Injections
advertisement

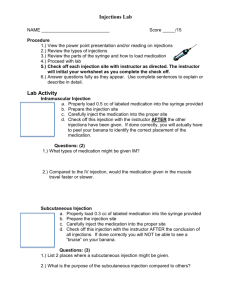
Injections Anesthetic Administration Veterinarians are responsible for evaluating anesthesia requirements for every animal. This protocol must be documented on each patient record by the veterinarian or by animal health technicians under the direct orders of the veterinarian, prior to the start of surgery. Pre-anesthetic, anesthetic and anesthetic reversal agents will be administered only on the order of the veterinarian. The person who administers the medication (gives medication to the animal) will initial the medical record, next to the name of each drug given, at time of administration. SQ, IM and IV Injections A new, sterile syringe and needle will be obtained and used for every injection. Never re-use or re-autoclave any syringes or injection needles. Read the label of every medication at the time you are obtaining medication and again before you administer the medication to ensure the administration of proper medications. Double check the patient’s medical record and the patient’s ID neckband prior to medication administration. All new employees will be observed by an experienced animal health technician or veterinarian in their medication injection and blood collection technique and cleared for performance of both procedures after their level of competency is assessed. Any technician who is unable to administer medication as prescribed or successfully collect blood after two attempts will ask for assistance from another technician or the attending veterinarian. SQ: Used to administer medication into the subcutaneous space between skin and muscle. With the free hand, raise a fold of skin over the area near the shoulder blades behind the neck. This prevents irritation and scratching at the injection site by the animal. Next, clean the injection site by swabbing with alcohol and clean cotton ball. (This is particularly important during public vaccination clinics.) Place needle and syringe closely perpendicular to the fold and roughly parallel to the animal’s trunk. Pull the skin fold back over the tip of the needle until it has penetrated to the center of the fold. Aspirate slightly to confirm that the needle is not in a blood vessel prior to giving any SQ injection. After aspirating slightly, inject medication. If blood is present in the needle hub after aspiration, remove the needle and syringe and select another injection site. IM: Used to administer medication into the muscle mass. After selecting the injection site, clean the site by swabbing with alcohol and clean cotton ball. Grasp the muscles between thumb and fingers and insert the needle perpendicularly. Aspirate slightly to confirm that the needle is not in a blood vessel prior to giving the injection. Absence of blood in the hub of the syringe after aspiration indicates the syringe is not in a blood vessel. Inject the medication and withdraw the needle. If blood is present in the needle hub after aspiration, remove the needle and syringe and select another injection site. IV: Used to administer medication directly into the vascular system by a venous structure. Before using this method, check your medication to confirm that it is compatible with this route of administration. In general, it will be helpful to have an assistant help restrain an animal for an IV injection. Distend the cephalic vein with a tourniquet or digital pressure provided by the assistant. Wet the dorsal surface of the foreleg with alcohol to help visualize the cephalic vein. Stabilize the vessel with the thumb of your free hand. With the needle of your syringe parallel to the vein and beveled side up, smoothly pierce the vein from the side opposite your thumb in a smooth forward movement. Check your location by aspirating a small amount of blood into the syringe. Release tourniquet or digital pressure, stabilize the syringe with your thumb to prevent needle from exiting vein, then slowly depress the plunger to inject the medication. NOTE: IN GENERAL IT IS MUCH SAFER TO GIVE ALL IV MEDICATIONS AT A SLOW AND MEASURED PACE. THIS IS CRITICAL IN THE ADMINISTRATION OF SOME MEDICATIONS SUCH AS KETAMINE AND YOBINE IN WHICH CASE FAILURE TO INJECT SLOWLY MAY INDUCE SEIZURES OR CAUSE CARDIAC ARREST AND DEATH. After administration of an IV injection and withdrawal of the syringe and needle from the injection site, it is necessary to apply pressure to the injection site for hemostasis. Pressure may be applied with a free hand or finger or a small bandage made from a cotton ball and a piece of 1" tape. Blood seepage on an animal’s coat should be promptly cleaned with hydrogen peroxide and gauze sponges. Any technician who is unable to successfully locate a vein and administer an IV injection after two attempts will ask for assistance from another technician or the attending veterinarian. Blood Withdrawal Begin as with an intravenous injection. At the point of aspiration, simply continue to fill your empty syringe with blood. Release pressure distending the vein before withdrawing your needle. Place slight pressure over site of venipuncture after withdrawal for hemostasis. When collecting most blood samples, it is helpful to coat the inside of your syringe with heparin prior to obtaining blood. The presence of heparin will prevent the sample from clotting in the syringe. Care should be taken to discard all heparin from the syringe prior to blood withdrawal into the syringe. Too much heparin will dilute the blood sample thus altering some lab results. The amount of heparin that remains in the needle hub is sufficient to prevent the blood sample from clotting in the syringe.