination syringing with 0,05% Chlorhexidin solution should be performed Urogenital trichomoniasis Urogenital trichomoniasis is caused by Trichomonas vaginalis and is a result of their invasion into the lower part of genital tract and urethra. Ethiology. Trichomonas vaginalis is a flagellate protozoan and it is transmitted by sexual intercourse. It is not stable in outer environment, dies in few seconds under the influence of antiseptic solutions, in water it dies during 15-45 minutes, and also when they wash hands with soap, it is sensitive to drying. In human organism Trichomonas vaginalis can exist in 3 forms: common one (pear-shape form), amebiform with the expressed phagocytosis action (it can phagocytise mycoplasmas, N. gonorrhea and other bacteria that caused the recurrence of mycoplasmas or gonorrhea. This is the most spread disease among all the sexually transmitted ones. Its frequency rate reaches 5070% of sexually active women. According to the WHO statistics, 10% of world population suffer from trichomoniasis. Non-sexual transmission is very seldom: when they use sponges, underwear, towels. Incubation period lasts for 5-15 days, the main places of trichomonas parasitizing are mucose membranes of vagina, cervical canal, uterus cavity, uterine tubes, Bartholin gland's duct, urethra, urinary bladder. Inflammatory process develops in the infected mucous membrane: edema, hyperemia, exudation, desquamation affects epithelial cells. Clinical manifestations. Vaginitis, urethritis, endocervicitis, proctitis are the most common manifestations, ascendant infection meets rarely. Forms of genital trichomoniasis: fresh (acute, subacute and torpid forms) chronic trichomoniasis (with torpid form and duration of more than 2 months) trichomonas carriage (is characterized by the absence of symptoms, while Trichomonas vaginalis are present) At acute and subacute forms women complain of foamy vaginal discharge with foul odor, vulvar itching, dysuria. Objective data: erythema, maceration, vulva, perineum scratching, cervical erosion, erythema and edema of vaginal mucosa, foamy purulent discharge. At torpid forms clinical manifestations are mild or absent. Chronic trichomoniasis is characterized by vaginal discharge, itching, but there are no inflammatory manifestations, there can be frequent relapsing. Diagnosis. Diagnosis is confirmed by anamnestic data, objective examination, vaginal smears. Peculiarity of the mixed trichomoniasis-gonococcal infection is the longer incubation period. At first trichomoniasis and after gonorrhea is treated. Treatment. The main principles are: treatment of the woman and her sexual partner avoiding of intercourse until the patient and her partners are cured using of antitrichomonades treatment with local treatment, and hygienic procedures: shaving hair on pubis, everyday changing of underwear treatment of accompanying diseases of genital organs Antitrichomonade remedies are metronidazole (Trichopol, Clion, Metragil, Flagil), Fasigyn (Tinidazol), Atrican, Naxogyn, Tiberal, Solkotrichovak, Tergynan. Recently for treatment of trichomoniasis Metronidazole should be prescribed. On the first day they use 0,25g 4 times a day, on the next days — 0,25g 3 times a day. All dosage on treatment course is 5-6 g. Tinidazole is used in such regimen after meals: once 2 g (4 tablets each 0,5 g) 0,5g every 15 minutes 4 times 0,15g twice a day during 7 days Naxogyn is used in dose of 500 mg twice a day 6 days. During pregnancy and breast-feeding all these medicines are contraindicated. Clion-D is used in the form of vaginal tablets 1 tabl. for night during 10 days. Locally antiseptic solution can be used: Baliz-2, 0,002% solution of Chlorhexidin, Trichomonacid. Control of the treatment is fulfilled during 2-3 menstrual cycles. Prophylaxy. To prevent trichomoniasis condom using is recommended. If the sexual intercourse has happened without the condom, then the external genital organs should be washed with water ans soap, and after urination syringing with 0,05% Chlorhexidin solution should be performed. Urogenital chlamidiasis Urogenital chlamidiasis (chlamidiosis urogenitalis) is a rather spread infecti-onal disease, which is transmitted mostly sexually. In women it can be manifested as urethritis, vaginitis, bartholinitis, endocervicitis, cervical erosion, endometritis, salpingitis, pelvioperitonitis, proctitis etc. It can occur even in the newborns (infected during labor). Chlamidial infection occurs in 50% of cases among women with the inflammatory processes, besides these Chlamidias are often accompanied by gonorrhea (40%) and trichomoniasis (40%). According to the WHO statistics nearly 90 millions of the new infected are registered annually. The reason of its wide spreading is mild duration, complicated diagnostics and treatment. More often the women of 20-30 years age become ill. Ethiology and pathogenesis: Infective agent of urogenital chlamidiasis is gramnegative bacteria, Chlamydia trachomatis, preferentially it infects columnar epithelium and reproducts itself intracelluarly. There are two main forms of Chlamidia — elementary body and reticular body. Elementary bodies are the infective form of the agent, which transmit the infection, can exist outcellularly. The cell can be penetrated with few elementary bodies, that have tendency to conflowing, making one particle. During 48-72 hours infected cells are destroyed. Elementary bodies come out from cells and infect the new ones. Reticulative bodies are vegetative forms of Chlamidia and are the result of reproduction in the infected cells, a new generation of elementary bodies. Practically they don't cause the infection. Microscopy allows to identify both kinds of bodies. Chlamidia has a complicated antigenic structure. It is very sensitive to disinfectant substances. At 3537°C during 24-26 hours outcellular Chlamidia become nonvirulent, at temperature 951000C they die during 5-10 minutes. In cotton material they can survive up to 2 days at temperature 19-20°C. The source of infection is the ill person. Ways of transmission: sexual intrapartum (passing through the infected birth canal) nonsexual way (polluted hands, instruments, underwear, toilet, etc.) Besides infection of urogenital organs, Chlamidia trachomatis can cause pharyngitis, conjunctivitis, perihepatitis, otitis, pneumonia, other diseases (Reiter's syndrome). Clinical manifestations. Incubational period lasts from 5 to 30 days. The main primary form of chlamidial infection is endocervicitis with mild symptoms or without any. In acute stage purulent or mucopurulent discharge from the cervix, edema and erythema of the vaginal part of the cervix are observed. In chronic stage there is the mucopurulent discharge and pseudoerosion of the cervix. Chlamidial urethritis can be asymptomatic or it manifests itself by dysuria. There are no specific symptoms for clinical diagnostics of chlamidiasis. Salpingitis, caused by Chlamidia trachomatis, is characterized by the same symptoms like the process caused by other bacteria. The sequale of chlamidial salpingitis is infertility. Diagnosis is based on the history (both partners are ill, there is the infertility). Residual diagnosis is established after revealing chlamidias in the scrap from the cervix and vagina. The most exact are immuno-enzyme and immuno-fluorescent methods. Treatment. It is necessary to cure the woman and her sexual partner. The woman should avoid sexual intercourses, alcohol, psychical and physical overload. Medicines from the tetracyclin group are prescribed (Doxycyclin, Rondo-micyn, Morphocyclin), Sumamed, Tarivid, Macrolids (Clacid, Erythromycin). To prevent candidosis Diflucanum in dose 150 mg is used, Nistatin or Levorin (2.000.000 IU per day during treatment) are prescribed. Fromilid (Clarythro-mycin), an acid-resistant antibiotic from macrolid group is recommended. An important property of this drug is its possibility to cell penetration, that's why Fromilid is 8 times more active, than Erythromycin. It doesn't suppress immune system, activates phagocytomacrophagal system and some enzymes, that take part in destroying of pathogenic bacterias. The dose of fromilid is 500 mg twice a day during 7-14 days in case of fresh incomplicated chlamidiosis. In chronic forms the treatment course must be elongated till 3-4 weeks. At urogenital chlamidial infection medicines from ftorchinolon group, Ciprofloxacin (Ciprinol) are used. Ciprinol is prescribed in the dose of 0,5g orally or 0,2g intravenously each 12 hours during 10-14 days. During treatment the ultraviolet irradiation including sun radiation are contraindicated. Treatment of chlamidiasis demands from the doctor and patient accurate fulfilling of all the indications (dose and duration of the therapy), especially at chronic, longlasting forms of disease. At the same time accompanying urogenital diseases should be treated. To reduce side effects of antibiotics hepatoprotectors, antioxydants, polivitamins are used. Urogenital mycoplasmosis Ethiology. Microbal agents are Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma genitaloum, Ureaplasma urealiticum. In the etiology of the inflammatory diseases of female genital organs the associaton of mycoplasmosis with trichomoniasis, N. gonorrhea, Chlamidia trachomatis, anaerobes is of great importance. Mycoplasmas are transmitted sexually and they are highly spread among the population. Clinic. Mycoplasmas infection can occur in acute and chronic form, and has no symptoms, which are specific for this agent. It is often found in healthy women. Mycoplasmosis is characterized by torpid course, sometimes the latent forms of the reproductive system inflammation are observed. The agents may be activated under the influence of menstruation, oral contraceptives, pregnancy, delivery. Ureaplasma is identified in the patients with vaginitis, cervicitis, urethritis, in association with other bacteria the symptoms are typically and described in the part "Nonspecific inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs". Diagnosis. To reveal ureaplasmas the bacteriological method is used. Material is taken from the purulent discharge of Bartholin's glands, from uterine tubes at salpingitis, tuboovatian tumors at pelvic inflammatory disease. Test on the urease is done (colour index). It is based on the property of ureaplasms to product urease, that changes the pH and the colour of indicator. Serological diagnosis is also used. Immunogram in diagnosis of mycoplasmosis and other infection (Chlamidia, gonorrhea, trochomoniases, herpes simplex virus) is indicated. Treatment. Using of antimicrobal medicines from macrolid group (Erythromycin, Sumamed, Roxitromycin), Tetracyclin group (Tetracyclin, Doxycyclin), Fluorochinolones (Ciprofloxacin) is etiotropic treatment. They are prescribed for not less than 10-14 days with the following laboratory control. Another course of treatment is immunity stimulation (Immunoglobulin, Levamizol, T-activin, Ginseng Tincture). Prophylaxis. Examination of the risk group (prostitutes, women with infertility, inflammatory processes of genital organs), and keeping to the same measures for preventing sexually transmitted diseases are used. Candidiasis vulvovaginitis (Monilia vaginitis) Candidiasis is a polyorganic disease, caused by yeast fungi (Candida albicans, C. glabrata, C. tropicalis). It can be transmitted sexually. The most frequent localization is in vagina, vulva, but there can be candidiasis endocervi-citis, endometritis, salpingitis. Predisposing factors: endogenous long lasting diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, avitaminosis exogenous factors, that predispose fungal colonization and decrease the general reactivity of the organism (long treatment with antibiotics) and local immunity in vaginal mucosa high virulency of Candidas There are such kinds of candididas vulvovaginitis: primary antibiotics-induced (as a result of antibiotic treatment) as a sequale of changes in different systems of the organism (diabetes, pregnancy, using of estrogens) On the suppressed immunity of the organism fungi, that were previously saprophites, become pathogenic. They adher to vaginal epithelial cells, causing superficial inflammation and desquamation of vaginal cells. Genital candidiasis mostly doesn't cause a deep damage of mucosa and spreading of the process, but if the agent has high virulence, it can penetrate into intra- and subepithelium parts. In some cases there can be dissemination of candidiasis. Clinical manifestations: Candidiasis vulvovaginitis is characterized by vulvar itching, pruritus, cottage-cheese-like discharge. Examination reveals edema and erythema of genital mucos with whitish adherent discharge, that include pseudomicelium of fungi, exfoliated epithelial cells and leukocytes. Diagnosis. Diagnosis is based on the clinical manifestations, vaginal examination, colposcopy, bacterioscopic and bacteriological methods. Treatment. Acute form is treated by Orungal 200 mg twice a day during 3 days; at chronic form they use 100 mg twice a day during 6-7 days, then during 3-6 menstrual cycles 1 capsule on the first day of menstrual cycle is taken. High effectiveness is observed while using Diflucan in dose 150 mg per 1 reception, and Gyno-pevaril — one suppository (150 mg) during 3 days. In case of relapse one suppository (50 mg) twice a day for 7 days and application of Gyno-pevaril creme on glans penis during 10 days is recommended. The next step of treatment is normalization of vaginal ecosystem. Prophylaxis: rational antibiotic treatment with keeping to optional doses and duration of the therapy course, in-time using of antimycotic medicines with the preventive aim. Avoiding of premarriage and extramarital relationships, condom using for preventing fungal colonization of the female genital tract. Syphilis Syphilis is an infective disease, that is transmitted sexually. Etiology. The pathogene is Treponema pallidum. In microscopic examination it has spiral shape and is movable. Optional temperature for reproduction of Treponema is 37°C. It is very sensitive to different external conditions. It dies during boiling, drying, under the influence of different chemical agents and 90% ethanol. While working with the infected persons hands are cleaned with ethanol. It prevents from infection at contact with syphilitic rash having Treponema pallidum on its surface. At 40°C (temperature for keeping blood for transfusion in refrigerator) Treponema pallidum dies in 24 hours. The source of infection is the infected person. Ways of transmission: sexual perversion (oro-genital, homosexual contacts) transplacental — congenital syphilis, when a child is infected by transplacental transmission professional — while examining the ill person with wet surfaced rash transfusion (very rarely) — as a sequale of blood transfusion from the ill person Clinical manifestations. 3-4 weeks pass from the moment of agent penetration into organism and till the first manifestations of the disease. This is the so-caled incubational period. The microbe is already in human organism, but there are no complications and signs of the disease. After finishing of incubational period the first signs appear only in the area of agent inoculation. This is the so-called primary lesion (ulcerated shancre). It appears as a painless indurated papula on skin or mucos with erosion or necrosis of the surface. Is a hard-based, well-circumscribed lesion. There is no inflammation around it and it has smooth surface with serous discharge. Its size is from several mm to few cm, and it can be coated with whitish discharge like old fat. On mucos of genital organs or anus it is like fissure. Sometimes shancre can gangrenize. Indurative edema belongs to the atypical forms of shancres. Labia major enlarges in size, they are firm and painless. Chancre on pubis, thighs and cervix can occur rarely. If the shancre is situated on the genital organs, then after nearly 7 days the inguinal lymphatic nodes enlarge on one side (scleradenitis, bubo), rarely on both sides. They are firm, movable, painless. They are not connected with skin and have no suppuration. This is the primary syphilis, that lasts for 6-8 weeks from the appearing of the shancre (the first 3-4 weeks is primary seronegative period, when Wassermann reaction is negative, and next 3-4 weeks, when Wassermann test is positive). Diagnosis in this period is based on the history taking (sexual contact, incubation period, examination of sexual partner, revealing of Treponema pallidum on shancre surface, positive serological reactions (Wassermann's, immunofluorescence). Without identification of the agent or positive serological reactions diagnosis of syphilis is not proved. After 6-8 weeks of shancre development, the body temperature may rise, there is the night headache, bone pain can appear. This is the so-called prodromal period. During this time the agents are reproducted intensively, they appear in blood (treponems sepsis) and there is disseminated rash on skin and mucosal layer. There appear the signs of secondary syphilis. Firstly roseolas (little red macula 0,5-1 cm in size) appear on body skin. They disappear for a while after the finger pressure, don't protuberate over the skin level. After some period papulas, very rarely pustulas or hair shedding appear. In this time on skin and mucos of the female genitals papula (erosion nodes) can appear. They are firm, without inflammation, up to 1 cm in diameter, with moist surface, rich in microbal agents (Treponema pallidum), that make them very infectious. There are no subjective feelings. As a result of irritation these nodes enlarge, indurate and transform into the so-called condyloma lata, 0,5-1 cm and more in diameter, indurated, prominating above skin level, without signs of acute inflammation, painless, with smooth or tuberous, sometimes with moist surface. There are plenty of agents on the surface of condyloma lata and they are very contagious. They should differ it from viral pointed condylomas (soft, on the pedicle, with lobular, like cauli-flower structure). Diagnosis is confirmed by presenting erosional papulas and condyloma lata, positive serological reactions (Wassermann's reaction, reaction of immobilization of Treponems). Treatment of syphilis is provided by penicillin antibiotics (bicillin, retarpen, extencillin) in venerologic dispensary, according to the instructions of the Ukrainian Ministry of Health Care. Prophylactic measures: avoiding of extramarital relationships, using of condom. If coitus was without condom or it has been torn, then the external genital organs should be washed with soap and warm water, and during the first 2 hours the cleaning of genitals should be performed. AIDS Agent of AIDS is retrovirus, which affect immune system of organism. There are two types of Human immunodeficiency virus, that caused acguired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): HIV-1 andHIV-2. HIV-1 is spread in all the countries of the world. HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is very sensitive to heating, while at boiling it dies immediately, as well as after applying of 70% Ethanol, 0,2% solution of Natrii hypochlorate and other desinfective solution. But this virus survives in its dried form during 4-6 days in 22°C temperature, in lower temperature even more. The source of infection is the ill person or viral carrier. People with AIDS are infective all over the life. The quantity of people with HIV in many times prevalents the quantity of ill person with AIDS. Infected person becomes contagious in a very short time — 1-2 weeks after infection. The ways of infection: sexual, which insures natural viral transport from one person to another, as well as sequel of homosexual contacts parenteral way of infection occurs when they break the sanitary rules making injections, especially intravenous, when injections are made with one syringe, with changing only the needle professional way of infection of medical personnel occurs when blood of the person with AIDS contacts with lesioned skin (microtrauma, fissure etc) or mucosal layer during manipulations (injections and others) transfusional way occurs very rarely, when the infected blood is transfused to the healthy person transplacental — from the infected mother to the child So, HIV infection can be transmitted from people to people in direct contact: "blood to blood" or "blood to sperm". Transmission of virus through saline during kissing is less possible. The virus isn't transmitted by insect stings. Clinical manifestations of AIDS: Incubation period can last from 1 month to 10 months or even to years. Clinical manifestations may vary, they can be divided into some periods. In 30-50% of the inspected persons in 2-4 weeks an acute period can be observed: fever, tonsillitis, enlarging of neck lymphatic nodes, liver, spleen. This lasts for 7-10 days, and then the disease becomes latent. The only sign of illness at this time may be the enlarged peripheral lymphatic nodes. They are movable, not connected with tissues, some of them are painful at palpation. Such enlarging of the nodes can indicate to the AIDS, if it lasts for more than 1,5-2 months. Later the so-called AIDS-associated or premorbid complex of symptoms is developed. It can last from 1 to 6 months during some years. In this time many different symptoms and diseases which are not specific for AIDS (up to 200) are developed. That is the long-term fever, generalized enlarging of peripheral lymphatic nodes, periodical diarrhea, weight loosing (more than 10%), oral cavity candidiasis, leukoplakia of tongue, folliculitis, different skin lesions. This period lasts wave-likely while health becomes better till the clinic remission, when person considers himself absolutely healthy. The last period is AIDS. In such persons different infectious diseases occur (up to 170) on the base of immunodeficiency, caused by HIV-infection. Nervous system is damaged (in 30-90% of patients), poor orientation, bad memory and demention are develops. Pneumocystic pneumonia (lung inflammation) occurs up to 60% with severe, sometimes with fulminant passing. In 60% of cases severe and long-termed diarrhea is observed. Kaposhi's sarcoma very often progresses and becomes the reason of death at young age In significant part of patients having AIDS, malignant processes like Lymphoma and others are developed as a result of virus influence on immune mechanism of human being. Skin and mucosa are damaged with Candida fungi (candidiasis, Herpes simplex and Circular herpes virus with severe, relapsing duration, they don't undergo to usual methods of treatment. Diagnosis. In AIDS the following diagnosis are mentioned: epidemiological history (homosexualism, drug abuse, prostitution, intravenous injections etc.) a long-term enlargening of peripheral lymphatic nodes, loosing of body weight, long-term fever and diarrhea revealing of antibodies to HIV in blood by immuno fluorescent analysis and others. 5 ml of venous blood is taken, and it is kept in refrigerator at the tempreature of+2 — +4°C. Serum is taken out after appearing of the blood the clot and sent to the laboratory not later than in 1-3 days. Treatment. There are no medicines for treating AIDS. But remedies, that inhibit development of the disease are used. Nowadays there is an effective preparation for treatment of HIV infection and AIDS — Krixivan (protease inhibitor). Triple therapy of Krixivan base (Krixivan+AZT+ZTS) has high effectiveness, decreases quantity of viruses in blood to lower level. Immunostimu-lators, immunomodulators, symptomatic therapy depending on the pathology is used. Prophylaxis: sanitary and educational work among inhabits avoiding of pre- and extramatrial relationships using of condoms (decrease the transmission in 200-500 times) prophylaxis of drug abuse, parenteral (subcutaneous or intravenous) injectons of medicines proper sterilization of medical instruments, using syringes and needles of single use using special defence agents by medical workers contacting with patients' blood and other biological substances (special closes, double gloves, goggles, masks) control of donor blood VIRAL DISEASES The quantity of viral diseases of genital organs has been significantly incincreasing for the last time, especially among young people. Viral infections can occur in latent form, with less symptoms and with expressed clinical manifestation. That's why it is very difficult to diagnose them. These diseases have especially negative influence on the pregnancy. There is a risk of viral transmission to fetus. They can cause fetus diseases or defects of development, leading to fetus death or miscarriage." Every pregnant woman with miscarried fetus must be examined on these infections presence, because in the majority of such women Cytomegalovirus, Gripp virus, Hepatitis A and B virus, Papillomavirus are revealed. Besides the influence on fetus, according to the recent investigations, viral infection causes malignant growth in the female genital organs. Herpesvirus infection Herpes virus diseases of genital organs are caused by Herpes simplex virus, mostly of the second type (HSV-2). Source of the infection are infected persons and carriers. It may be revealed in young sexually active women. It can be transmitted during orogenital contact. The virus is located mostly in mucos membranes of urogenital tract in men and cervical canal in women, also in the nervous ganglions of lumbar and sacral parts of sympathetic nervous system. Genital herpes is transmitted sexually. During pregnancy it may cause miscarriage and malformations. Genital herpes is considered to be all-life persistant infection, that's why it has a relapsing passing. Clinical manifestations. According to the clinical signs, the disease duration is divided into typical, non-typical, and asymptomatic one (viral carrier). Typical passing of the disease is characterized by genital and extragenital signs. Extragenital signs: rising tempreature, mialgias, headache, nausea, viral rash on face, bad sleep. Genital signs are present on the lower parts of genital system — vulva, vagina, cervix, near urethra os perineum. Single or plural vesicles up to 2-3 mm in size, with erythema and edema, which exist for 2-3 days appear in mucous membranes. After vesicle rupture erosion with incorrect form, covered with yellow discharge appears. The erosion re-epitheliazes without scars in 2-4 weeks. Patients complain of pain, irritation, itching in area with viral lesions. Clinical manifestations are in three forms: I — acute primary II — chronic recurrent III — atypic Depending on the localization, genital herpes is divided into three stages: the first one — herpes lesions of external genital organs the second — herpes lesions of the vagina, cervix, urethra the third — herpes lesions of the uterus, adnexa, bladder Diagnosis is based on history taking, complaints, objective examination, revealing of HSV-2 or its antibodies in the patient's serum. The most informative method of identification is isolation of the virus from discharge of the cervix, vagina, uterine cavity, urethra. For express-diagnosis a method of fluoriscine antibodies and immunoperoxydase method are used. There is electromicroscopic method of HSV-2 identification and the method of viruses inoculation on tissue culture with the following studying of their properties. Treatment is difficult because of the relapses of the disease and possibility of reinfection. Antiviral medicines belong to three main groups (according to the action mechanism): replication inhibitors of viral nucleic acid interferon and compounds, that have interferon-inductive action compounds with other antiviral action Difficulties of treatment are caused by virus peculiarities (they are obligate intracellular parasites). As a result of investigation of virus nature on molecular level, new medicines were created. They have the influence on viral growth and development of the virus. They are Zovirax (Acyclovir, Valacyclovir), Alpizarin, Foscarnet, Valtrex, Herpevir. Acyclovir is used in dose of 600-1200 mg per day, orally or intravenously. Local therapy by 3% Megasin ointment, 3% Bonaphton or 3% Alpizarin is also used. For treatment of the recurrent herpes antiviral medicines, herpal vaccines, antirecidive immunotherapy are used. Condylomas acuminata Ethiology. Condylomas acuminata are caused by Human Papillomavirus of 16 and 18 types. They are transmitted sexually. Resistant to disinfective agents viruses may be killed by high temperature during sterilization. Incubational period of condyloma acuminata lasts from 1 to 9 months. The disease often occurs in sexually active persons. Papillomavirus causes genital cancer. These patients have in 1-2 thousands times more chances to acquire a malignant process, than healthy people. Condylomas acuminata can transform into cancer in 6-26% of cases. Clinical manifestations: On the onset of disease single pink, sometimes grey warts, with thin pedicle, rarely with wide base appears on skin surface of labia majora, perineal area and mucosal layer of urethra, anus, vagina, cervix. Condylomas acuminatum can grow significantly and fuse. They looks like cauliflower, with lobular structure, and have long-term duration. Some patients with long-term duration of the process can have big condylomas, like tumor. They can be complicated by abnormal vaginal discharge, due to the secondary vaginal infection. Condylomas may cause some difficulties at walking, intercourse. During pregnancy and delivery they can cause bleeding. In 1517% of patients regression may occur, especially during pregnancy. Clinical diagnosis. Lobular surface, soft consistency, thin pedicle should be taken into consideration. Differential diagnosis for genital warts includes condylomata latum, which have wide base, brown or red colour, and no lobular structure. Also other manifestations of syphilis are present there. Treatment. If genital warts are large, laser vaporization is performed. It is more effective, than criodestruction or surgical diathermy. For treatment of small condylomas 30% solution of Podophyllin, Condilin or Resorcin are used. Modern effective remedy is Solcoderm. Molluscum contagiosum Ethiology. Molluscum contagiosum is caused by virus, that is transmitted by contact with the ill persons or during using their things. In adults the main way of transmission is sexual contact. Children are infected more often. Incubation period lasts from 2 till 9 months. Clinical manifestations. On skin the small firm dome-shaped papules 5-7 mm in diameter, occasionally enlarging to 1-3 cm conglomerates is appeared. The fleshcolored papules have specific central umbilication. Lesions are located on the external genital organs, perineum, pubis, hips, face. Molluscum contagiosum can persist for a long time. Clinical diagnosis. After direct pressure by forceps white caseous material can be got. Treatment. The lesions are pressed by forceps and cleaned by Iodine solution or Betadine, garlic juice or cryotherapy. Cytomegalovirus infection Infectional agent is Human cytomegalovirus. The percentage of the infected women according to the world literature is very high. In Western Europe it is from 50 to 85%. Among pregnant women with usual miscarriage 70% are infected. After invasion cytomegalovirus persists in organism for a long time, spreading by saline and sexual contacts. Clinical manifestations. The main signs of the infection are extragenital symptoms: CNS-lesions, thrombocytopenia, liver disorders, pneumonia. Infecting of the fetus during pregnancy leads to intrauterine development defects (microcep-falus, deafness), diseases of the newborn (cerebral paralysis, miasthenia). It is manifested by cervicitis, cervical erosions, vaginitis, vulvitis and other inflammatory diseases, that have subclinical passing. Diagnosis: Blood and urine tests for virus presence are performed. Cyto-scopic analysis of saline and urine sediments are based on the properties of Cytomegalovirus to penetrate into the cells and to make big intranuclear inclusions. Infected cell becomes bigger, it is the so-called cytomegalovirus cell, "an owl's eye". Serological methods: indication of antibodies components to HCMV (1:8 and more is considered to be positive). Non-direct immunofluoriescence method and DNAdiagnostics (chain polymerize reaction) are used. Treatment. The main purpose is the correction of the immune system disorders. Preparations for immunity stimulation (Levamizol, T-activin, Immunoglobulin, Ginseng tincture) are used. Application of ointment and injection of leukocyte interferon, immunoglobulin with high titred cytomegalovirus antibodies ("Citotect") into cervix are used. Wide spectrum of antiviral preparations (Valtrex, Acyclovir, Ribavirin, Gancyclovir, Bonaphton) are less effective. Prophylaxis. Avoiding of pre- and extramarital sexual contacts, using of condom, keeping the rules of personal hygiene. Tuberculosis of genital organs Genital tuberculosis is the secondary disease. Very often clinical focus is in lungs. The disease is caused by Mycobacteria tuberculosis, which is transmitted hematogenically from lungs or intestine to genital organs. Mostly women from 20 to 40 years of age become ill. Tuberculosis infection is found in 5-8% of patients with inflammatory diseases of genital organs, and in 1-3% of patients with salpingoophoritis. Mycobacteria tuberculosis contaminate into genital organs mostly in childhood, but clinical manifestations appear in the puberty period, with the beginning of sexual life and after supercooling. Tuberculosis damages uterine tubes (85-90%), rarely uterus and ovaries, and more rarely — the cervix, vagina, external genital organs. According to Aburela E. and Petersuc B. (1975) classification, there are four main forms of specific process in the female genital organs: tuberculosis of genital organs with microdamages mostly with productive character, and latent duration tuberculosis of genital organs with macrodamages mostly with exudativeproliferative or caseous character, and lasts like salpingoophoritis and endometritis, accompanying with ascites or adhesive peritonitis associative tuberculosis of genital organs and tuberculosis of other organs (lungs, kidneys) or tuberculosis of genital organs, combined with the other gynecological diseases (endometriosis, sclerocystic ovaries, uterine myoma) clinically curable genital tuberculosis with posttuberculosis changes (petrification, adhesions, degeneration) Pathomorphological examination reveals inflammatory changes. Morphological specificity of them is in presence of tuberculous granuloma in productive phase of inflammation a focus of caseous decomposition with exudative phase of the process. If antituberculosis medecines are used in exudative inflammation phase, the exudate resolves with complete or almost complete renewing of tissue structure. Destruction of the tissue is substituted by the connective tissue in productive phase of the process. Separation of the focus from intact tissue take place in case of caseous damage resolvation of perifocal infiltration and fibrose transformation of the destruction zone with the capsule. In such focus Mycobacterium tuberculosis can stay for a long time and in some cases it causes relapsing. Clinical manifestation. At "small" forms of tuberculosis pain syndrome is absent. Dominant sign may be menstrual dysfunction (hypomenorrhea or algodysmenorrhea). Pain appears in case of large damage. Almost all the patients with genital tuberculosis suffer from reproductive disorders, i.e. primary or secondary infertility, ectopic pregnancy. If the changes in endometrium are significant, amenorrhea (uterine form) can develop. General changes in the patient's organism are accompanied by the signs of tuberculosis intoxication: disorders of general state, weakness, sweating, sub-febrile temperature. Diagnosis. Diagnosis is based on the history data (contact with tuberculosis patients, previous tuberculosis of bones, lungs, bronchitis, pneumonia, long-lasting subfebrile condition), objective examination (tuberculosis changes in organs or their sequel), bacteriological examination, additional methods of examination, including histological. For confirming the diagnosis of tuberculosis special tests are used (Mantu, Koch's). The Mantu test identifies only the specific sensitization of the patient and has less diagnostic value. For diagnosis the Koch's test is important. General, local and focal reactions appear after subcutaneous injection of 20 IU of tuberculin in patients with tuberculosis. General one is manifested by high temperature, headache, weakness. Focal reaction manifests itself in 48-72 hours by enlarging of adnexal infiltration, they become more painful. The Koch's test can be confirmed by changes in hemogram (high quantity of leukocytes at the expence of the low amount of monocytes, eosinophiles and lymphocytes), proteinogram (low amount of albumin and high amount of globulines), immunogram. C-reactive protein and high level of sialic acid appear in blood. Bacteriological method is very important, it is in revealing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in uterine and adnexal tissue. Material for inoculation is discharge from uterus and vagina, punctate from ovarian tumor or tissues taken during laparoscopy. Laparoscopy is a valuable method, it allows to perform visual examination of abdominal cavity and to take tissual samples for bacteriological and histological analysis. Rentgenological examination of genital organs and thoracic cavity are necessary, especially in patients with first manifestations of the process in the uterus or adnexa. Hysterosalpingography allows to estimate uterine cavity state, uterine tubes, their permeability and other changes, caused by tuberculosis. Histological examination of endometrium after uterine cavity curettage is important, too. Ultrasonic echography for estimation of morphological changes in uterus and its adnexa is also used. Treatment of genital tuberculosis is complex and includes rational regimen, dietotherapy, vitamins, symptomatic therapy and climatic health-resort cure. The main is the antibiotic therapy. Antituberculosis agents, being in Mse now, are: Rifampicin, PASA, Ethambutol, preparations of Izonicotine acid. For preventing mycobacterium persistation, combination of remedies (Izoniazide + Rifampicin) are used. If the process is revealed for the first time, or it has acute or subacute passing, three preparations are prescribed: antibiotic, one preparation of Izonicotine acid (Izoniazide, Saluzid) and PASA. The last one has not only bacteriostatic action, but also prevents from development of microorganisms resistention to antibiotics and preparations of izonicotine acid, that's why they can be used for a long time. Treatment lasts for 1,5-2 years, during the first 3-6 months the combination of 3 medicines is used, and later on for 6-8 months 2 agents are taken. After that supportive therapy is performed till 2 years. Intramuscular and oral usage of medicines are combined with injection of some dose of medicine in focus of lesion. Lidase with antibiotics and hydrocortisone are used for this purpose by means of colpocentesis to the damaged organ. These medicines may be used during hydrotubations. 1 % solution of chimo-tripsin is used through posterior fornix and by electrophoresis. In some cases surgical treatment is used. In spring and autumn antirecidive therapy is performed. Rehabilitation of such patients is provided in specialized health resorts (Odessa, Alupka). For resolvation of residual affects after tuberculosis physiotherapy and pelotherapy are used.