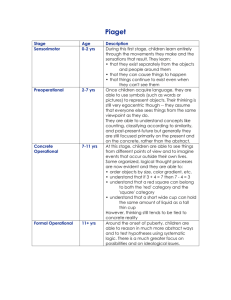
1. A child is presented with two identical beakers containing the
advertisement

1. A child is presented with two identical beakers containing the same amount of liquid. The child is asked to pour the liquid from one beaker into a tall, thin beaker. If the child says that the tall, thin beaker now contains more liquid, the child has not reached Piaget’s stage. a) sensorimotor b) preoperational c) concrete operational d) formal operational 2. Ally tried to build her new puzzle using the same strategy she always used. When that didn’t work, Ally tried a new approach. When she tried the new approach, Piaget would say she had a) accommodated b) assimilated c) demonstrated reversibility d) conserved 3. An adult rolls one of two identical balls of clay into a long, thing rod and then asks a child which shape contains more clay. If the child states that the amounts are equal, the child has entered the stage. a) sensormotor b) concrete operational c) formal operational d) preoperational 4. A teenager who is concerned about the effects of the terrorist attacks on the United States on September 11, 2001 on racial prejudice has reached Piaget’s stage. a) formal operational b) preoperational c) sensorimotor d) concrete operational 5. Which statement reflects Piaget’s thinking about the cognitive stages? a) All people pass through the same stages but not necessarily in the same order. b) All people progress through the stages in the same order but not at the same rate. c) All people progress through the stages in the same order and at the same rate. d) Very bright children sometimes skip stages 6. Three year old Danielle says “Airplane!” when she sees a helicopter for the first time. She is using the process Piaget called. a) Assimilation b) Centration c) Conservation d) Accomodation 7. Four year old Kendra rolls her ball of clay into the shape of a wiener to make “more” clay. Her actions demonstrate that she has not acquired the concept of a) Reversibility b) Animism c) Centration d) Conservation 8. Not all individuals reach the stage of formal operations. a) true b) false c) N/A d) Only baboons reach formal operations 9. According to Piaget, a group of three year old children who are pretending that they are characters in a popular cartoon are demonstrating processes. a) physical b) cognitive c) socioemotional d) genetic 10. An infant who tries to reach for a toy that has been placed behind her mother’s back has developed the concept of . a) Assimilation b) Egocentrism c) Object permanence d) Conservation Answer Key: 1 (c), 2 (a), 3 (b), 4 (a), 5 (b), 6 (a), 7 (d), 8 (a), 9 (b), 10 (c) Sources of these questions came from: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0070914028/student_view0/chapter4/multiple_choice_quiz.html http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/novella/QuizProcessingServlet Santrock, J., Mitterer, J., Psychology 2:Canadian Edition. McGrawHill In-Psych., accompanying CD Rom. The understanding that objects still exist even if they can’t be seen/heard/touched: a. b. c. d. object permanence conservation cognitive development assimilation What are the four stages of Cognitive Development (in the correct order): a. b. c. d. pre-operational, concrete, sensorimotor, formal sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete, formal cognitive, formal, sensorimotor, preoperational formal, sensorimotor, concrete, accommodation A four month old infant first puts a new object into their mouth as their knowledge of objects is that they are for eating or sucking. This is an example of: a. b. c. d. schemes cognition accommodation assimilation Because five year old Frankie likes spiders, he believes that everyone likes spiders. This is an example of: a. b. c. d. assimilation object permanence conservation egocentrism 14 month old Amanda believes that her teddy bear, which is hidden under her bed, does not exist. What stage is Amanda in? a. b. c. d. concrete formal sensorimotor preoperational As teachers, using the technique of scaffolding in the classroom to teach a new concept assists in the process of: a. b. c. d. assimilation construction achievement accommodation Genetic Epistemology is: a. b. c. d. the study of DNA the study of how knowledge emerges in a person the study of how genes determine knowledge a mad genetic scientist Answers: A B D D C D B 1) Piaget’s main method of research was: a) intelligence tests b) observation of his own children and children in schools c) observation in a laboratory setting d) questionnaires of parents and teachers 2) Piaget believed development was a result of: a) genetics alone b) biology and the environment c) social conditioning alone d) pure instinct 3) The concrete operational stage occurs during what ages? a) 2 – 7 b) 7 – 9 c) 12+ d) 7 – 11 4) The definition of assimilation is: a) changing an existing schema to fit a new idea b) fitting new information into existing knowledge c) altering or creating new knowledge in response to new information d) associating to ideas to be equal 5) A left-handed child begins going to a new school. He finds out that his new school has only right-handed desks. The child adjusts by sitting at an unusual angle in the desk while writing. This adjustment in his sitting pattern is an example of: a) preservation b) conservation c) accommodation d) none of the above 6) Fred is smarter than Jeff; Fred is not as smart as Debbie. Who is the smartest of the three, or is it impossible to tell? If a child can give the correct answer this hypothetical question that child has reached the stage of: a) concrete operations c) formal operations stage b) intuitive stage d) conceptual operations 7) It is sometimes useful to present information to learners at a level of abstraction slightly higher than that at which they are comfortable. a) True. Only if this happens are they likely to move to higher levels of abstraction. b) False. Learners cannot assimilate information that is presented to them at a higher level of abstraction than that at which they feel comfortable. c) False. Learners cannot accommodate to information that is presented to them at a higher level of abstraction than that at which they feel comfortable. d) False. Equilibration cannot occur when information is presented at a higher level of abstraction than that at which learners feel comfortable. 8) If a child says, “I don’t live in Canada, I live in Ontario!”, what developmental stage is this child in? a) Pre-operational b) Formal operational c) Sensorimotor d) Concrete operational 9) When a child realizes the cause-and-effect relationship of their actions they are in the: a) pre-operational stage b) concrete operational stage c) formal operational stage d) sensorimotor stage 10) Rule: If a card has a vowel on one side, then it has an even number on the other. Of the cards shown, which would need to be turned over to tell if this rule is true? E a) the E and the 4 c) all of them K 7 b) the E d) the E and the 7 Answers: 1) b 2) b 3) d 4) b 5) c 6) c 7) a 8) a 9) d 10) d 4 Multiple Choice Questions: 1. Accommodation refers to a) incorporating new information into your schema b) adjusting your schema to fit in new information c) the equilibrium reached when making sense of new information 2. A child is bouncing a ball over and over again in the kitchen. What type of play is this child engaging in? a) games with rules b) symbolic play c) pretend play d) practice play 3. A child is asked what they think is in the Smarties box. The child says that there are Smarties in the box. Then she finds out that there isn’t Smarties but rather pink gems in the box. When asked what she thinks her friend (who does not know what’s in the Smarties box) will say is in the box, the child says, “pink gems.” This child is demonstrating: a) assimilation b) accommodation c) egocentrism 4. According to Piaget the best predictor of academic success is: a) one-to-one time with teacher b) good home environment c) completion of all assignments at a high level d) more independent learning than cooperative learning 5. Which is NOT one of Piaget’s four classroom principals: a) fluency precedes accuracy b) child process information differently at each developmental stage c) al students should be working at the same academic level d) horizontal elaboration precedes vertical integration 6. One of the main critiques of Piaget’s theory is: a) he observed monkeys not humans b) he observed adults not human c) it was a stage based theory 7. What theorist expanded on Piaget’s theories of child development? a) Skinner b) Vygotsky c) Santa d) Freud