Heredity: State Objective: 3d & 3f
advertisement

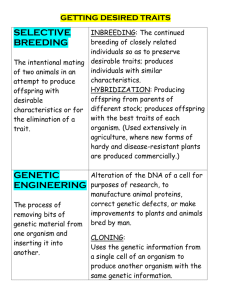
Heredity State Objectives 3d & 3f ___________ (Deoxyribonucleic acid) • • • • Chemical inside cell that contains __________________________ information _________________________ how an organism will look & behave Shaped like a __________________ ladder Rungs hold ______________________ information that is a pair of bases Reproduction • Reproduction is the process of producing a _________________________ organisms • The purpose is to transfer _______________________ Sexual Reproduction • New organisms is produced from the ______________________ DNA of _____________ different cells called sex cells. – Male is called _______________________ & Female is called __________________________ • ___________________ occurs when an egg and sperm unite to form a new organism with half of each parent’s DNA • ___________________ sexually reproduce from male and female parts of a flower • Sex cells are formed by the process of ___________________________ Meiosis • During meiosis, the chromosome pairs ___________________ and are distributed to 4 different cells. The resulting sex cells have only _________________________ as many chromosomes as the other cells in the organism. Heredity • The _________________________ of traits from parent to offspring • _____________________: physical characteristics of an organism –Example: eye color, hair color, & height Passing Traits to Offspring • Sex cells have ___________ chromosomes and the two sex cells combine to form a zygote with 46 chromosomes • During fertilization the offspring receives ____________ of its genetic information from its mother and the other half from its father. Genetics • The _______________ of how traits are passed from parent to offspring by looking at genes – _______________ are small sections of DNA on a chromosomes that has information about a trait • Each ______________________ has a gene for the same trait (eye color from mom & eye color from dad) – Traits are determined by _____________________ on the chromosomes • Each gene of a gene pair is called an _____________________ – Inherited traits are ________________________ by the alleles on the chromosome The DNA Code • Chromosomes are made of _______________________________. • Each chromosome contains thousands of genes. • The sequence of bases in a gene forms a _______________________ that tells the cell what protein to produce. Genes on a Chromosome • Chromosomes are made up of many ____________________ joined together like beads on a string. • The chromosomes in a pair may have _____________ alleles for some genes and the same allele for others. Genome • Scientists map a genome to identify all the organisms genes & figure out where they are located – A _______________________ is the complete sequence of an organisms DNA The Sex Chromosomes • The __________________ chromosomes carry genes that determine whether a person is male or female. – also carry _________________________ that determine other traits. – _________________ = female – _________________ = male Types of Alleles • _________________________ Alleles describe a genetic factor that is always expressed. – It ________________________ a recessive trait from showing up in offspring. – Represented by ________________________ letters (B) • ___________________________ Alleles describe a genetic factor that is not always expressed. – It only expresses itself when __________________ of the recessive traits are ______________________ – Represented by ______________________________ letters (b) Examining & Studying Traits • Two ways scientist study traits – _________________________: outside expression of a gene • Blue Eyes – _______________________: the two alleles a person has inherited that can only be seen on the DNA • BB, Bb, or bb • Two categories of genotypes – ___________________zygous: inherited two identical alleles • BB (pure dominant) or bb (pure recessive) – ___________________zygous: inherited two different alleles • Bb (hybrid) Punnett Squares • Shows all possible ___________________________ of alleles that children can inherit from parents • Mom’s genotype for brown eyes (__________) • Dad’s genotype for brown eyes (___________) • Offspring’s Phenotype – 75% brown, 25% __________________ • Offspring’s Genotype – 25% ___________, 50% Bb, 25% bb Punnett Square Practice • What is the genotype and the phenotype for each parent? ___________________ • What are the possible genotypes and the phenotypes for the offspring? _____________________ Co-dominance • In co-dominance, the alleles are neither dominant nor recessive. As a result, _______________ alleles are expressed in the offspring. • FW FB = black & white, FB FB = black, FW FW = white Incomplete Dominance • In incomplete dominance, one allele is not completely dominant over the other allele. As a result, both alleles have a _____________________________ expression. • RR = red, WW = white, RW = pink Pedigree • Geneticist use pedigrees to ________________________ a human trait to learn how the trait was inherited • A _______________________ is a chart or “family tree” that tracks the members of a family that have a certain trait. • Circles stand for __________________________ • Squares stand for _________________________ • A line connecting a square & circle shows they are married • Shaded = person ____________________ the trait • Half-shaded = _________________________ one allele for the trait but does _________________have the trait • No shading = person does _______________________have or carry the trait Pedigree Practice • What does this symbol stand for? Male or female • What does the shading of this symbol represent? _________________________ Biotechnology • __________________________________ is the manipulation of living things to make useful products – Causes __________________________ in an organism • Examples of genetic biotechnology Selective Breeding • ___________________ Breeding is an intentional mating of organisms to produce offspring with specific traits • Pure breeding – Crossing two individuals that have ________________________ or similar sets of alleles. • Example: breeding only fast horses, breeding only labs – Con – _____________________ genetic variety therefore makes it harder to adapt, resist diseases, and higher chance of genetic disorders • Hybridization – Crossing two genetically _______________________ individuals. The Hybrid organism is bred to have the ________________________ traits from both parents. • Example: Labradoodles, corn produces lots of kernels with one resistant to disease – Con – doesn’t always turn out the planned way & is time consuming • Can ___________________ easily __________________ weather the dominant or recessive trait will appear Genetic Engineering • Genetic engineering _________________________ the genetic material of a living organism by removing genes from one organism then transferring them into the DNA of another organism. (gene splicing) • Uses: – Make medication and treat ______________________________ – _______________________ human genetic disorders – Improve crops • ________________________ were the first success with genetic engineering because they are one celled and not as complex. • Ex. Insert bacteria DNA into rice, wheat, and tomatoes to enable plants to survive in colder temps, poor soil conditions, and resist insect pests. Gene Therapy • Gene ____________________ is an experimental technique that uses genes to treat or ________________________ disease by inserting working copies of a gene directly into the cells of a person with a genetic disorder • Researchers are testing several approaches to gene therapy, including: – ___________________________ a mutated gene that causes disease with a healthy copy of the gene. – ____________________________, or “knocking out,” a mutated gene that is functioning improperly. – ____________________________ a new gene into the body to help fight a disease.